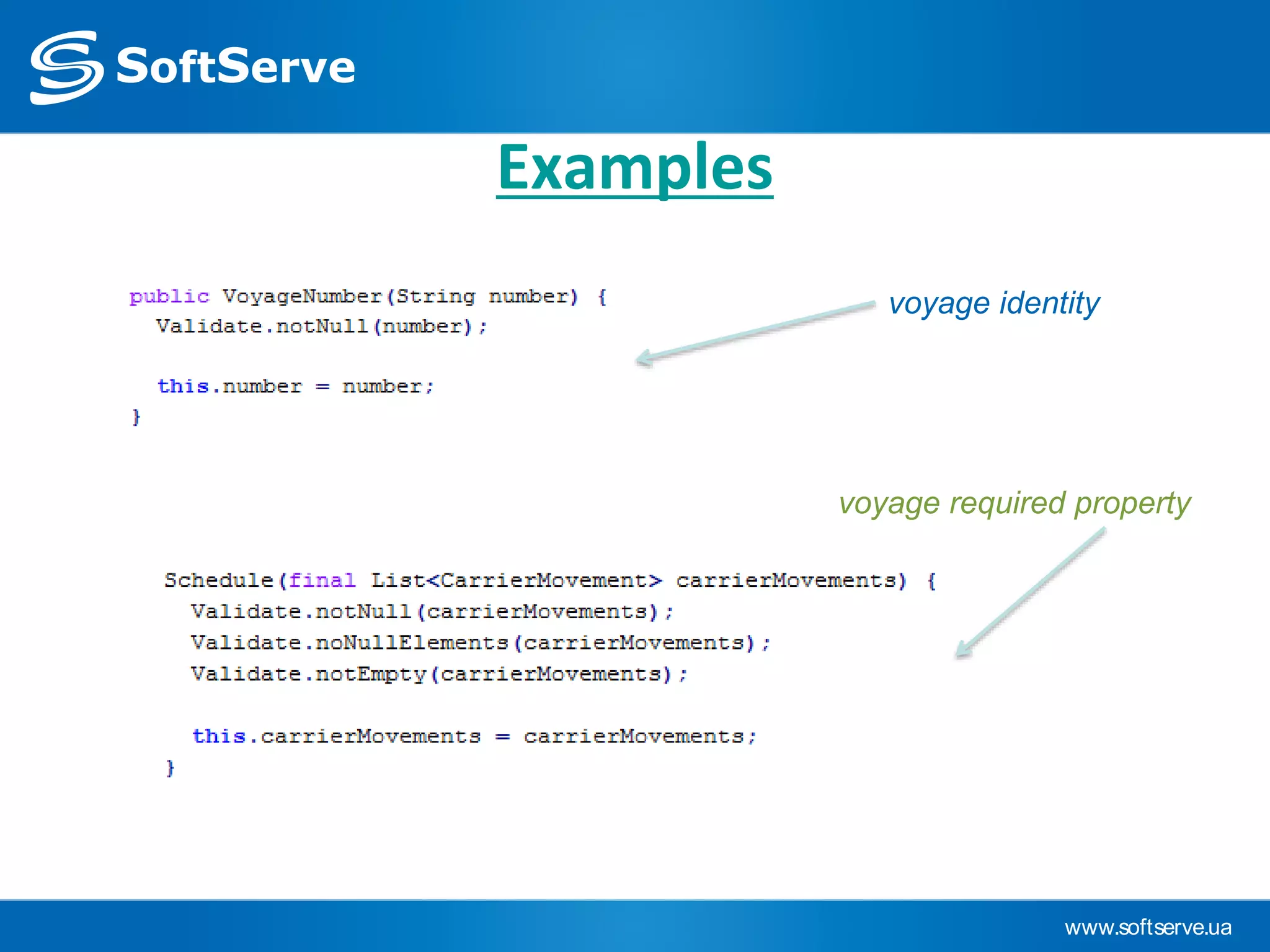
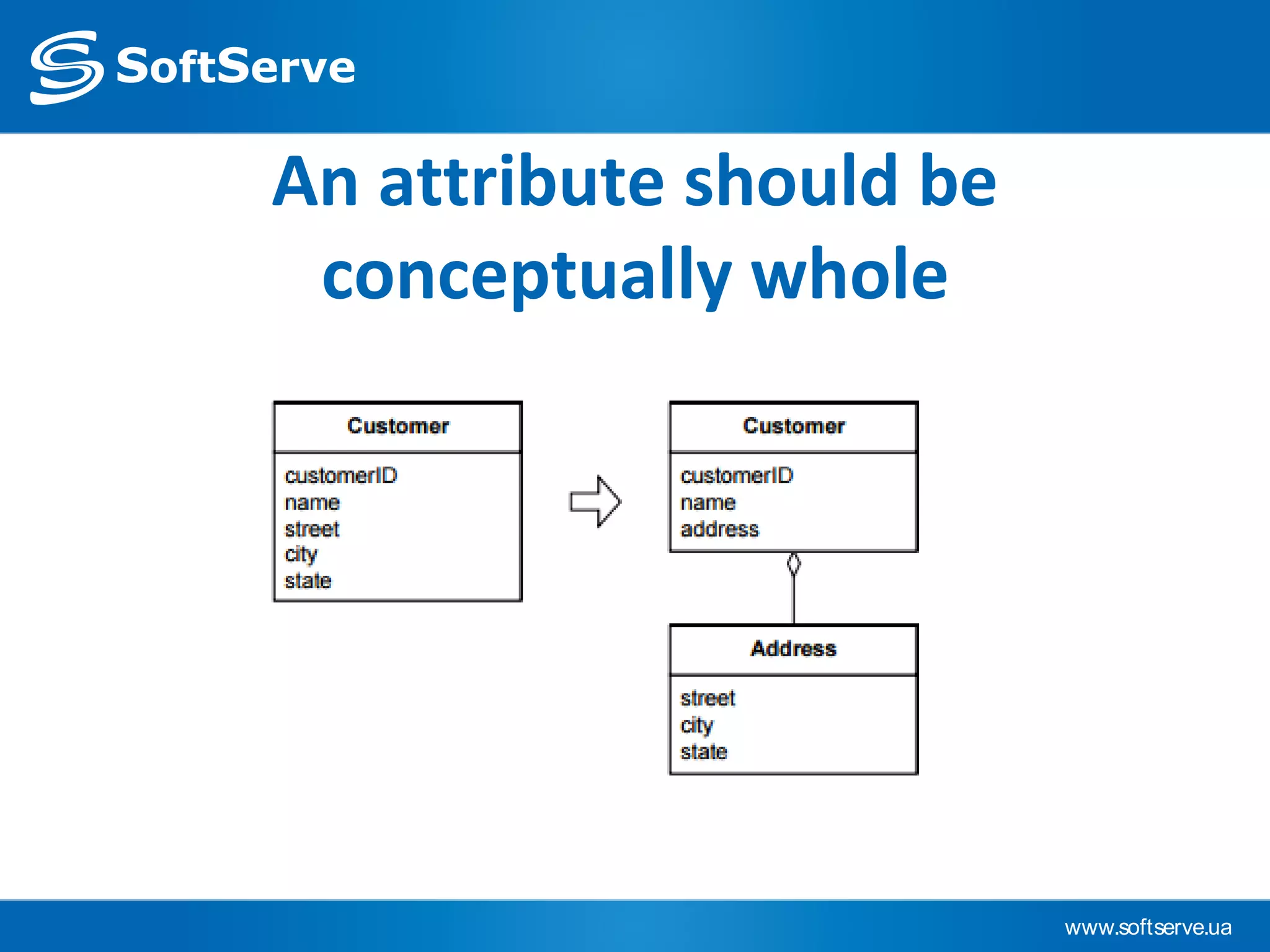
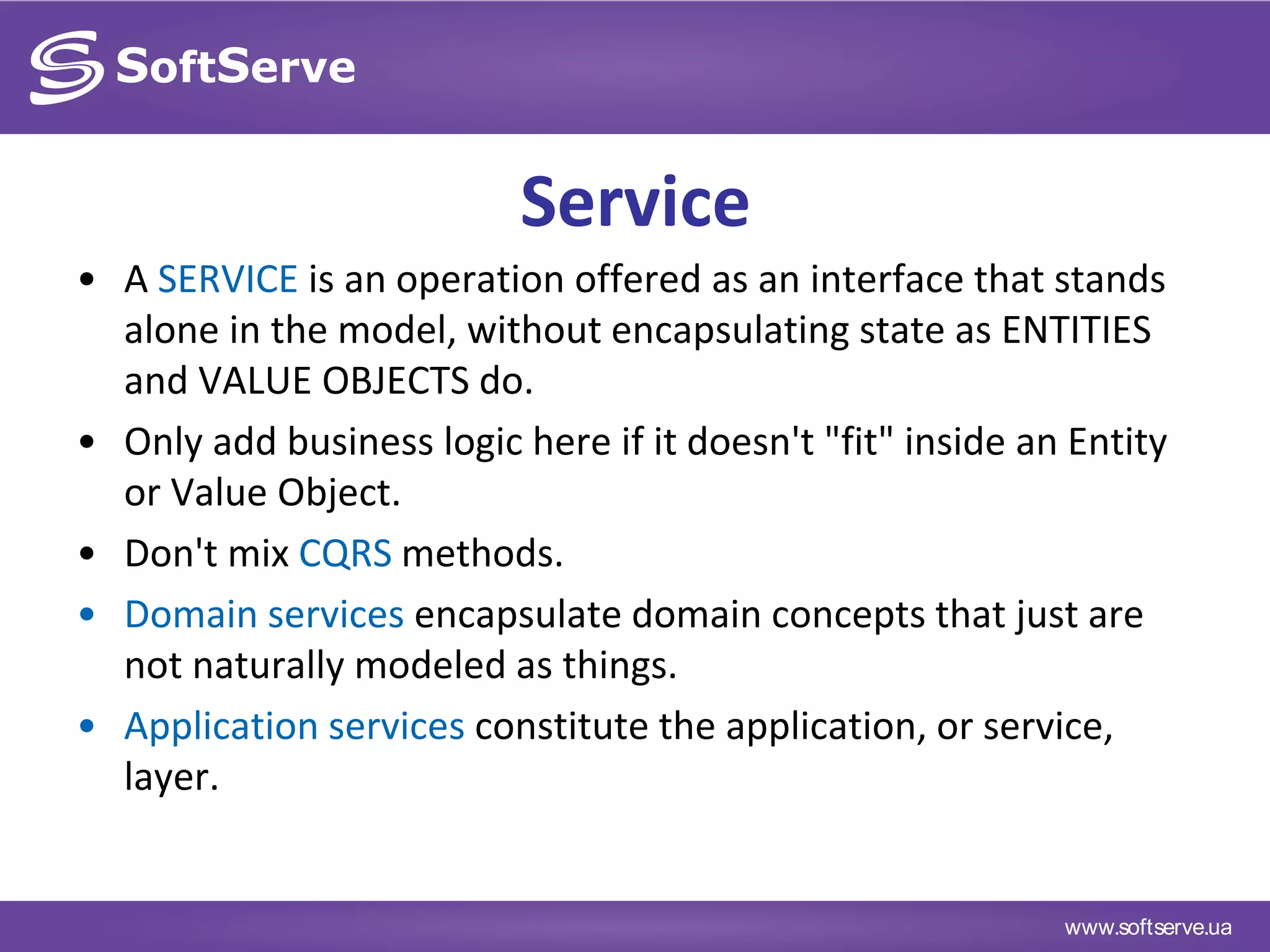
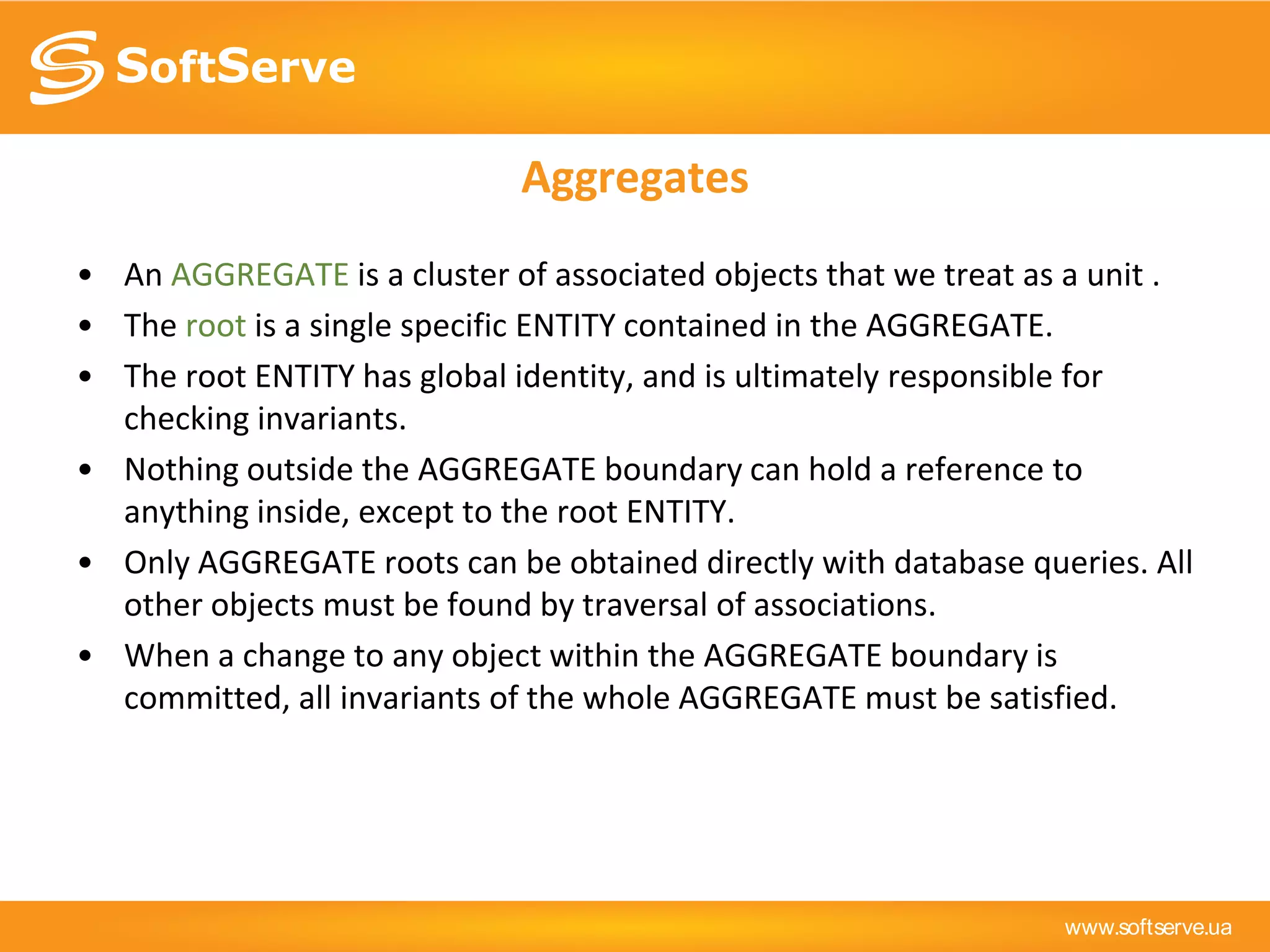
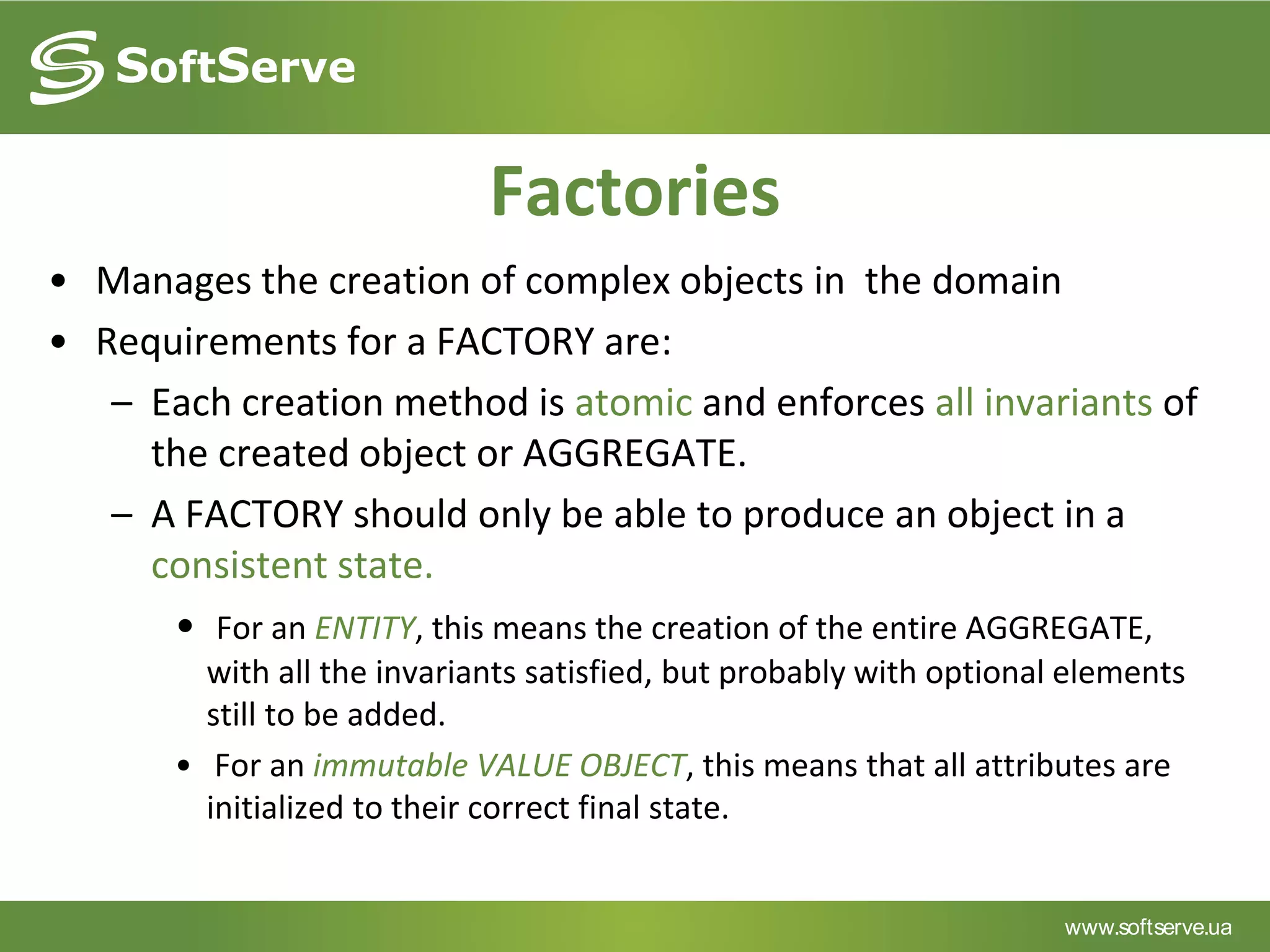
This document provides an overview of key concepts in Domain-Driven Design (DDD) including the model, ubiquitous language, entities, value objects, services, aggregates, factories, and repositories. It defines each concept, provides examples, and references additional resources for learning more about DDD.