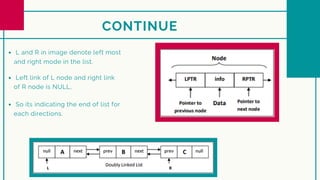
Doubly linked lists allow nodes to link in both directions by including pointers to both the next and previous nodes. Each node contains three pieces of data - the node value and pointers to both the previous and next nodes. This allows traversal in both forward and backward directions. Doubly linked lists require more memory than singly linked lists since each node needs an extra pointer, but provide advantages like easy deletion of nodes and ability to traverse the list in either direction.

![1] EXPLANATION
• It is also called two way linked list.
• In this list in which node are linked together by multiple links.
• So we access successor(next) node and predecessor(previous) node.
• Therefore each node in a list points both node.
• This help us to traverse in both direction.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doublylinkedlist-230123093809-1261551a/85/doubly-linked-list-pdf-3-320.jpg)
![In figure 5 , 10 and 15 are the info
part of doubly linked list.
1020 , 1030 and 1035 is link part
(address) of this list.
2] EXAMPLE
Left link of L node and right link
of R node is always NULL,
we can see here that lpt contain
previous node of address and rpt
contain next node of address so
we can traverse in both direction.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doublylinkedlist-230123093809-1261551a/85/doubly-linked-list-pdf-5-320.jpg)
![We can delete a node with little trouble,since we have pointers to the previous and next
nodes.
A node on a singlylinked list cannot be removed unless we have the pointerto its
predecessor.
3] ADVANTAGE
Main advantage of doublylinked list is we can traverse in any direction, Forward or
reverse](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doublylinkedlist-230123093809-1261551a/85/doubly-linked-list-pdf-6-320.jpg)
![4] DISADVANTAGE
It requires more memory compared to singlylinked list because we need an extra
pointer to point previous node.
Operations require more time compared to singly-linked lists.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doublylinkedlist-230123093809-1261551a/85/doubly-linked-list-pdf-7-320.jpg)