Embed presentation

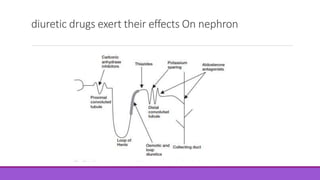
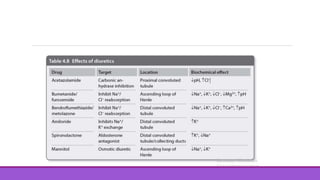



This document discusses two diuretic drugs: Mannitol and Spironolactone. Mannitol is an osmotic diuretic that works by not being reabsorbed and increasing the osmolality of the kidney filtrate, causing water to be excreted. It can be used to treat increased intracranial pressure. Spironolactone is an aldosterone antagonist that works in the distal convoluted tubule and collecting ducts by competitively blocking aldosterone and its stimulation of sodium reabsorption in exchange for potassium. It has uses in treating ascites, nephrotic syndrome, and primary hyperaldosteronism.





