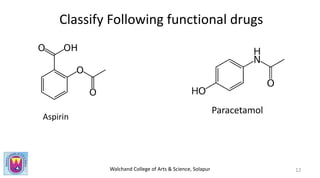
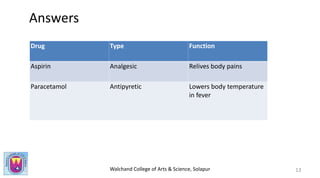
This document discusses drugs and their classification. It begins by defining a drug and explaining the qualities of an ideal drug. Drugs are then classified in two main ways: by their chemical structure and by their therapeutic action or medicinal use. Functional drugs are classified that modulate physiological functions like analgesics, antipyretics, and antihistamines. Chemotherapeutic agents are used to cure diseases caused by microbes and include antiseptics, antimicrobials, antibiotics, and anticancer drugs. The document provides examples of common drugs that fall under different functional and chemotherapeutic classifications.