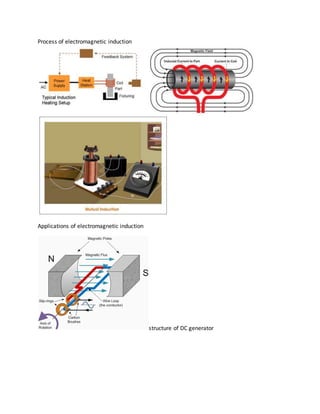
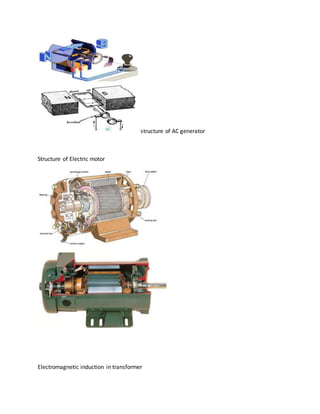
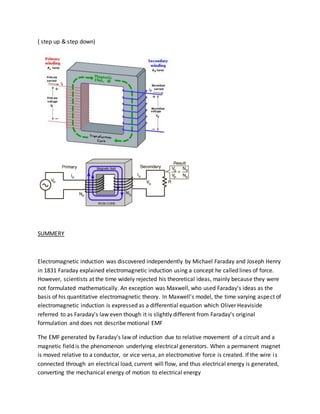
This document discusses electromagnetic induction. It provides objectives to develop knowledge of electromagnetic induction and identify related terms. Key terms discussed include electromagnetic induction, induced EMF, alternating current, direct current, magnetic flux, self induction and mutual induction. Facts provided include that magnetic flux is the product of magnetic field and area, and electromagnetic induction was discovered by Faraday and Henry in 1831. The document also includes a concept map and related examples of electromagnetic induction applications and devices like generators, motors and transformers.