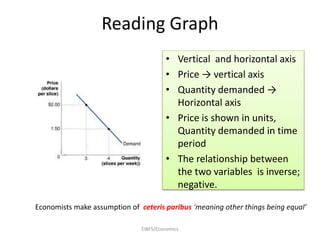
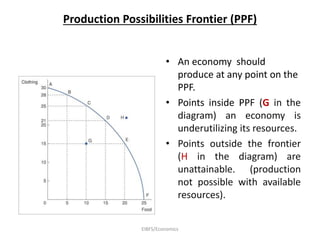
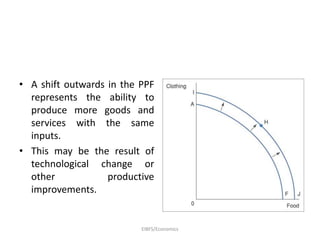
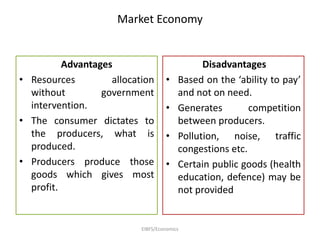
Economics is defined as the science that studies human behavior in relationship to scarce resources that have alternative uses. It addresses the economic problem of how to allocate, distribute, and utilize limited resources to meet unlimited human wants. A market economy allocates resources through supply and demand, while a planned economy involves government deciding production and allocation. Most countries use a mixed economy that combines aspects of market and planned systems. Positive economics makes empirically testable statements, while normative economics involves value judgments. Microeconomics focuses on individual and firm decisions, while macroeconomics studies the overall economy.