Embed presentation
Download to read offline



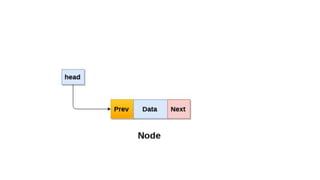
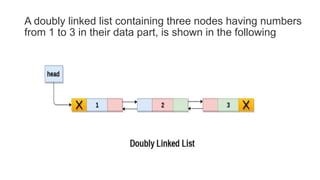

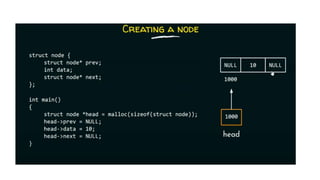

Each node in a doubly linked list contains a pointer to both the previous and next node, allowing traversal in both directions. A node consists of data, a next pointer, and a previous pointer. Doubly linked lists overcome the limitation of singly linked lists by allowing traversal in both directions since each node stores the address of the previous node as well as the next.







