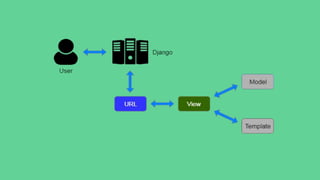
The document is a tech talk by Amanpreet Singh on Django, highlighting its features such as security, scalability, and versatility. It covers various aspects of Django including the model layer, view layer, template layer, and the request-response cycle, along with key concepts like migrations, managers, and middleware. The talk emphasizes Django's design architecture while explaining its components and functionalities through an overview of model definitions, queries, and error handling.