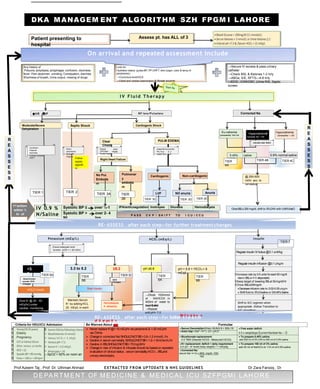
This document provides guidelines for the management of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in patients presenting to the hospital. It outlines an algorithm with multiple tiers of treatment based on the patient's symptoms, vital signs, lab results and response to initial therapy. The initial focus is fluid resuscitation and insulin therapy to lower blood sugar levels. Ongoing assessment of electrolytes, pH, bicarbonate and osmolality are recommended to guide further treatment and monitor for complications. Criteria for admission to higher levels of care like the ICU are also presented.