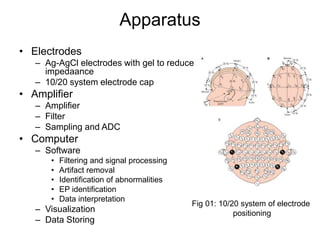
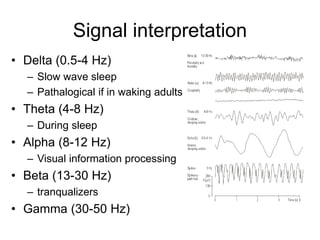
EEG records electric potentials from the brain using electrodes on the scalp. It can measure spontaneous brain activity as well as evoked potentials in response to stimuli. EEG uses Ag-AgCl electrodes applied to the scalp with gel to reduce impedance, connected to an amplifier, computer, and software for processing, artifact removal, data interpretation, and storage. EEG can diagnose epilepsy and other neurological disorders, study cognitive processes, and has high temporal resolution, but suffers from low spatial resolution and potential artifacts corrupting the data.