The document discusses economic reforms in India's aviation sector since 1991. Key points:
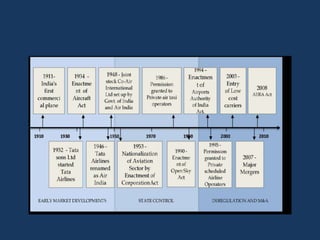
- Before 1991, India's economy was influenced by protectionism and public ownership. The aviation industry was government-owned.
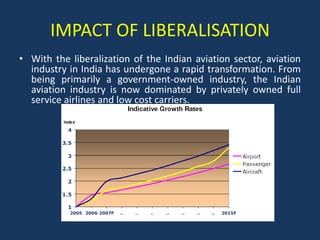
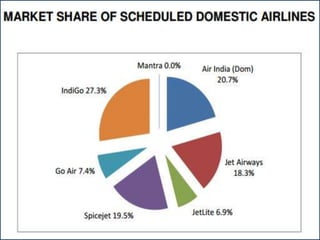
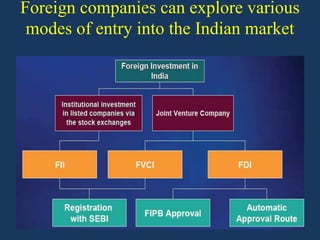
- Economic liberalization in 1991 privatized the aviation sector and opened it to foreign investment and private carriers. This led to rapid growth and transformation of the industry.
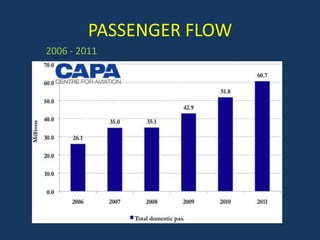
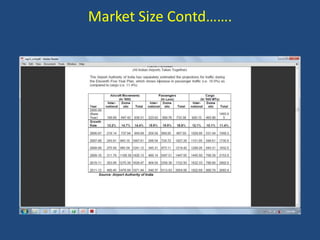
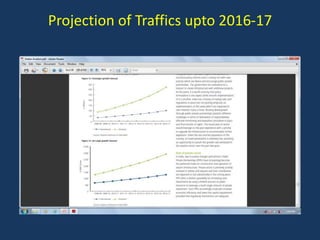
- Reforms included allowing foreign airlines and carriers, privatizing airports, reducing taxes, and increasing international routes. As a result, passenger traffic quadrupled and the sector is projected to contribute significantly to GDP.
- Going forward, the sector is expected to continue strong growth through airport development, regional connectivity, and city-side