1. The document discusses implementing blockchain using cloud computing. Blockchain provides a distributed ledger and enables secure transfer of assets without intermediaries. It consists of blocks, miners, and nodes.
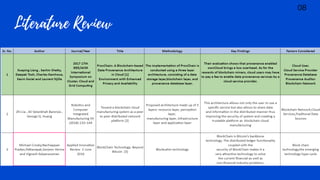
2. Several research papers are reviewed that propose using blockchain for data provenance in cloud storage. Blockchain can provide tamper-proof records and transparency of data accountability. It also enhances privacy and availability of provenance data.
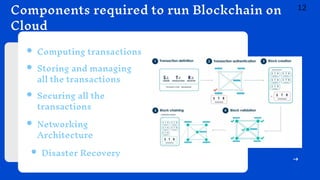
3. Implementing blockchain using cloud computing provides benefits like better decentralization, efficient ownership tracking, increased data security, faster disaster recovery, and geo-independence. Security challenges like 51% attacks are also discussed.







![Toward a blockchain cloud
manufacturing system as a peer to
peer distributed network platform [2]
Platform Evaluation.
Case Study Evaluation where
data can be shared in a
distributed manner.
Security Evaluation.
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsrmseminar-210501065059/85/Distributed-Systems-for-Blockchain-using-Cloud-9-320.jpg)






![Real-time auditing for all
data access in the cloud
storage application.
ProvChain: A Blockchain-based Data
Provenance Architecture in Cloud
Environment with Enhanced Privacy
and Availability [1]
Transforming the
provenance data and
uploading the record to
the blockchain network
Validation
Performance and Overhead
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsrmseminar-210501065059/85/Distributed-Systems-for-Blockchain-using-Cloud-21-320.jpg)
![Toward a blockchain cloud
manufacturing system as a peer to
peer distributed network platform [2]
Platform Evaluation.
Case Study Evaluation where
data can be shared in a
distributed manner.
Security Evaluation.
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsrmseminar-210501065059/85/Distributed-Systems-for-Blockchain-using-Cloud-22-320.jpg)
![Private Securities
Insuarance
BlockChain Technology: Beyond
Bitcoin [3]
Notary
Decentralised Storage
Decentralized proof of
existence of documents
Applications
of
Blockchain
in
Financial
and
Non-
Financial
Areas
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsrmseminar-210501065059/85/Distributed-Systems-for-Blockchain-using-Cloud-23-320.jpg)
![Distributed Cloud Computing:
Applications, Status Quo, and
Challenges [4]
Reducing Latency
Computation at the Edge: Managing VMs
1.
2.
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsrmseminar-210501065059/85/Distributed-Systems-for-Blockchain-using-Cloud-24-320.jpg)
![AUTHENTICATION
An attacker carries out various attempts to access a user’s personal key stored in the user’s computer or smartphone in order
to hack the bitcoin.
SECURITY INCIDENTS
51% Attack
Improved Blockchain
1.
2.
Blockchain Security in Cloud Computing: Use Cases, Challenges, and
Solutions [5]
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsrmseminar-210501065059/85/Distributed-Systems-for-Blockchain-using-Cloud-25-320.jpg)

![References. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7973733 [1]
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0736584518
30022X [2]
https://j2-capital.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/AIR-2016-
Blockchain.pdf [3]
Distributed Cloud Computing: Applications, Status Quo, and
Challenges [4]
Blockchain Security in Cloud Computing: Use Cases, Challenges, and
Solutions [5]
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsrmseminar-210501065059/85/Distributed-Systems-for-Blockchain-using-Cloud-27-320.jpg)
