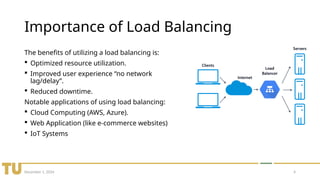
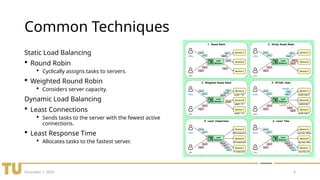
The document discusses load balancing in distributed systems, highlighting its importance in optimizing resource utilization and improving user experience. It outlines various challenges such as dynamic workloads and fault tolerance, as well as common and advanced techniques for load balancing. Future trends include edge computing, energy efficiency, and AI integration for smarter allocation.