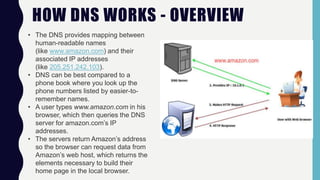
The DNS system provides a mapping between human-readable domain names and IP addresses. When a user enters a domain name like www.amazon.com, their browser queries a DNS server to obtain the IP address for Amazon. The DNS server returns Amazon's IP address so the browser can request data from Amazon's web host. If the local DNS server does not have the requested address in its cache, it will forward the query to another DNS server with a larger cache, like one provided by an ISP, to find the IP address.