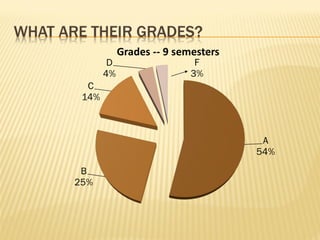
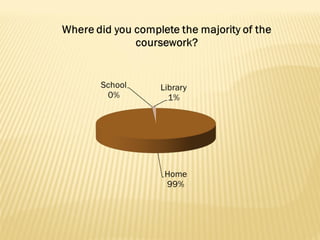
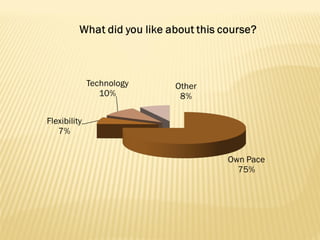
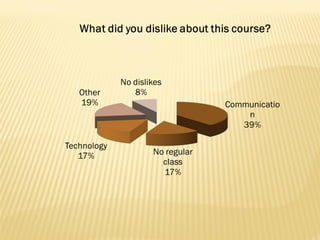
The document summarizes trends in online learning and discusses strategies for implementing successful online education programs. Key points include:
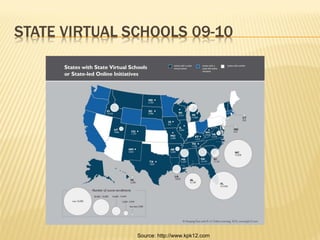
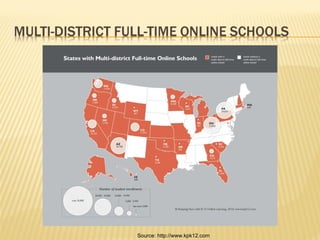
- Online learning in K-12 has grown rapidly in recent years and is expected to continue growing. Nearly 30% of higher ed students took an online course in 2009.
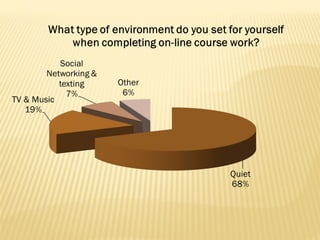
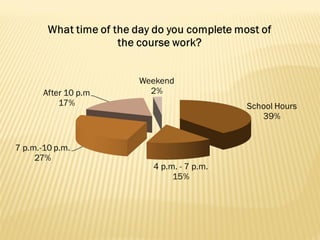
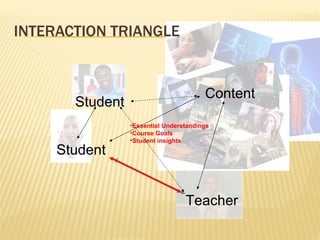
- Effective online courses require high-quality content, strong teacher-student interaction, proctored assessments, and support for struggling students. Student self-motivation and time management are important skills.
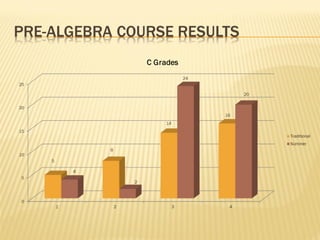
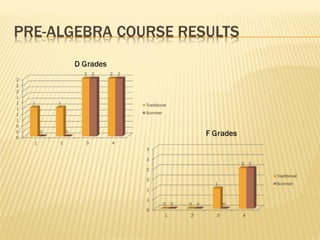
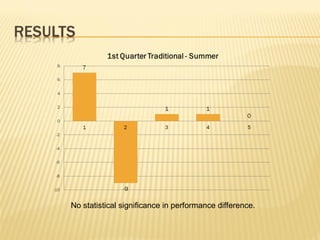
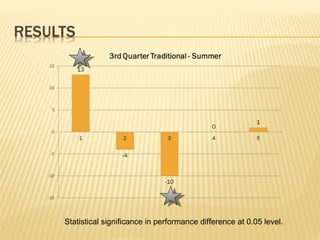
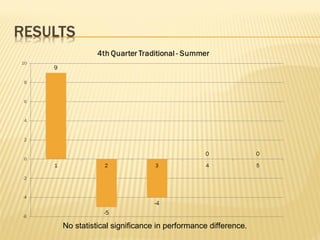
- Research on an online math course found no significant difference in performance between online and face-to-face students. Policymakers are encouraged to expand access to online learning options.




































![Achievement and Self-Esteem Beliefs – Students require a high degree of self-motivation, and [they] must perceive that their success depends on their own contributions, rather than those of the course or teacher. Responsibility/Risk Taking – Students have to take the initiative [to] complete tasks, even when all the information may not be given and the correct way to proceed may not be clear. Technology Skills and Access – Students in on-line courses not only must be skilled at using on-line resources but also should have better-than-average access to them. Organization and Self-Regulation – Even more than other academic activities, on-line environments seem to require students to have excellent organization and study skills. Roblyer, M.D. and Marshall, J. (2002). Prediction success of virtual high school students: Preliminary results from an educational success prediction instrument.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningonline111018a-111021060734-phpapp01/85/DuPage-Online-Meeting-42-320.jpg)