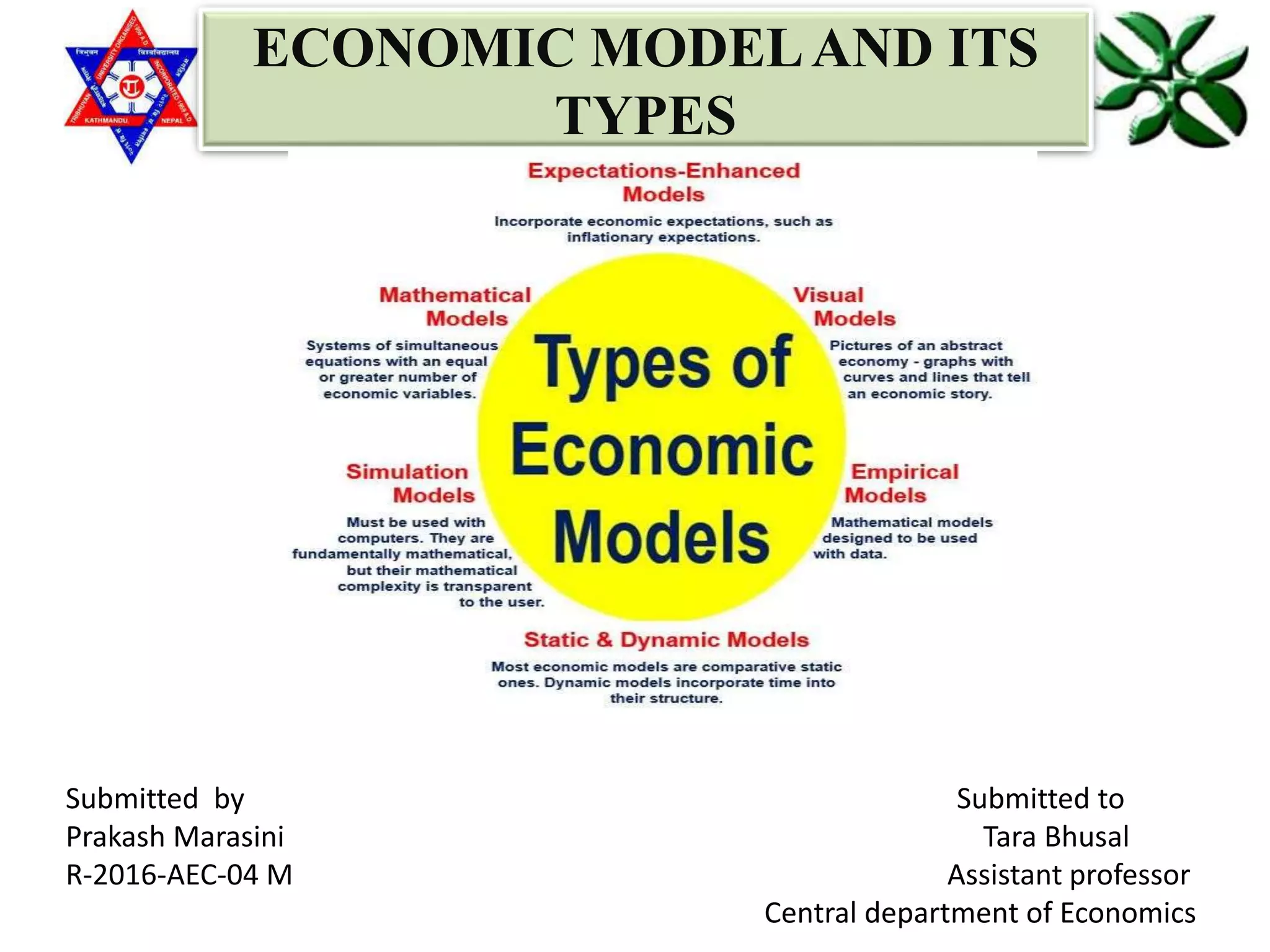
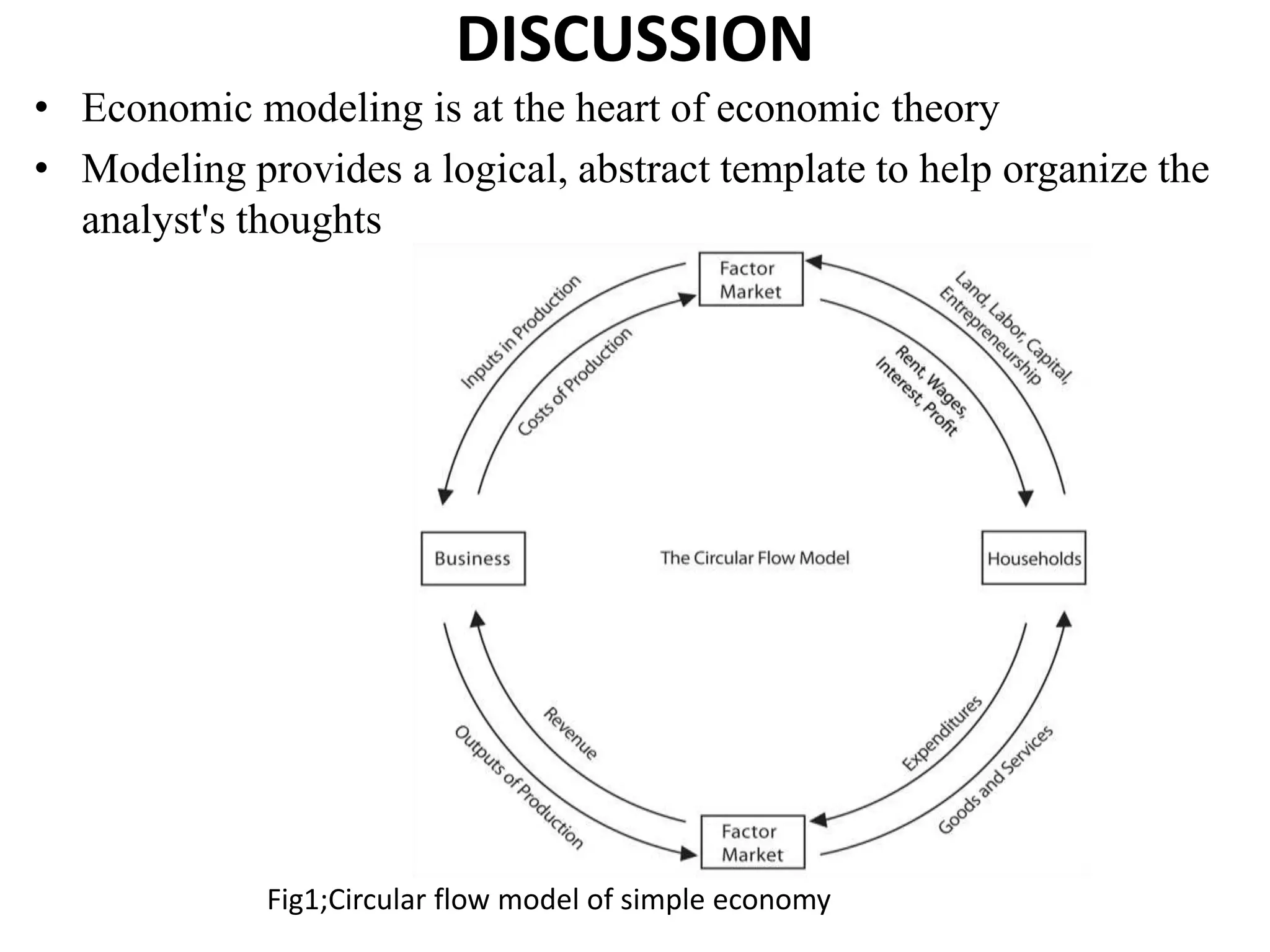
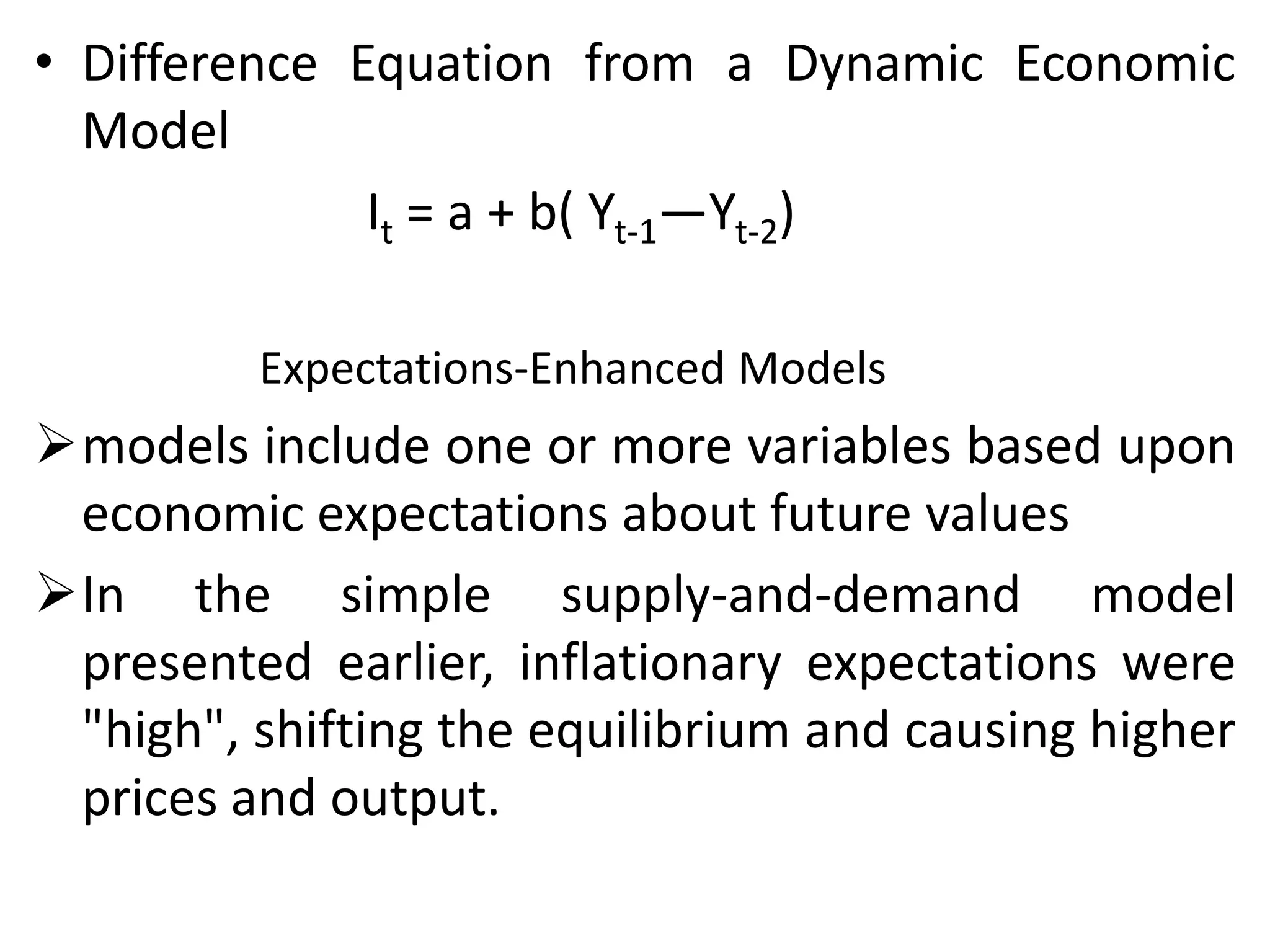
Economic models can be classified in several ways: as stochastic or non-stochastic, discrete or continuous, quantitative or qualitative, general or partial equilibrium models. Models can also be visual, mathematical, simulation-based, static or dynamic, linear or non-linear, and expectations-enhanced. Economic models are simplified descriptions of reality that are used for forecasting, policy proposals, planning, and justifying policy. They provide a logical framework for investigating economic behavior and fitting theories to observations.