This document presents a proposed model to assess the bearing stress of normal weight concrete at failure. The model analyzes the final failure pattern of concrete specimens under axial compression, considering factors like the direction of slip planes, mechanical properties of concrete, relative element height, and the bearing ratio (the ratio of total surface area to load bearing area). Previous studies found that bearing strength increases due to confinement from surrounding concrete. The proposed model aims to conservatively predict bearing strength by accounting for these parameters and the failure mechanism of diagonal shear failure along inclined planes. It compares results to test data and design codes.
![Al-Sahawneh E.I., Hassan R.H., Amjad A.Y., Khair Al-Deen B / International Journal of
Engineering Research and Applications (IJERA) ISSN: 2248-9622 www.ijera.com
Vol. 3, Issue 1, January -February 2013, pp.793-802
A Proposed Model At Failure Stage To Assess The Bearing Stress
Of Normal Weight Concrete
1
Al-Sahawneh E.I., 2Hassan R.H., 3Amjad A.Y., 4Khair Al-Deen B.
1,2,3
Civil engineering department Al-Balqa’ Applied University, Amman, Jordan
4
Civil engineering department University of Jordan, Amman, Jordan
ABSTRACT
Experimental investigations indicate that effect provided by the surrounding concrete.
the bearing strength of concrete is increased by Research works proved that the bearing stress is
the confinement effect provided by the enveloping greatly influenced by the characteristics of
concrete. Various empirical formulas have been mechanical properties of concrete, area of local load
used in international codes relating the bearing distribution, and the cross-section of the loaded
strength of concrete to the compressive strength member. The most important variables of
and the ratio of the total surface area to load experiments have been the ratio of the total surface
bearing area (A/Ab) (known as bearing ratio). This area to load bearing area (A/Ab) (known as bearing
study presents a new approach developed for the ratio) and the relative element height.
bearing strength of concrete loaded through rigid The bearing strength was first investigated by
steel plate by way of analyzing the final failure Bauschinger (1876) and he was the first in proposing
pattern of concrete prism and cube specimen a cubic root formula as result of his experiments in
under axial compression considering slip planes sandstone. Meyerhof and Shelson (1957) suggested
direction, mechanical properties of normal weight an expression for bearing strength that includes the
concrete, relative element height and the effect of cohesion and the angle of friction of the concrete
the bearing ratio. The main objective of the material as a consequence of conducting several tests
present paper is thus an attempt to put forward of footing-like blocks with large A/Ab ratios and
an analytical approach which conservatively observed the formation of the splitting wedge and the
predicts the bearing strength of normal weight characteristic failure cone and pyramid at failure of
concrete and accounts for all of the parameters concrete blocks. Au and Baird [1] also noticed a
mentioned above. The method depends on the formation of an inverted pyramid under the loading
final failure pattern mechanism of concrete prism bearing plate and developed a theory for concrete
and cube under axial compression load and bearing strength on the assumption that the inverted
considers the possible failure mode of diagonal pyramid would cause horizontal pressures prior to
shear failure, direction of shear failure planes, failure.
characteristic compressive strength of normal Niyogi [2] carried out tests on plain and reinforced
weight concrete, relative element height and the concrete blocks and studied the effect of specimen
effect of the A/Ab ratio. The results of the size, geometry of the plates , strength of concrete ,
proposed approach herein are compared with test the nature of the supporting bed (rigid and elastic)
data existing in the literature and the output and the mix concrete proportions on the bearing
values of standard design procedure available in resistance of concrete. The mainly remarkable results
some international codes. were that the bearing strength was almost constant
Keywords-Bearing strength, diagonal shear failure, for specimens with aspect ratios (length / width)
bearing ratio, and direction of failure planes greater than 2 and the ratio decreases as
increases, where is the bearing stress and is the
I. INTRODUCTION specified compressive cylindrical strength of
In practice, the bearing strength of concrete concrete. Niyogi proposed the following equation for
elements is regularly encountered for the design of the bearing strength for blocks concentrically loaded
bridge bearing on concrete piers, anchorages in post- through square plates:
tensioned concrete beams and building columns on
concrete pedestals. Experiments on concrete
(1)
structural members under local pressure
demonstrated that the concrete compressive strength Where a is the block side dimension and a' is the
at the bearing area is increased by the confinement plate side dimension as shown in Fig. 1.
793 | P a g e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dr31793802-130220232921-phpapp01/75/Dr31793802-1-2048.jpg)
![Al-Sahawneh E.I., Hassan R.H., Amjad A.Y., Khair Al-Deen B / International Journal of
Engineering Research and Applications (IJERA) ISSN: 2248-9622 www.ijera.com
Vol. 3, Issue 1, January -February 2013, pp.793-802
Virginia Tech investigated how the shape of the
bearing plate, size of the bearing plate, concrete
strength, and concrete density affects the ultimate
strength of the concrete. The research showed that the
shape of the bearing pad had no effect of the ultimate
bearing strength of the concrete when the A/Ab ratio
is between 2 and 16.
Axson, D. [6] in 2008 tested reinforced and
unreinforced light weight concrete prisms and
cylinders taking into consideration the effect of A/Ab
ratio. The fractured cylinders and prisms have a
shape of a cone below the bearing pad. Axson
compared the bearing stress values obtained in tests
Fig. 1 . Niyogi's 2D Bearing Stress
with the equation of the ultimate strength of the local
zone in normal weight concrete published by
Several design codes have used the square-root National Cooperative Highway Research Program
formula by Hawkins [3] .Hawkins′ model predicts Report 356.
that the failure will occur due to sliding on planes
Two important conclusions can be inferred from this
that are inclined to the direction of principle stresses review. The first one is that these studies suggest that
at angle α as shown in Fig. 2. failure of concrete subjected to a bearing load
condition is due to sliding action along planes that are
inclined to the direction of principal stresses. The
second one is that the failure mechanism is constant
through all the different investigations, namely the
formation of inverted cone or pyramid at failure.
These observations lead to the assumption that the
failure mechanism of plain concrete under local
pressure can be modeled by a failure criterion defined
with the concepts sliding along failure planes.
II. RESEARCH SIGNIFICANCE
The state of stress in the bearing zone is of
Fig. 2. Hawkins' Failure Model
an outstandingly complex and is influenced by
several parameters, such as the relation between the
Hawkins developed a general expression to estimate
area over which the load is applied, the size and
the bearing strength of concrete loaded concentrically
shape of the cross-section, the relative element height
through rigid plates as:
and the specified compressive strength. It is broadly
accepted that the concrete element under
(2) concentrated load over a limited contact area fails to
Where is the specified compressive cylindrical the formation of inverted cone or pyramid underneath
strength in psi., R is the A/Ab, ratio and K is a the loaded surface, which moves downwards,
coefficient that depends on the concrete tensile bursting or splitting the block apart. A distinct
strength and the angle of friction, both determined theoretical explanation of that failure mechanism for
experimentally. Hawkins suggested a value of K=50 the determination of bearing strength of concrete has
for design purposes. The biggest problem associated not been executed. Therefore, so far several design
with this model is the difficulty in determining the codes have employed the empirical square-root
angle of internal friction of the concrete material. formula by Hawkins.
R. Ince, E. Arid [4] in 2004 tested six series of Special attention in this paper is paid to the
concrete cube specimens under local pressure and the comparison of the suggested approach with the
maximum loads obtained from the test results were experimental research data and the existing in design
analyzed by means of Bazant's size effect law. The codes calculation methods of the bearing strength
experimental data and statistical investigations
indicated that the bearing strength at failure decreases III. THE BEARING STRESS OF PLAIN
as the specimen size increases and with the CONCRETE IN DESIGN CODES
increasing size of specimen, the height of pyramid SPECIFICATION
beneath bearing plate decreases relatively. 1-ACI318 and AASHTO Design Codes.
Research performed by Bonetti [5] in 2005 at The American Concrete Institute's Building Code and
Commentary (ACI 318-11) as well as the American
794 | P a g e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dr31793802-130220232921-phpapp01/75/Dr31793802-2-2048.jpg)
![Al-Sahawneh E.I., Hassan R.H., Amjad A.Y., Khair Al-Deen B / International Journal of
Engineering Research and Applications (IJERA) ISSN: 2248-9622 www.ijera.com
Vol. 3, Issue 1, January -February 2013, pp.793-802
Association of State Highway and Transportation to 2, but for the condition that the pressure
Officials (AASHTO 2010) address the bearing distribution over the loaded area is non-uniform the
strength of concrete in very similar ways as proposed square root of the A/Ab ratio multiplied by 0.75 is
by Komendant (1952) but with some modifications. limited to 1.5 (AASHTO 2010).
The ACI 318-11 [7] suggest the design bearing
strength as a function of the characteristic
compressive strength of concrete and a square root
function between the bearing area and total surface
(4)
area . The ACI 318-11 states that design bearing For non-uniform distributed loads
strength of concrete shall not exceed (0.85 A1),
except when the supporting surface is wider on all
sides than the loaded area, then the design bearing
strength of the loaded area shall be permitted to be Where the supporting surface is sloped or stepped, A2
may be taken as the area of the lower base of the
multiplied by but by not more than 2 for largest frustum of a right pyramid, cone, or tapered
unconfined concrete as shown by Equation 3. wedge contained wholly within the support and
having for its upper base the loaded area, as well as
side slopes of 1.0 vertical to 2.0 horizontal as shown
(3)
in Fig. 4.
where is design bearing stress of unconfined
AASHTO also has different factors than ACI 318-
concrete, MPa; = 0.65 (strength reduction factor);
11. For the condition of pure bearing is equal to
is characteristic compressive cylinder strength of 0.70. In anchorage zones in normal weight concrete
unconfined concrete at 28 days. MPa; A1 is bearing
and lightweight concrete is equal to 0.80 and 0.65
load area, mm2; and A2 is area of the lower base of
the largest frustum of a pyramid, cone, or tapered respectively.
wedge, mm2. It is assumed that load spreads out into
the concrete block at a slope of 2 horizontal to 1
vertical to the level at which spreading first reaches
the edge of the block. A2 is calculated at this level, as
clearly described in Fig. 3.
W = width for
computing A2
Fig. 4. Determination of A2 for a
Stepped Support.
2- (After Fig. C5.7.5-1 from
AASHTO 2010)
Russian Design Code (SNiP 52-01-03).According to
the Russian design code [9], the design of concrete
Fig. 3. Illustrates the application of the frustum to elements for a local compression is performed with
find A2 in stepped or sloped supports (After the increase of concrete compressive strength due to
Fig.R10.14 from ACI 318-11) the triaxial state of stress developed underneath the
loaded area and the bearing strength can be expressed
The AASHTO [8] bearing strength equation is very by:
similar to the ACI 318-11equation but with an (5)
additional provision. The factor defines how the A/Ab
ratio will affect the strength and under normal Where N is the local normal compressive external
conditions the square root of the A/Ab ratio is limited force ; =1 in case of a uniform local load
795 | P a g e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dr31793802-130220232921-phpapp01/75/Dr31793802-3-2048.jpg)
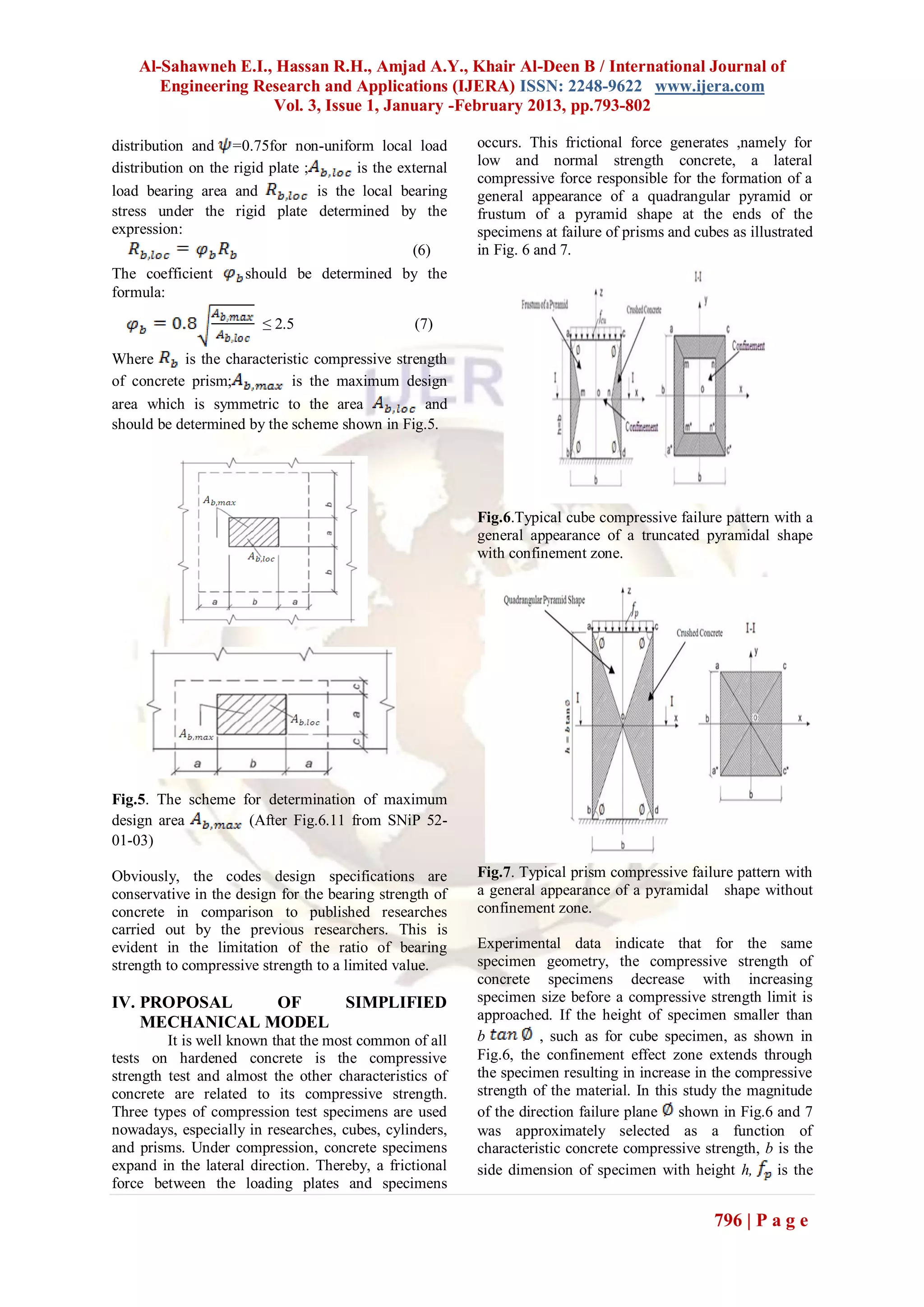
![Al-Sahawneh E.I., Hassan R.H., Amjad A.Y., Khair Al-Deen B / International Journal of
Engineering Research and Applications (IJERA) ISSN: 2248-9622 www.ijera.com
Vol. 3, Issue 1, January -February 2013, pp.793-802
characteristic prismatic strength and is
characteristic cube strength The choice of the
specimen slenderness ratio (height to diameter of
cylinder or side of prism) of 2 or the height of
specimen ≥ b ,such as for prism specimen ,as
shown in Fig.7, is not only because the confinement
effect zone is vanished but a slight increase from this
ratio does not seriously affect the measured value of
compressive strength.
Based on the aforementioned interpretations and
from the findings of the experimental and statistical
investigations of bearing strength of concrete, the
following conclusions may be drawn:
1-For a concrete element with constant cross
sectional area subjected to axial load applied through
a constant bearing rigid plate area and shape, the
Fig.8. Proposed approximate final failure pattern of
bearing compressive strength at failure decreases as
concrete block under local bearing pressure.
the specimen height increases.
2-For a concrete element with a constant height Considering the proposed mechanical model, the
subjected to axial load applied through a constant concrete bearing ratio is suggested to be evaluated by
bearing rigid plate area and shape, the bearing the formula:
compressive strength at failure increases as the cross
sectional area of specimen increases.
3- It was observed that the apex angles of the (8)
pyramidal failure values under the rigid plate at vary
from 38° to 56° approximately. Where is specific bond stress aroused between
It may be concluded that the concrete element under sliding surface planes of concrete block under local
axial local pressure revealed typical type of failure pressure. is the integrated sliding surface of
mode and identical response to size effect. Therefore, the concrete block ,with h height and BxB cross
on the apparently reasonable justifications, a sectional area, due to the bearing compressive
simplified mechanical model is directly related to the
strength; - integrated sliding surface of a concrete
final failure mode of concrete prism and cube
specimen has been worked out to assess the bearing prism under axial compressive strength with a height
strength of normal weight concrete. This approach is equals b .as clearly shown in Fig.8.
based on the concept of quasi-plastic failure mode of For the realization of expression (8) it is initially
brittle material along the sliding failure surface, necessary to know the angle of sliding planes Ø of
principally the invariant direction of slip planes with normal weight concrete. Seminenko .I.P[10]
respect to the direction of applied stress when suggested the angle of sliding plane Ø at failure of
maintaining the physical and geometrical similarity unconfined normal weight concrete specimen
of slip planes system. subjected to axial compression by to be evaluated by:
A graphical description of the above assumptions and
variables involved is presented in Fig. 8. In the Fig.,
is bearing stress, b is the width of the rigid square
(9)
plate, B is the side dimension of the prismatic
concrete block ,Ø is angle of sliding plane and h is Where is the ratio of the characteristic prismatic
the height of the prismatic concrete block. strength with a height to width ratio greater than 2
to characteristic cube strength of normal weight
concrete specimen of the same material constituents
and cross sectional dimensions.
For example, when =0.800 then =61.07 and
when =0.645 then =67.99
In conclusion, we consider necessary to give an
analytical calculations that is applied to the Fig.8 for
the evaluation of the integrated surface area to
determine the bearing ratio within the theory limits of
sliding
797 | P a g e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dr31793802-130220232921-phpapp01/75/Dr31793802-5-2048.jpg)
![Al-Sahawneh E.I., Hassan R.H., Amjad A.Y., Khair Al-Deen B / International Journal of
Engineering Research and Applications (IJERA) ISSN: 2248-9622 www.ijera.com
Vol. 3, Issue 1, January -February 2013, pp.793-802
(10)
=
+ (11)
The formulae (10 and 11) apply to square blocks
loaded through square plates and cylinders loaded
through circular plates.
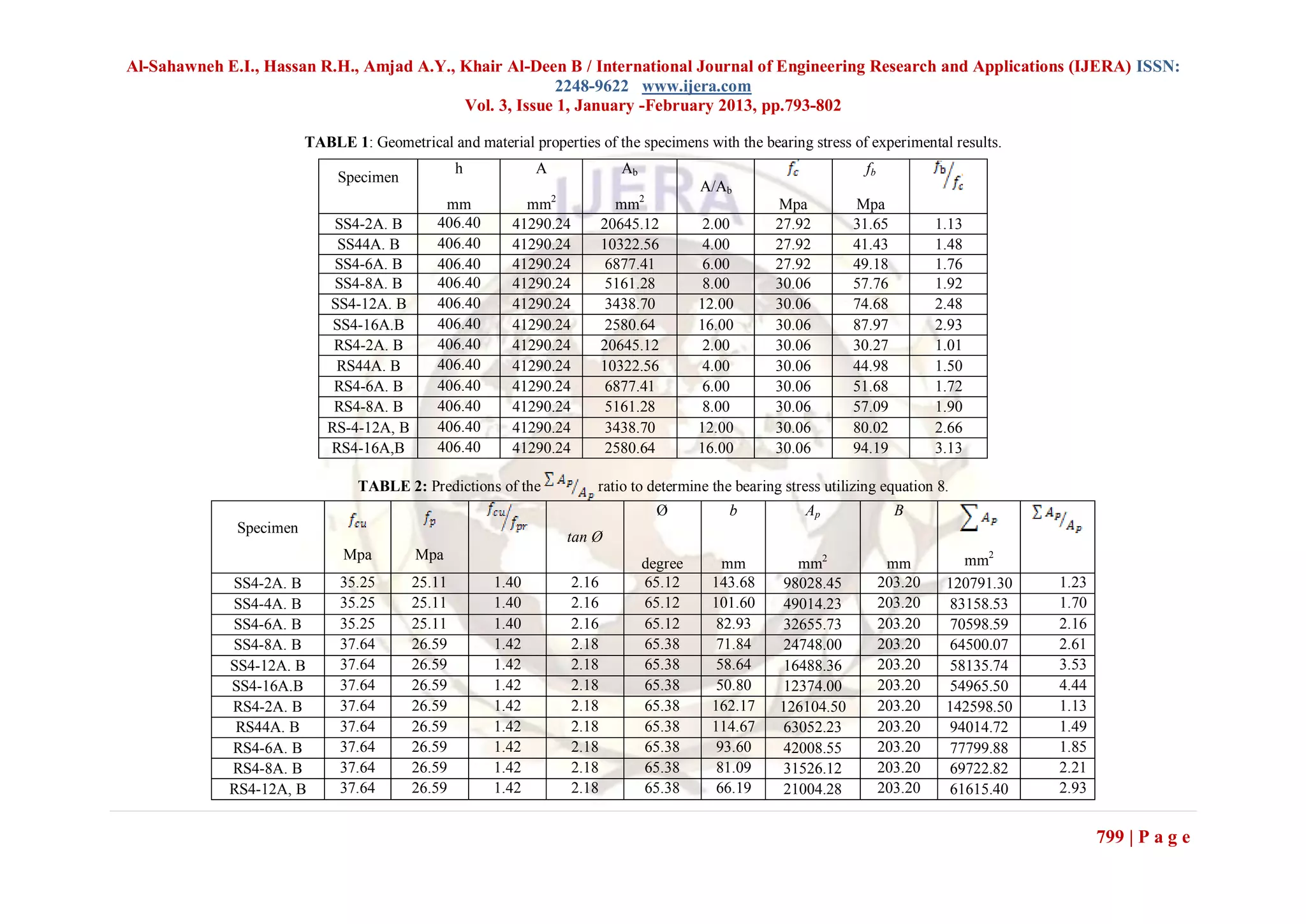
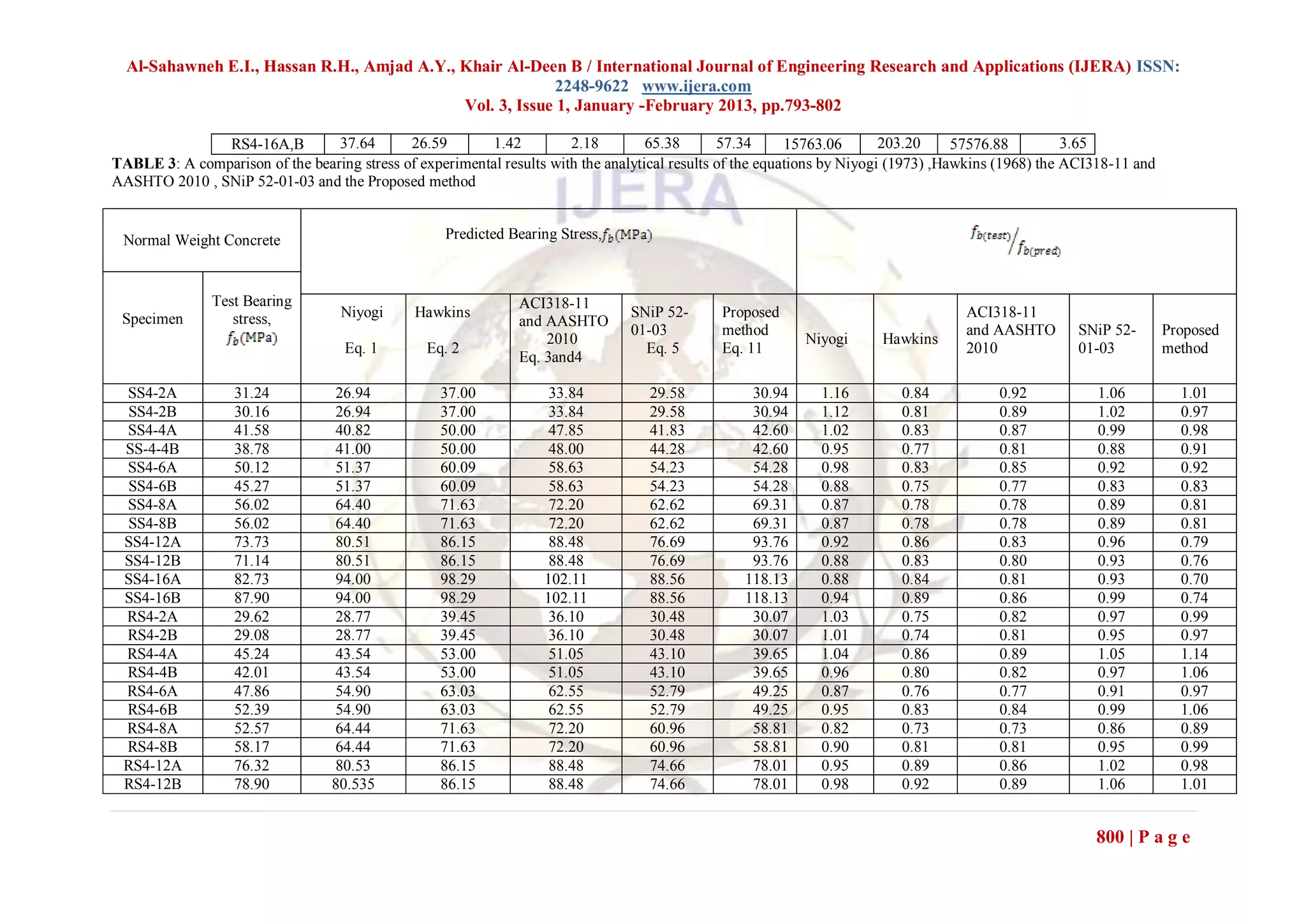
V. VERIFICATION ANALYSIS WITH
DESIGN CODES AND TEST DATA
To investigate the accuracy and suitability of the
proposed approach, a verification analysis of the
performance of the proposed approach was evaluated
against actual test data extracted from [5] and [11] as
shown in Figs.9 and 10, where the values of
obtained are plotted against the A/Ab ratios .In the
research [11], the diameter of the concrete cylinders Fig. 9. Comparison of experimental data versus
varied from 152 mm up to 610 mm, while the suggested proposed method.
diameter of the circular bearing plate was always
152 mm. The height of the specimens varied from
230 mm up to 914 mm. The specimens had a
cylinder compressive strength of 30 MPa and 20
MPa. The test data of square prism loaded with
square plate (SS) and square prism loaded through
circular plate (RS) with the geometric and material
properties extracted from the research [5] are
reported in Table 1. In Table 2, consequently, are
illustrated the procedures followed to calculate the
ratio. Table 3 presents a comparison of
the prediction results of the proposed method for
the bearing stress data gathered from Table 1 along
with data induced from using the equations by
Niyogi (1973) ,Hawkins (1968) the ACI318-11 and
AASHTO 2010 , SNiP 52-01-03. The reported
cylindrical strength for normal weight ( ) values
in Table 1 were converted to cubic concrete Fig. 10. Comparison of experimental data versus
strength (fcu) the according to the Neville's expression suggested proposed method.
[13] as follow:
(SI un its) (12)
On the basis of statistical handling of data, the cubic
concrete strength were converted to the prismatic
concrete strengths for normal weight by the
expression:
(SI units) (13)
798 | P a g e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dr31793802-130220232921-phpapp01/75/Dr31793802-6-2048.jpg)
![Al-Sahawneh E.I., Hassan R.H., Amjad A.Y., Khair Al-Deen B / International Journal of
Engineering Research and Applications (IJERA) ISSN: 2248-9622 www.ijera.com
Vol. 3, Issue 1, January -February 2013, pp.793-802
VI. CONCLUSIONS [8] America Association of State Highway
The proposed failure model shows a Transportation Officials. (2010). "AASHTO
reasonable agreement with available tests results. LRFD Bridge Design Specifications." 5th.
The analysis of the numerical results yields a Washington. DC
satisfactory correspondence between the theoretical [9] SNiP 52-01-03. Concrete and reinforced
predictions of the established model for bearing concrete structures. Design Code (СНиП 52-
stress of normal weight concrete and the 01-03. Бетонные и железобетонные
experimental data. Applications of the new model конструкции. Нормы
to a number of actual failure data sets have shown проектирования).Moscow 2004: CITP
that the model can fit the failure data much better Gosstroja SSSR, 80 p. (in Russian).
compared to Hawkins ,the ACI318-11 and [10] Seminenko .I.P.An investigation of bearing
AASHTO 2010 models. The values from the capacity of concrete core encased in steel shell
proposed model given in Table3 for in axial compression // Izvestija vuzov.
have an average equals to 0.92 Building and architecture; 1958; No 11-12, pp.
44 - 57.
with a standard deviation 0.11 for a coefficient of
[11] Adebar P. and Zhou Z. "Bearing Strength of
variation of 0.12. A very slight difference is
Compressive Struts Confined by Plain
observed in the results obtained with the use of
Concrete" ACI Structural Journal, V. 90, No.
proposed approach, therefore an extensive research
5, October 1993, p. 534- 641.
is still required
to improve the reliability of suggested failure
mechanisms under local pressure
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Al-Balqa’
Applied University, in particular the members of
the civil department in the faculty of engineering
technology for their valuable advices and technical
supports during this work.
REFERENCES
[1] Au, T. and Baird, D.L. " Bearing capacity of
concrete blocks. " ACI journal, Vol 56, No 9,
March 1960, p. 869-880.
[2] Niyogi, S. K. "Concrete bearing strength -
support, mix, size effect. "Journal of
Structural Division, ASCE, Vol 100, No ST8,
Aug, 1974, p. 1685-1701.
[3] Hawkins, N. M. "The bearing strength of
concrete loaded through rigid plates.
"Magazine of Concrete Research, Vol 20, No
2, March 1968, p. 31-40.
[4] R. Ince, E. Arici . "Size effect in bearing
strength of concrete cubes." ELSEVIER.
Construction and Building Materials ,No18,
2004, p. 603- 609
[5] Bonetti. R. A. (2005). "Ultimate Strength of
the Local Zone in Load Transfer Tests
"Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State
University. February 2005
[6] Axson, D. " Ultimate Bearing Strength of Post-
tensioned Local Anchorage Zones in
Lightweight Concrete . " Virginia Polytechnic
Institute and State University. May 21, 2008
[7] American Concrete Institute. (2011). "Building
Code Requirements for Structural Concrete
and Commentary (ACI318-11)." Farmington
Hills. Mich.
802 | P a g e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dr31793802-130220232921-phpapp01/75/Dr31793802-10-2048.jpg)