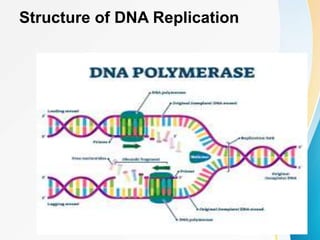
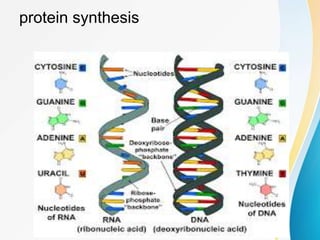
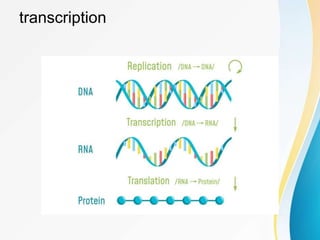
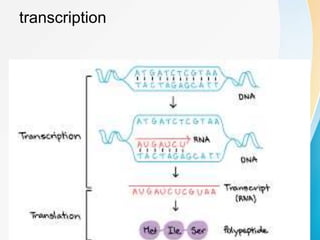
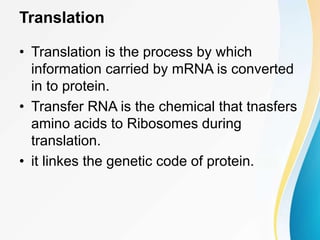
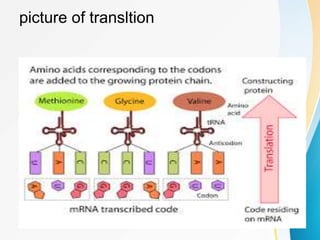
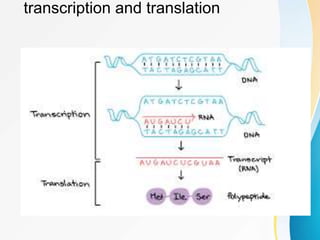
This document summarizes a presentation on DNA replication and protein synthesis. It defines DNA replication as producing two identical copies of DNA from one original molecule through semi-conservative replication. It describes the steps of DNA replication as unwinding, complementary base pairing, and joining. It also summarizes transcription as creating mRNA from DNA, and translation as using mRNA to create proteins with the help of tRNAs and ribosomes. The importance of DNA replication is that it is required for growth, repair, and tissue regeneration in living organisms.