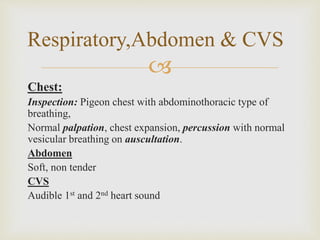
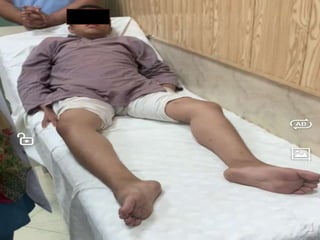
- The patient is a 14 year old boy with a 7 year history of gradually worsening difficulty walking. He now cannot walk and needs a wheelchair.
- Examination found proximal muscle weakness, calf hypertrophy, winging of the right scapula, and pectus carinatum. Investigations showed elevated CPK.
- He was diagnosed with Duchenne muscular dystrophy based on the clinical features and family history consistent with an X-linked recessive pattern of inheritance. Muscle biopsy confirmed the dystrophy.