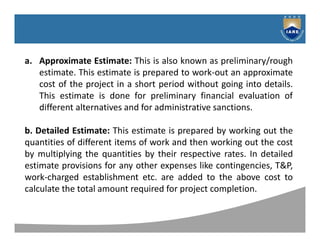
The document discusses different types of estimates used in construction projects, including approximate estimates, detailed estimates, quantity estimates, revised estimates, and supplementary estimates. It provides details on the purpose and process for each type. Specifically, it explains that an approximate estimate is a preliminary cost estimate created quickly without detailed design to evaluate the feasibility of a project and help determine if further planning is warranted.