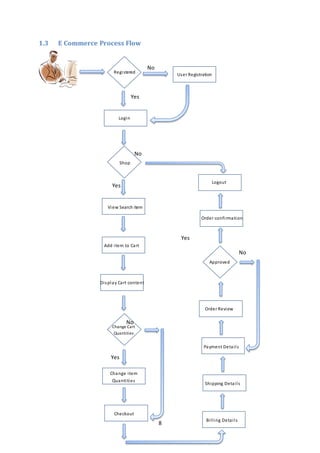
This document provides an overview of e-commerce, including its advantages and disadvantages. It describes different types of e-commerce platforms based on licensing models (on-premise, SaaS, open source), sales scenarios (B2B, B2C, C2B, C2C), and data exchange (integrated, interfaced). It also outlines the typical process flow for an e-commerce site, from entry point to product listing/search to checkout to order confirmation. Key components are described for pages like home, product details, cart, and checkout.