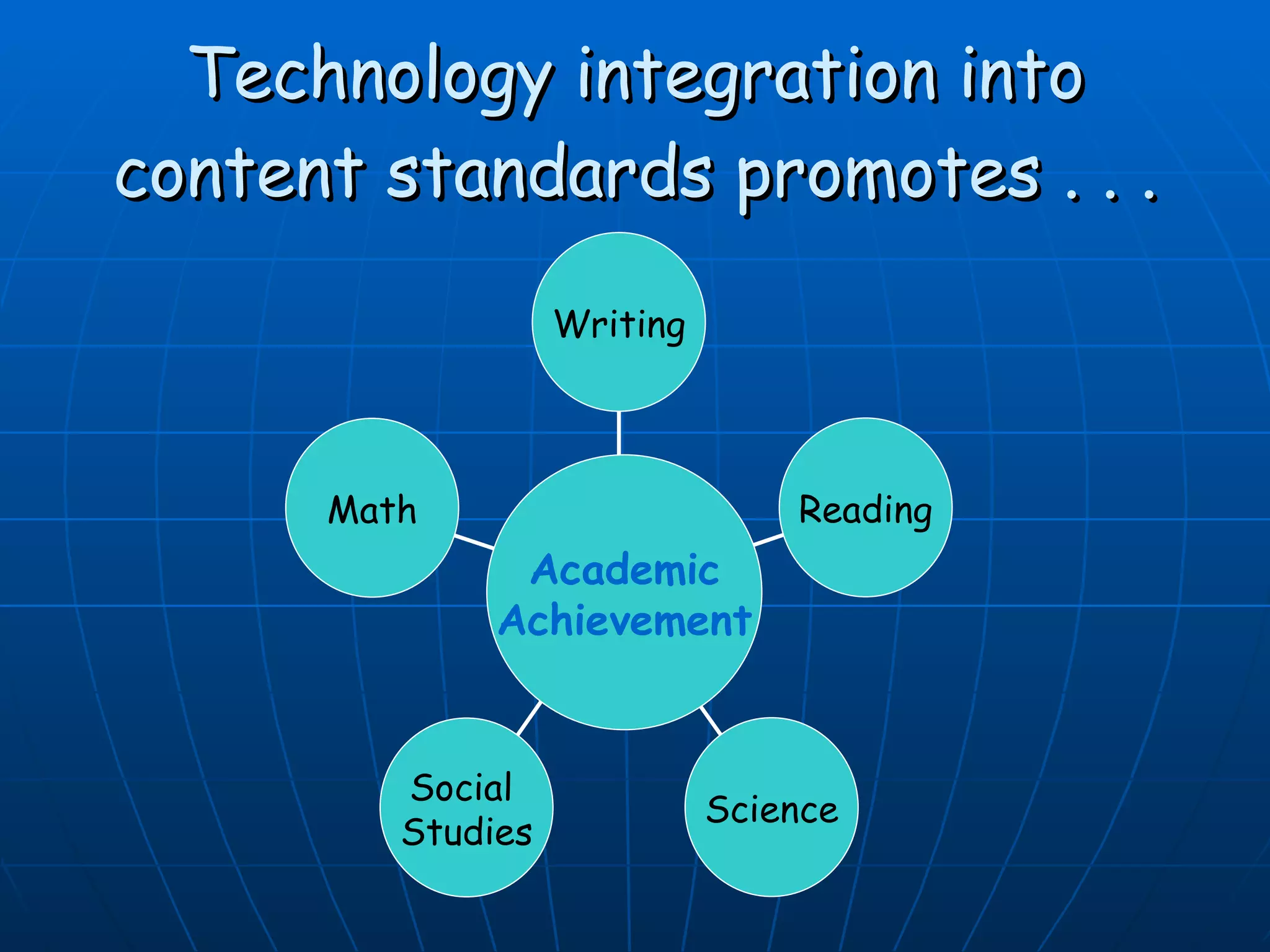
This document discusses research on the educational returns of investing in classroom technology. It finds that when used to support core educational standards, technology can:
1) Improve student achievement on tests and grades, and increase enrollment in advanced courses.
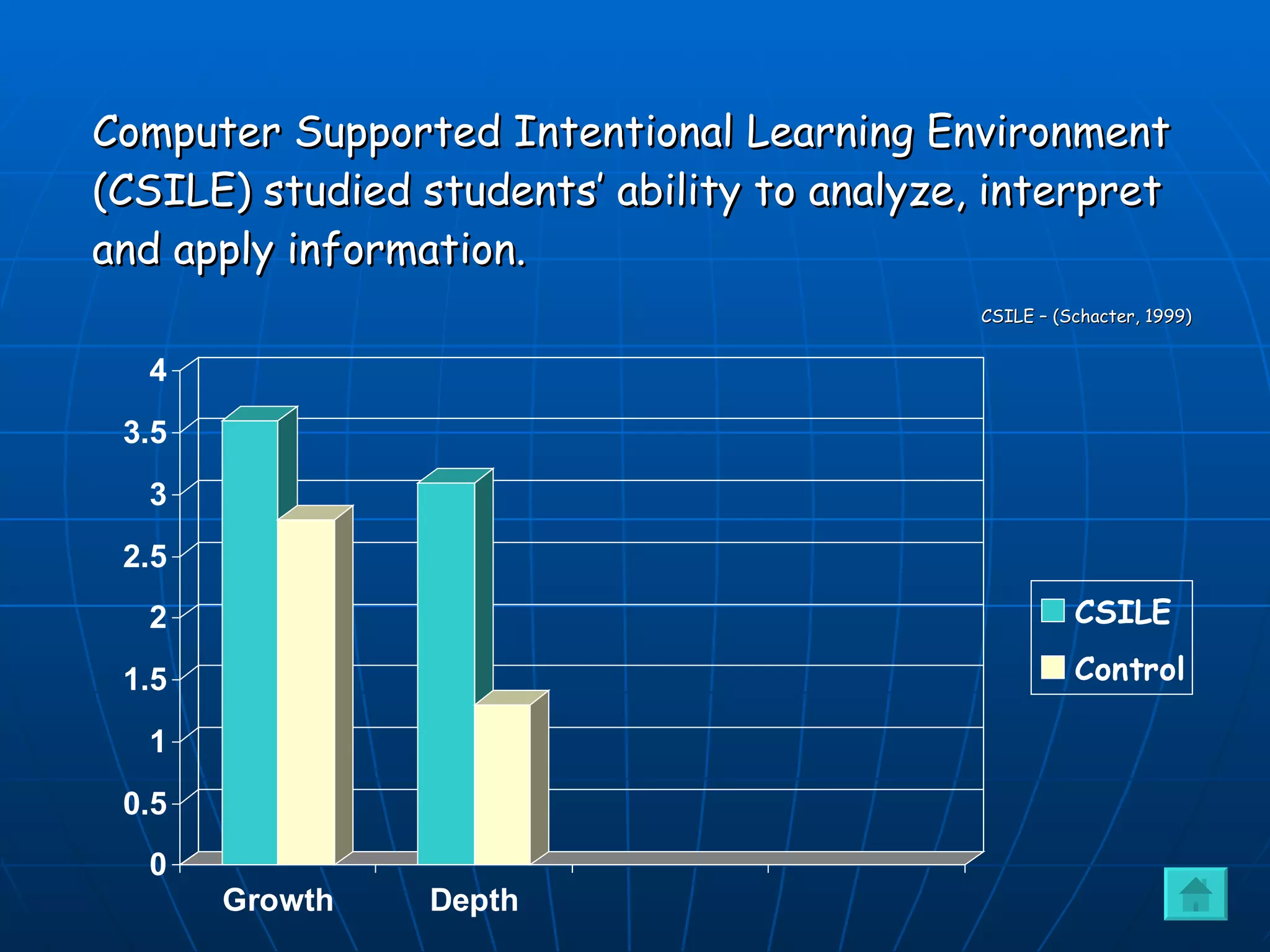
2) Develop students' problem-solving and critical thinking skills beyond grade level.
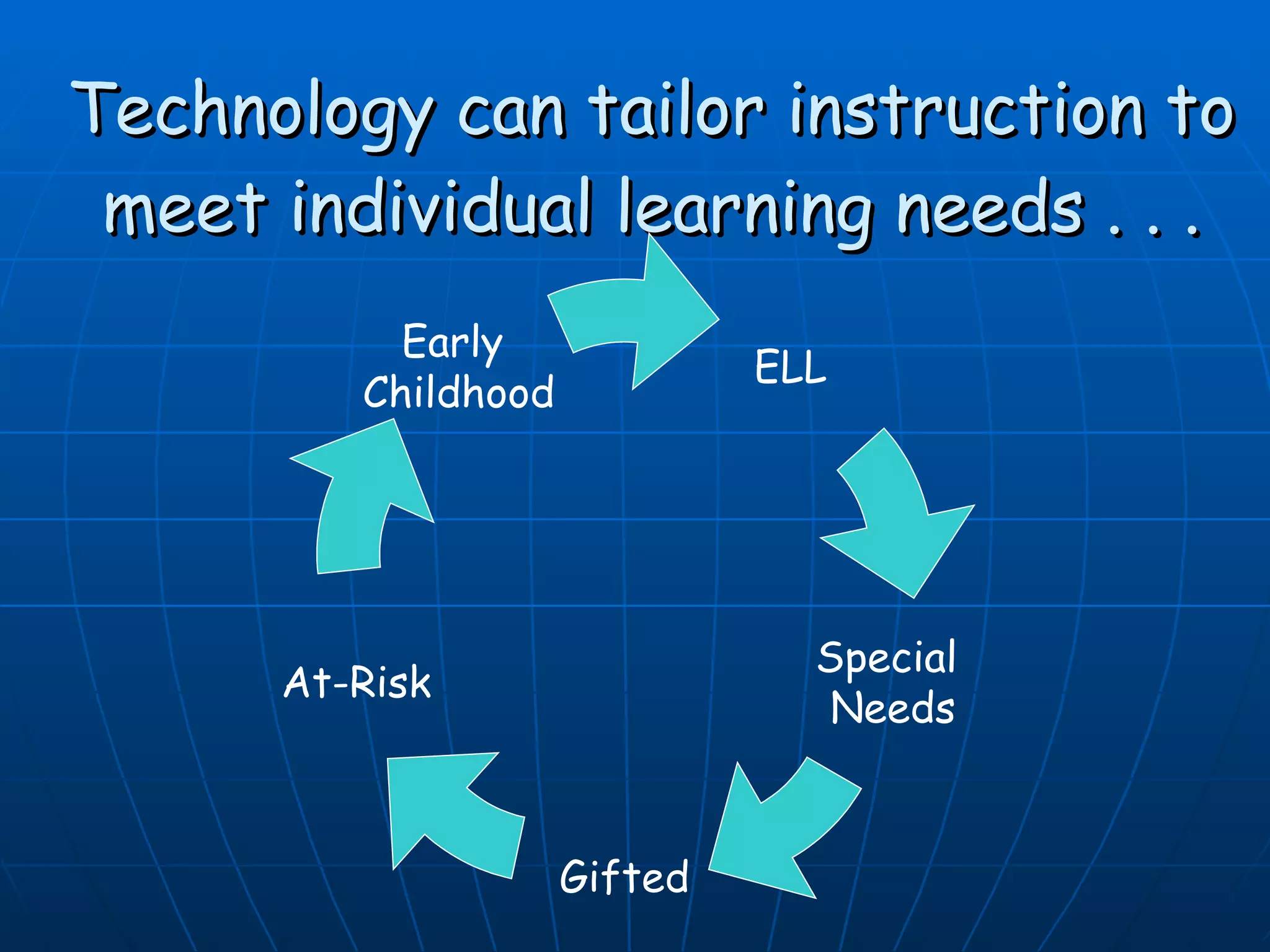
3) Tailor instruction to individual student needs like ELL, at-risk, gifted, and special needs students.
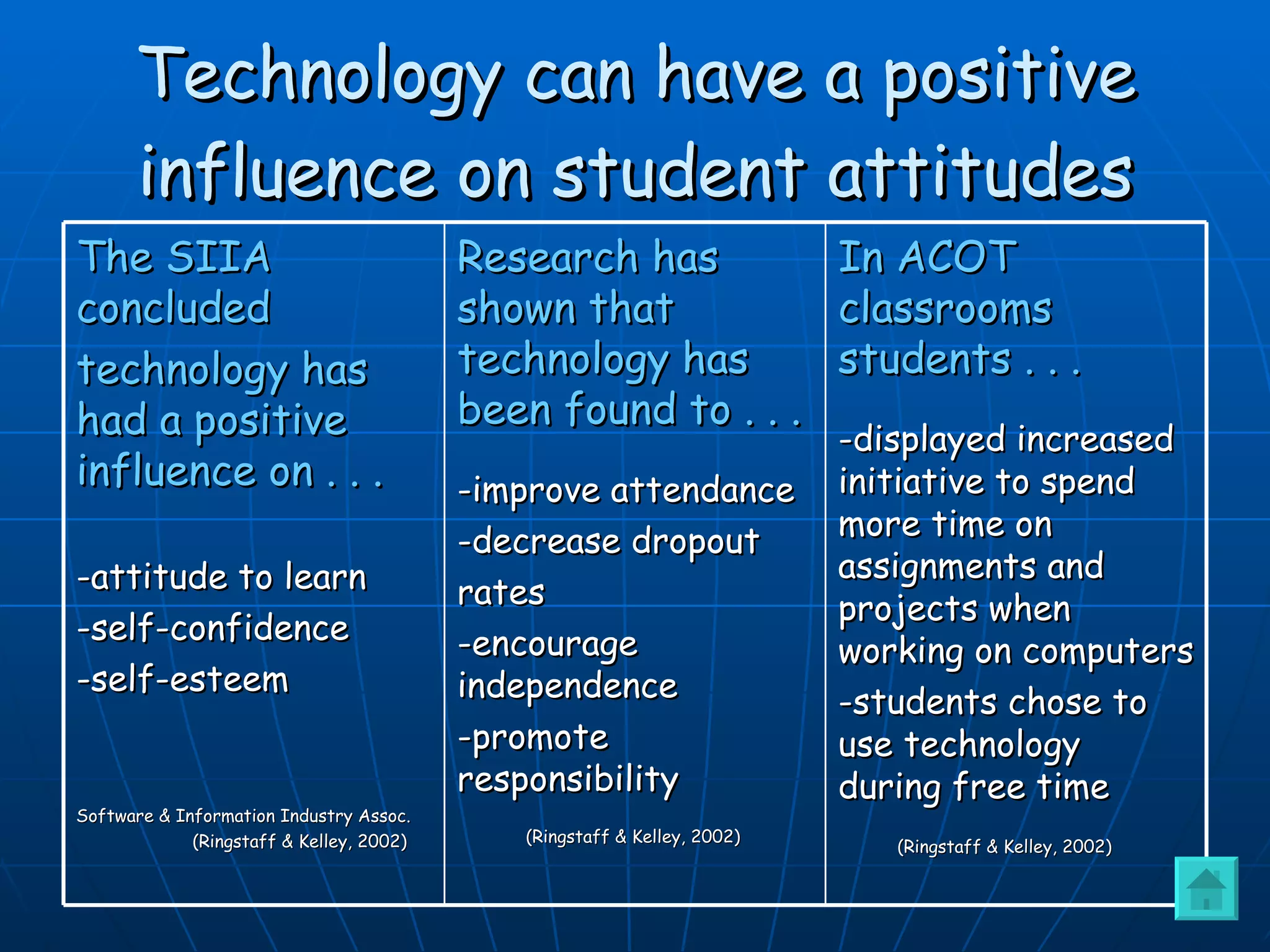
4) Have positive influences on student attitudes, confidence, independence, and responsibility. It can also improve attendance and decrease dropout rates.