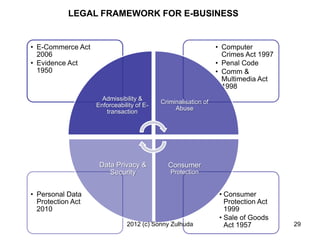
This document provides an overview of e-business law in Malaysia. It defines e-business and discusses why businesses engage in e-business. It covers topics such as web-based business models, consumer issues like identity theft, and what laws govern e-business. The document outlines Malaysia's Electronic Commerce Act of 2006 and discusses how it addresses legal issues in e-transactions, including the formation of e-contracts. It also provides guidance on how to legally set up an e-business website in Malaysia.