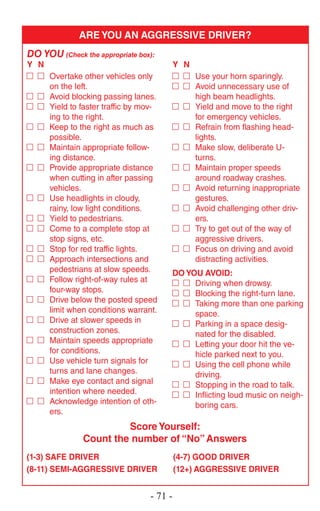
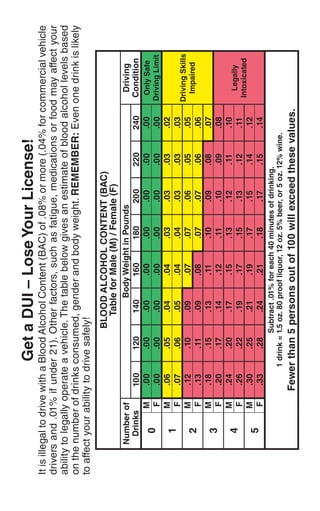
This document is the introduction to the 2014 California Driver Handbook. It was written by Brian P. Kelly, Secretary of the California State Transportation Agency. It introduces the updated 2014 edition of the handbook and notes that DMV has introduced an interactive iPad version and educational videos on their YouTube channel to help drivers study and prepare for the driver's license exam. It encourages both new and experienced drivers to use the handbook and other DMV resources to promote safe driving.


















![driving test, the driver’s name
must show on the contract as
the insured driver. You must
also wear your seat belt.
NOTE:Thebehind-the-wheeldriv-
ing test will be rescheduled if the
vehicle does not meet the above re-
quirements or if you refuse to use
yourseatbeltduringthedrivingtest.
For more information, refer to the
How to Prepare for Your Driving
Test (FFDL 22) Fast Facts bro-
chure, DMV videos, and sample
tests available online at www.dmv.
ca.gov.
Special Section -
Minors
Minors’ Permit Requirements
A minor is a person under 18 years
of age. Minors must have their ap-
plications (for a driver license or
any change of driver license class)
signed by their parent(s) or legal
guardian(s). If both parents/guard-
ians have joint custody, both must
sign.
NOTE: Minors may not work as
a driver for pay and they may not
driveaschoolbuscontainingpupils.
To get a permit you must:
• Be at least 151
/2 years of age, but
under 18 years of age.
• Complete the Driver License or
Identification Card Application
(DL 44) form.
• Haveyourparent(s)orguardian(s)
sign the DL 44 form.
• Pass the traffic laws and road
signs test. If you fail the test, you
must wait one week before retak-
ing the test.
• If you are 151
/2–171
/2 years of age,
youwillneedtoprovideproofthat
you:
– Completed driver education
(Certificate of Completion of
Driver Education) OR
– Are enrolled and participat-
ing in an approved integrated
driver education/driver train-
ing program (Certificate of
Enrollment in an Integrated
[Classroom] Driver Education
andDriverTrainingProgram).
For more information, refer
to the Provisional Licensing
(FFDL19)FastFactsbrochure
at www.dmv.ca.gov.
The provisional permit is not valid
until you start your behind-the-
wheel driver training with an in-
structor or reach age 171
/2.
If you have a permit and plan to
drive outside of California, check
licensing requirements in that state
or country.
NOTE: If you are at least 171
/2
years of age, you may obtain a per-
mit without completing driver edu-
cation or driver training. However,
you cannot get a driver license be-
fore you are 18 years old.
Minors’ Permit Restrictions
Your permit is not valid until you
begin driver training; your instruc-
tor will sign the permit to validate
it.Youmustpracticewithalicensed
- 10 -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infographictest-150415195908-conversion-gate02/85/DMV-manual-20-320.jpg)
















































































![They may renew the registration in
their home state before it expires or
register the vehicle in California.
The items needed to register any
out-of-state vehicle are:
• Completed and signed Appli-
cation for Title or Registration
(REG 343).
• Verification of the vehicle com-
pleted by the DMV, law en-
forcement agent, or an auto club
employee.
• Out-of-state title and/or last is-
sued out-of-state registration
card, if the title is not submitted.
• Smog certification, if required.
• Weightcertificateforcommercial
vehicles only.
• Appropriate vehicle registration
fees and use tax, if applicable.
• Completed Odometer Mile-
age Disclosure statement, if
applicable.
If the vehicle is purchased from a
dealerenrolledintheBPAprogram,
the documentation may be submit-
ted by the dealer to DMV.
Vehicle Theft Prevention Tips
IntheUnitedStates,avehicleissto-
len an average of every 21 minutes.
Vehicle theft results in costs to the
victim and it increases insurance
premiums. Also, vehicle thieves of-
ten use the stolen vehicles to com-
mit other crimes.
Vehicle thefts occur more often
where large groups of cars are
parked at any time of day for ex-
tended periods of time, such as
• Odometer Mileage Disclosure
Statement, if applicable.
• Appropriate vehicle registration
fees.
When you sell or transfer a vehi-
cle, report it to the DMV within 5
days. You can complete the Notice
of Transfer and Release of Liability
(REG 138) form online, download
andmailthecompletedform,orcall
the DMV at 1-800-777-0133 to re-
quest the form be mailed.
Out-of-State Vehicles
Vehicles registered in another state
orforeigncountrymustberegistered
in California within 20 days after
you become a resident or get a job
(refer to page 2 for information
regarding additional residency
criteria).
NOTE: If you are a California resi-
dent and acquire a new car, truck,
or motorcycle (this includes cer-
tain diesel powered vehicles) from
another state, ensure that it meets
California smog laws; otherwise,
it might not qualify to be regis-
tered here. The DMV cannot ac-
cept an application to register the
vehicle in California when the ve-
hicle does not qualify for registra-
tion(HealthandSafetyCode[H&S]
§§43150-43156).
Nonresidentmilitarypersonneland
their spouses may operate their ve-
hicles in California with their valid
homestatelicenseplatesoruntilthe
plates issued from the state of their
last assigned duty station expire.
- 96 -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infographictest-150415195908-conversion-gate02/85/DMV-manual-106-320.jpg)









