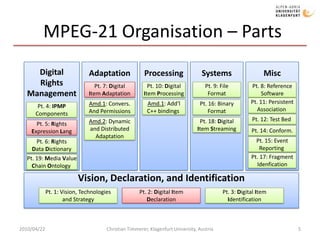
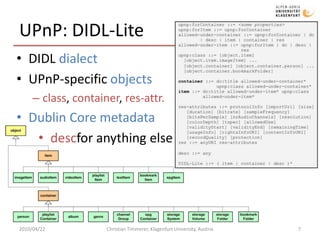
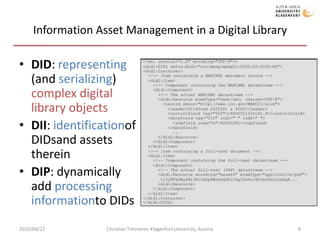
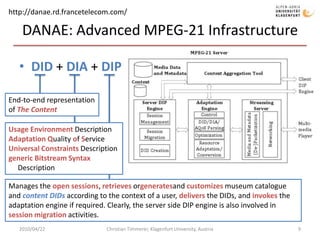
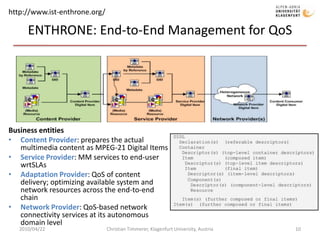
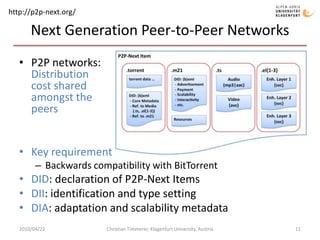
The document discusses MPEG-21 digital items in research and practice. It provides an introduction to MPEG-21 and its basic concepts of digital items, users, and the structure of resources, metadata, and relationships within a digital item. It then summarizes several research projects and practical applications that utilize MPEG-21 digital items, including DIDL-Lite, DANAE, ENTHRONE, P2P-Next, and information asset management at Los Alamos National Laboratory. The document concludes by noting challenges to large-scale interoperability but potential benefits from standards like MPEG-21 and MPEG Extensible Middleware.