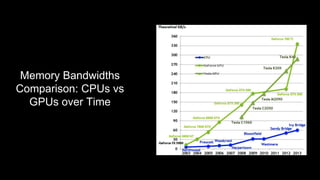
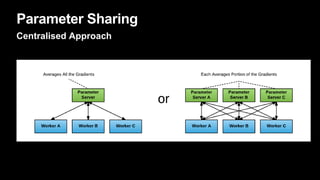
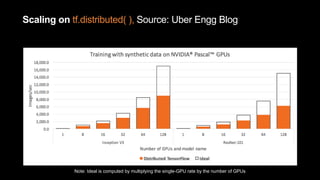
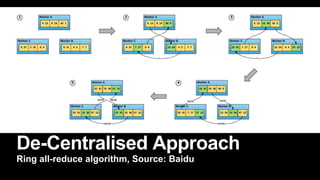
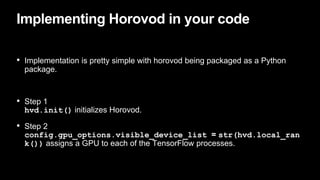
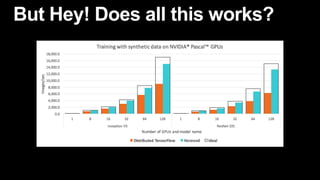
This document discusses distributed deep learning using a cluster of GPUs. It begins by comparing CPUs and GPUs, noting that GPUs are better for deep learning due to higher memory bandwidth and more cores. While GPUs provide better performance, training models across multiple GPUs is challenging. TensorFlow allows data parallelism across GPUs, but this centralized approach has scaling issues. The document then introduces Horovod, an open source library that uses a decentralized ring all-reduce algorithm to average gradients across GPUs. This approach scales nearly linearly and has lower communication overhead than TensorFlow's centralized parameter sharing. Implementation in TensorFlow involves initializing Horovod, assigning GPUs, wrapping the optimizer, and broadcasting variables.