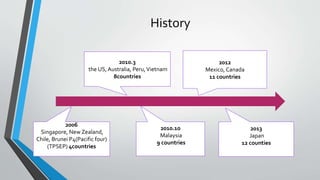
The document summarizes the Trans Pacific Partnership (TPP) agreement, including its history and perceived merits and demerits for the US and Japan. The TPP is a trade agreement between 12 Pacific Rim countries that aims to enhance trade and promote economic growth. It began in 2006 with 4 countries and expanded to include the US, Japan and others. Key negotiation issues include intellectual property, investment, environmental standards and more. Potential merits include increased trade and market access, while potential demerits include negative impacts on agriculture, wages, and limitations on domestic policies.