Embed presentation
Download to read offline

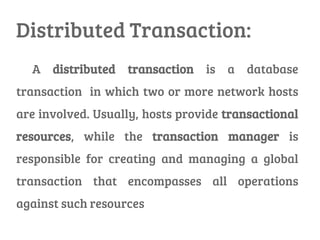
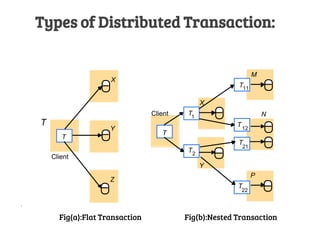
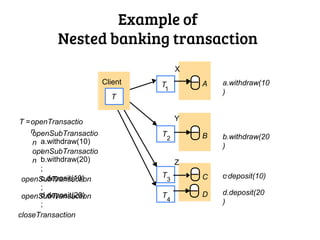

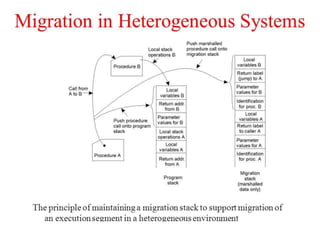
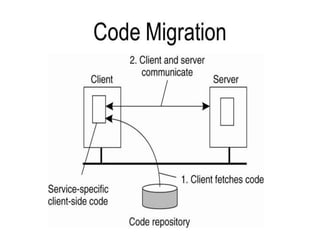
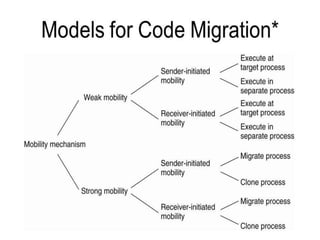
There are two types of distributed transactions: flat and nested. A flat transaction involves multiple hosts but has a single level, while a nested transaction can have subtransactions with their own transaction identifiers. An example is given of a nested banking transaction with withdrawals and deposits as subtransactions managed by a transaction manager across different clients. Distributed transactions allow for transactions spanning multiple network hosts and systems.








