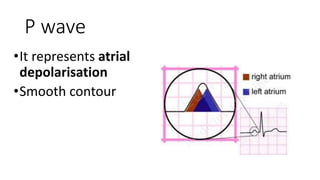
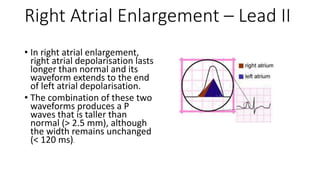
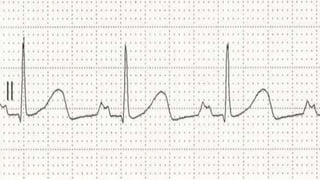
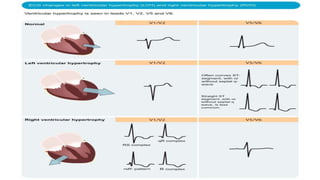
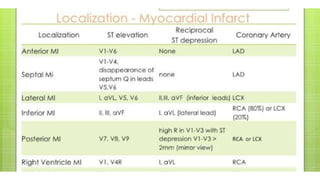
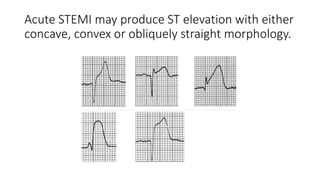
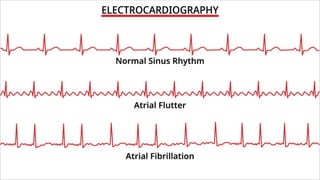
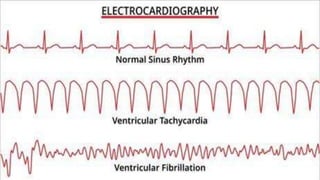
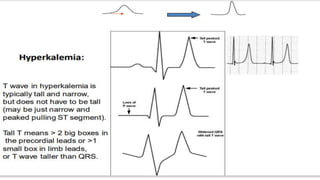
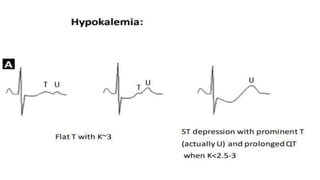
The document provides an overview of ECG waveforms, specifically focusing on P waves in atrial enlargement conditions. It details how right and left atrial enlargements affect P wave characteristics, along with descriptions of other heart conditions like atrial fibrillation and ventricular fibrillation. Additionally, it outlines the procedure for conducting an ECG, including patient preparation, equipment setup, and post-procedure steps.