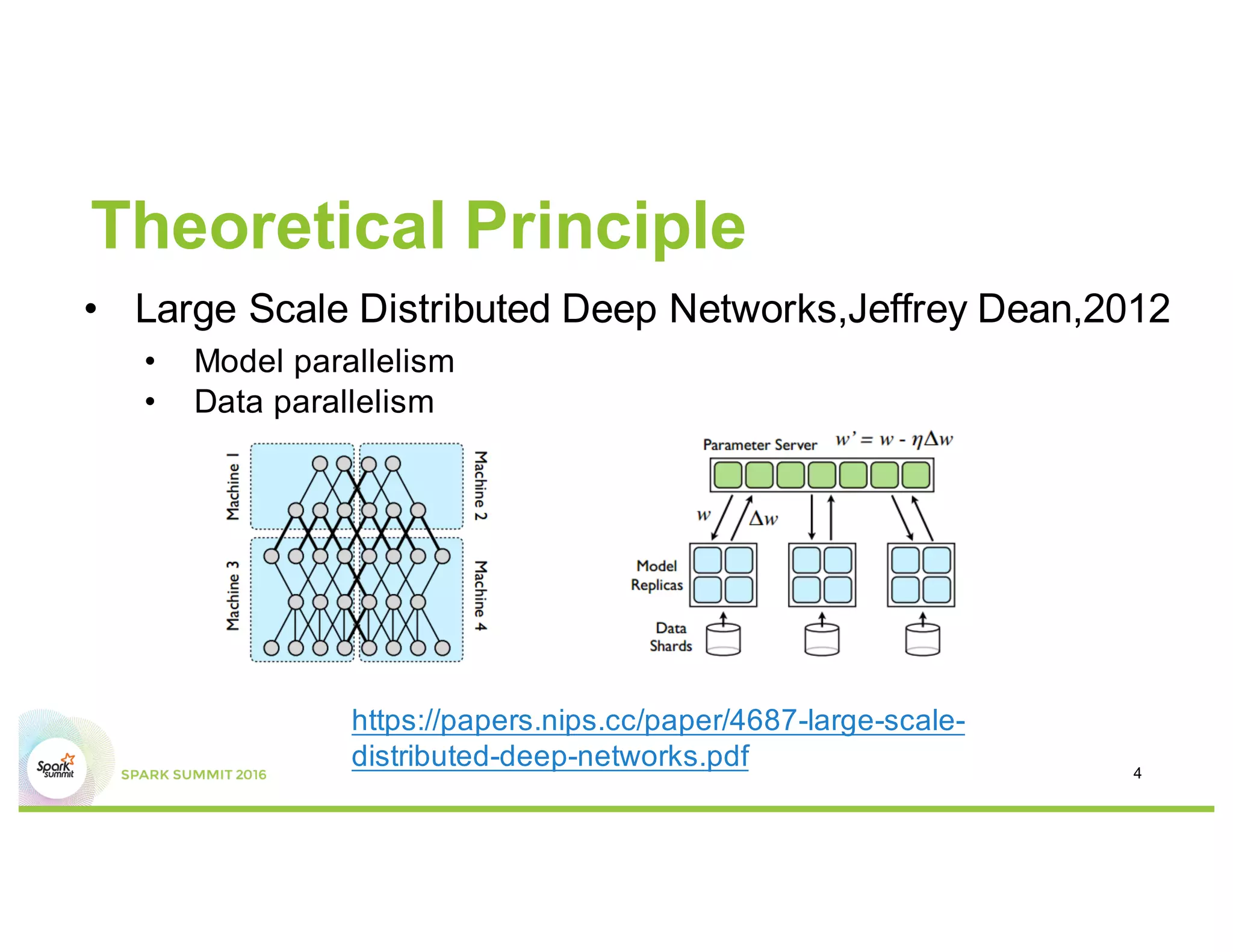
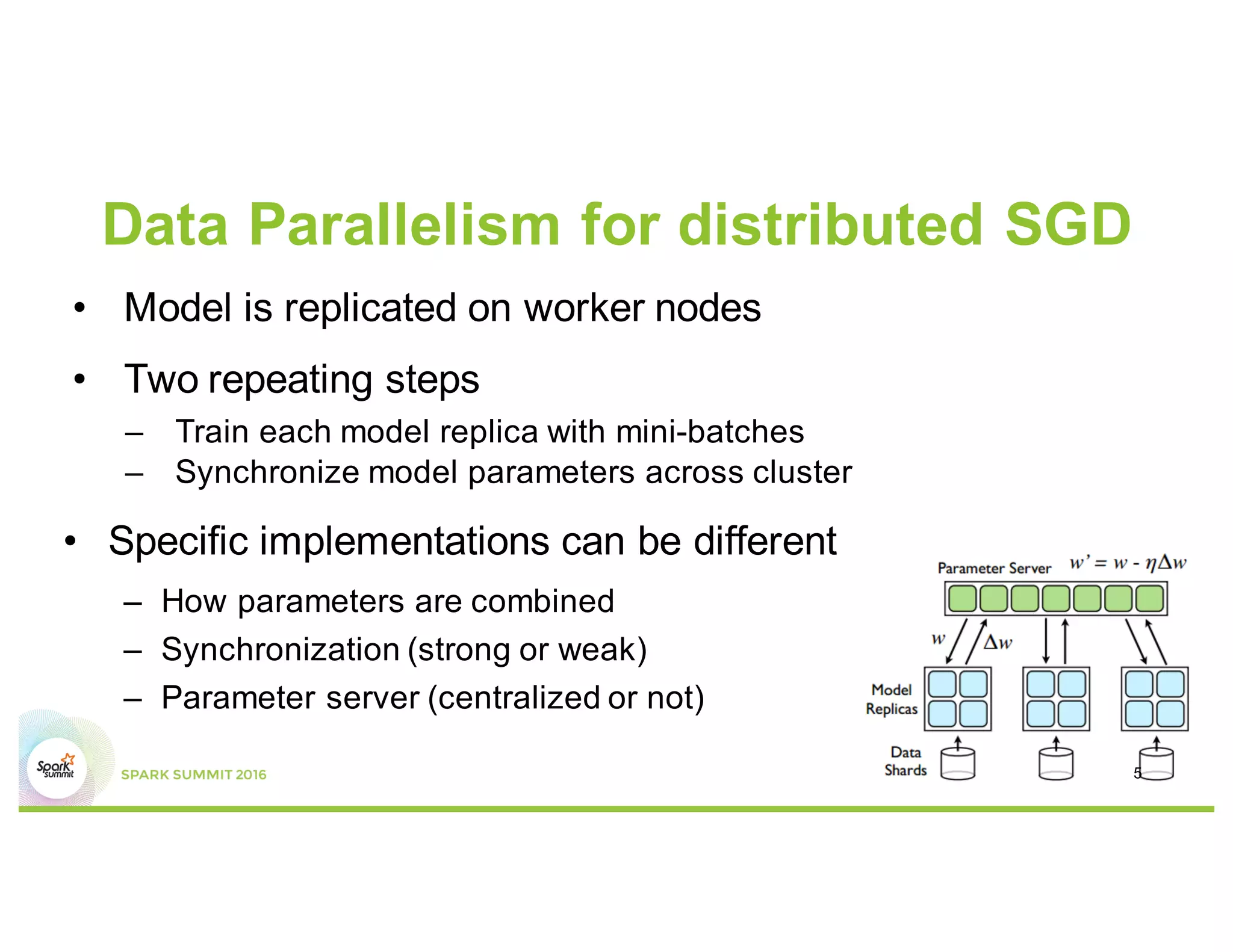
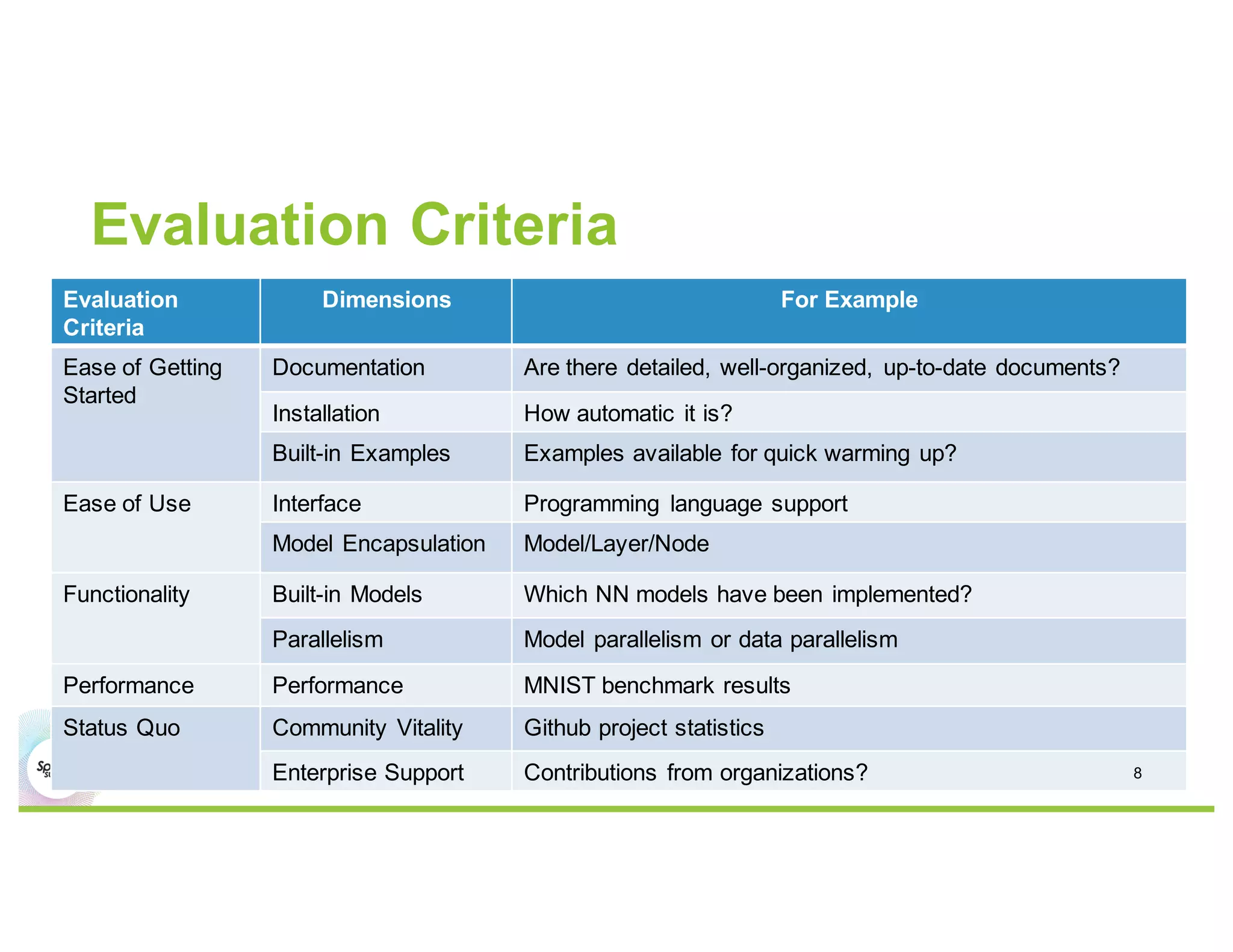
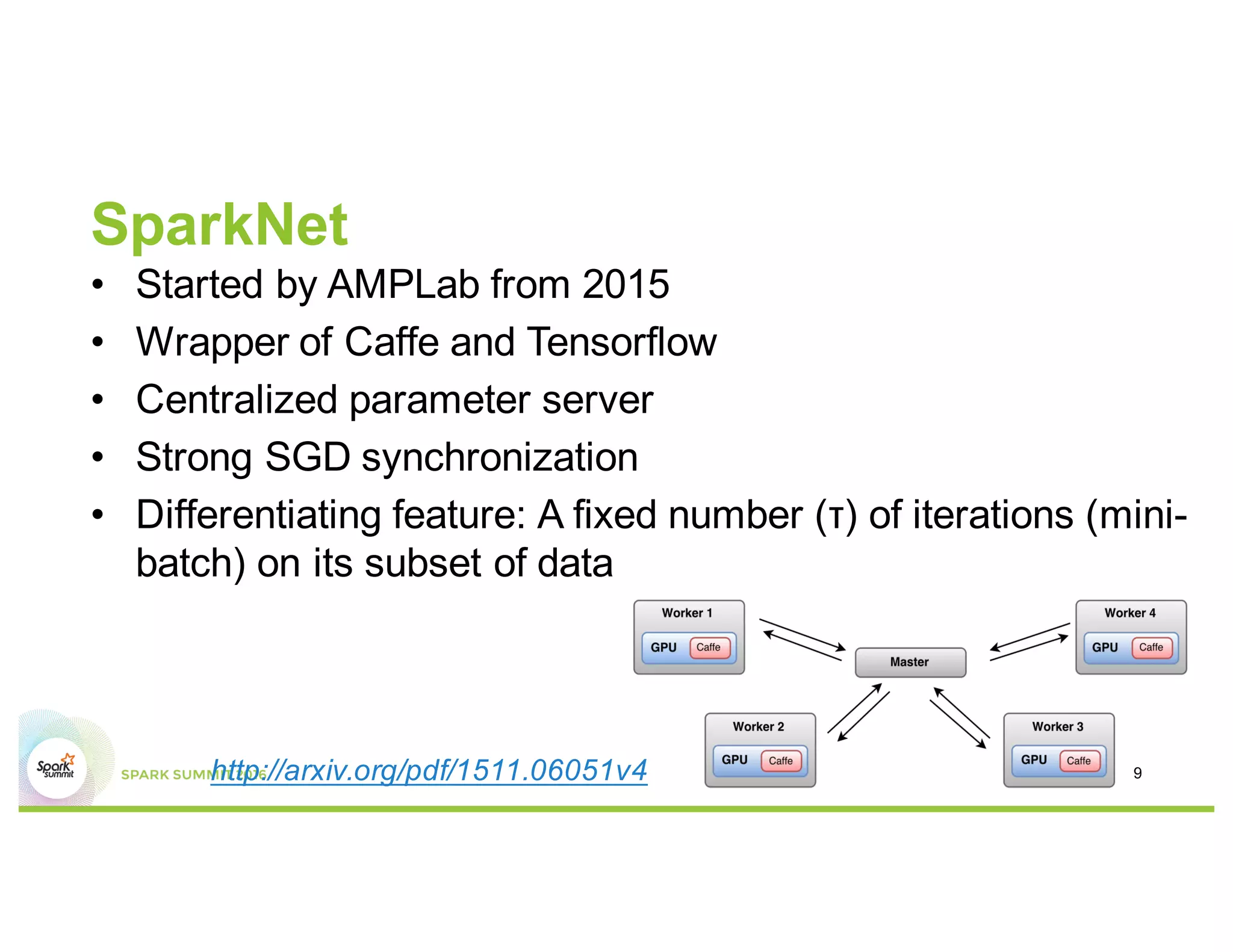
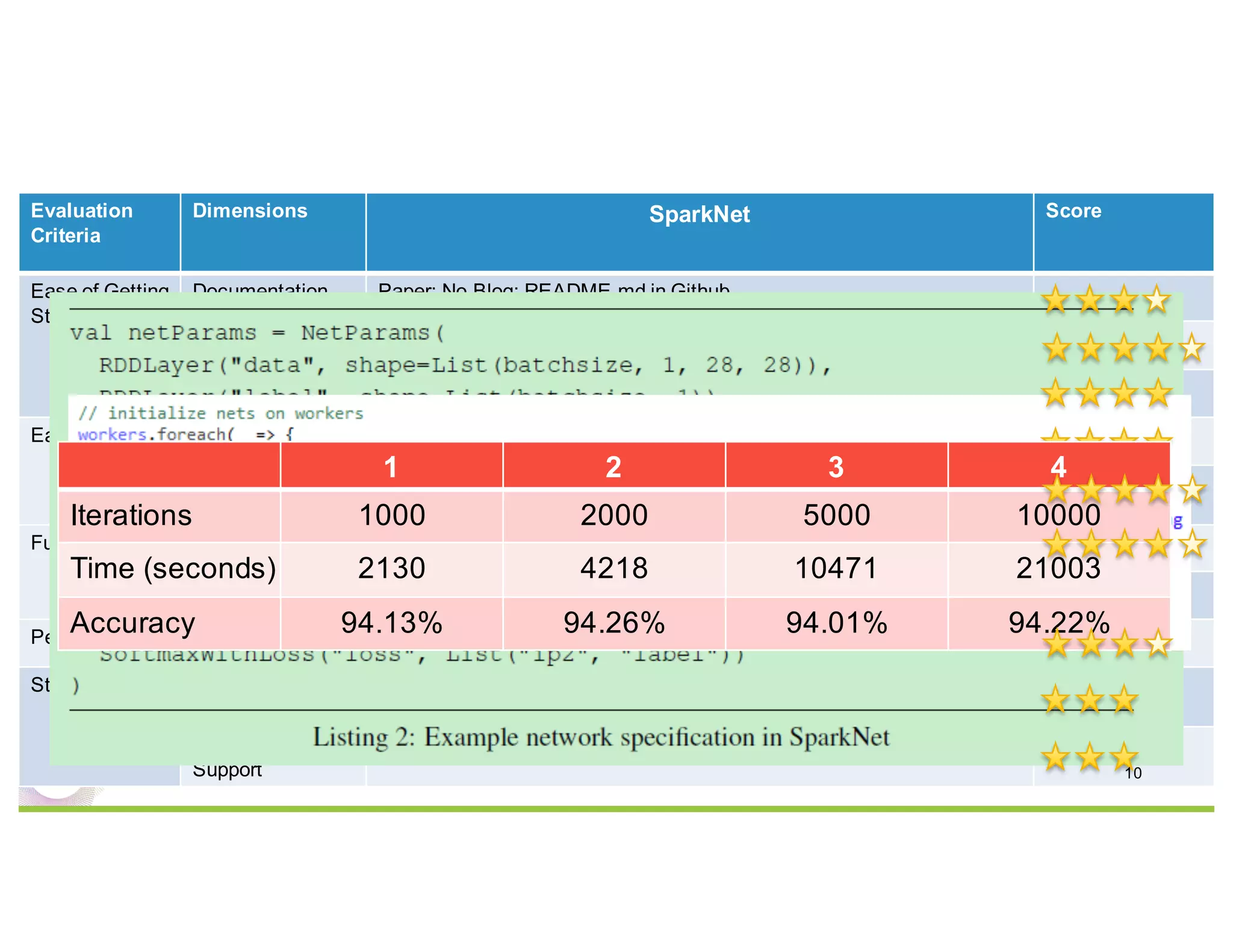
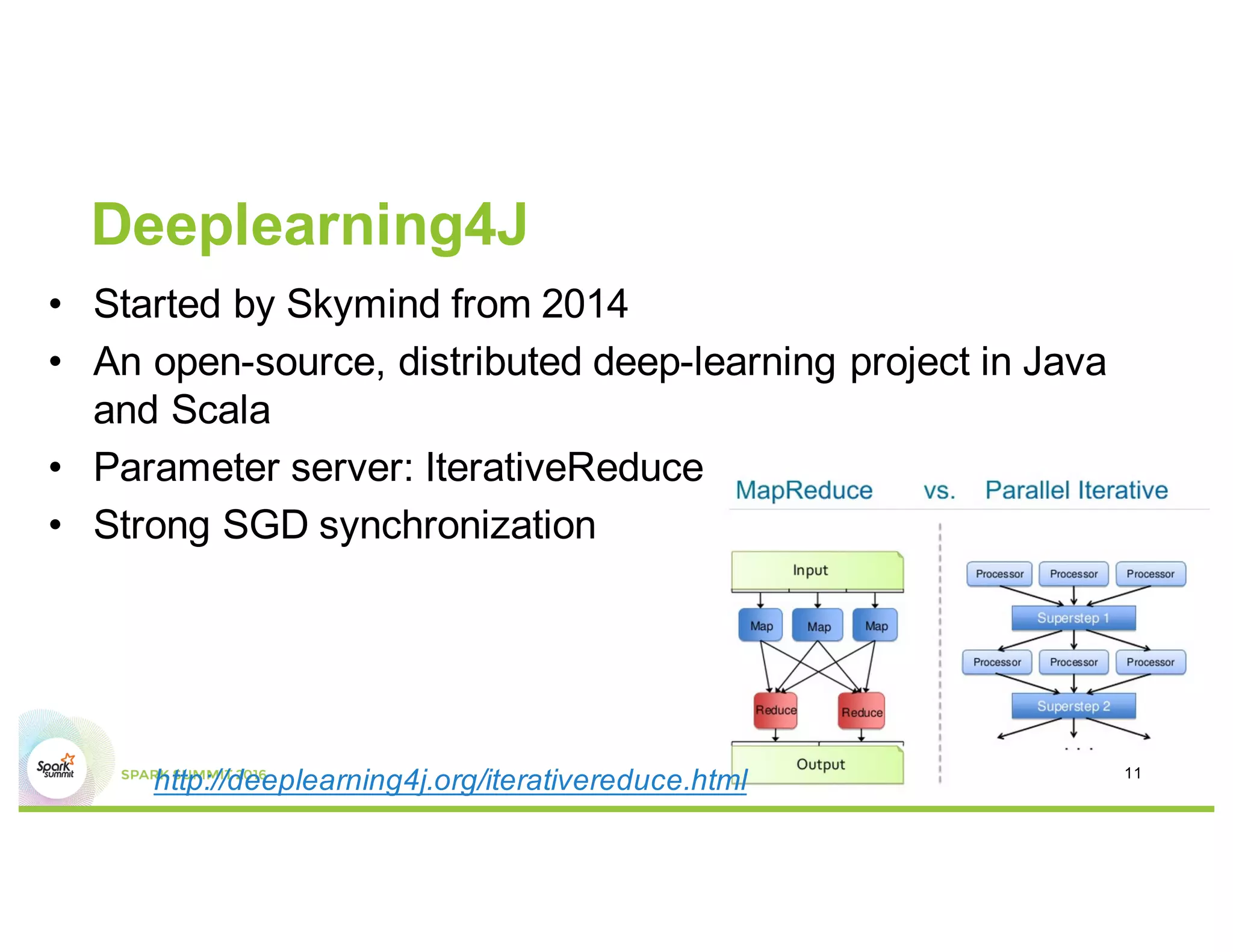
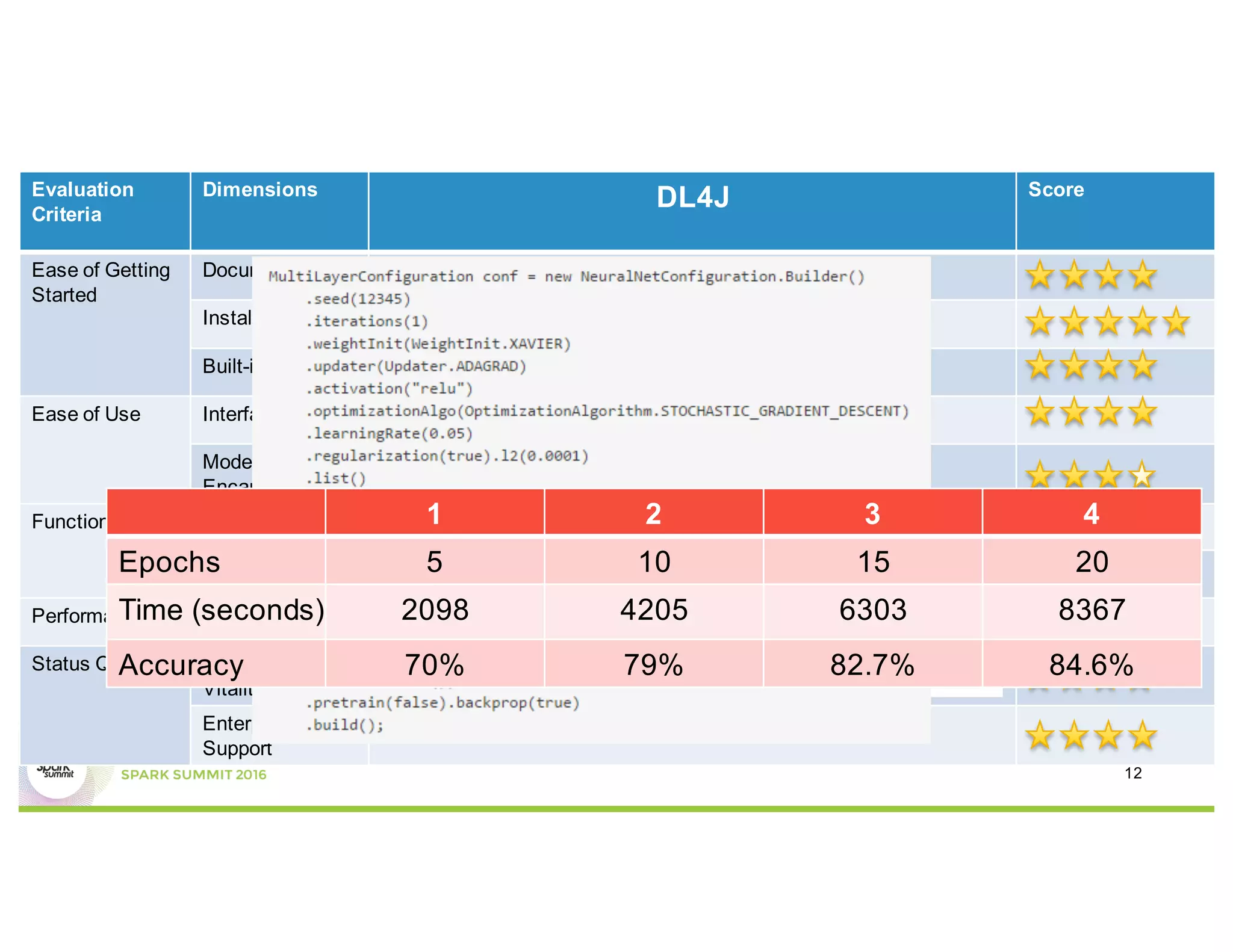
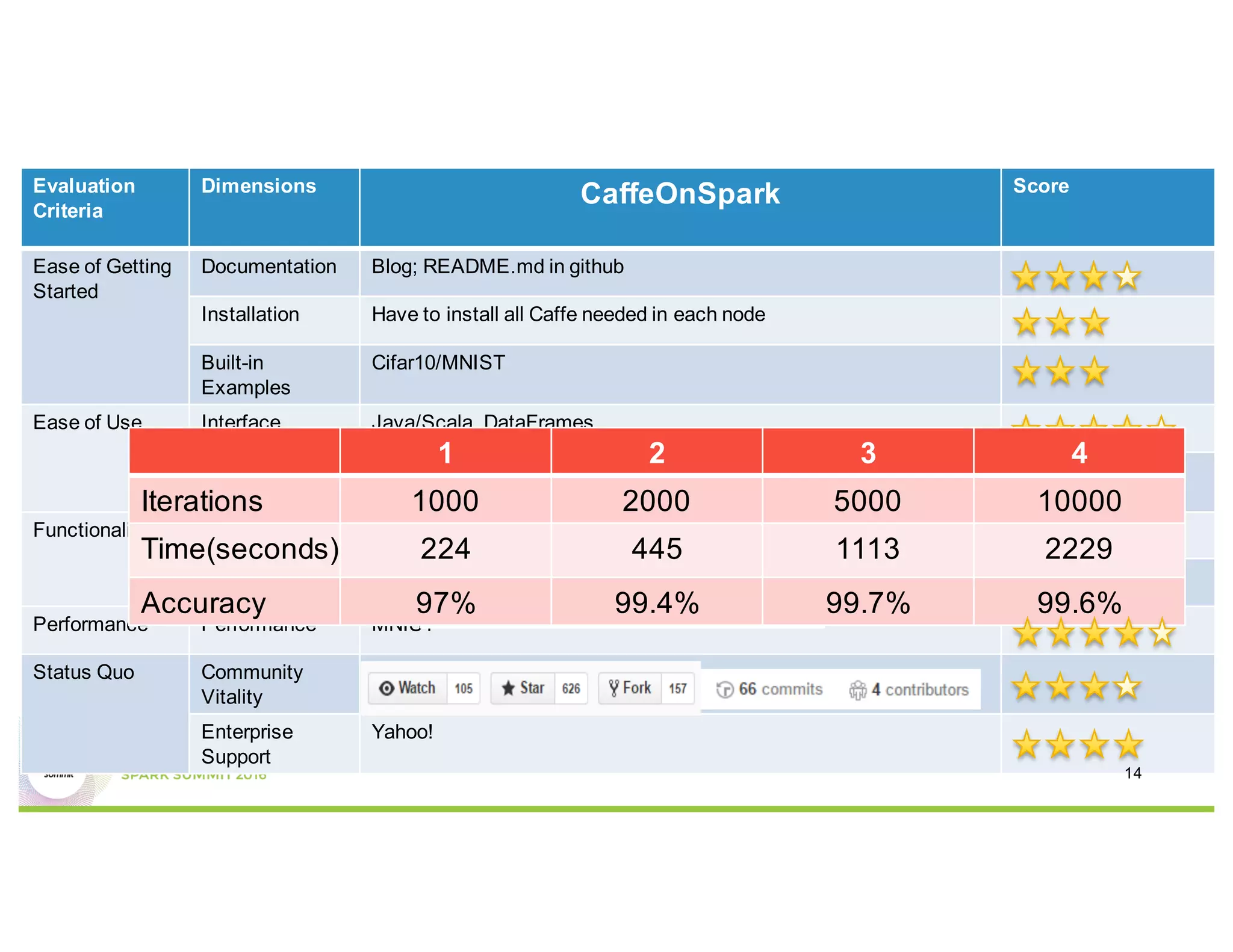
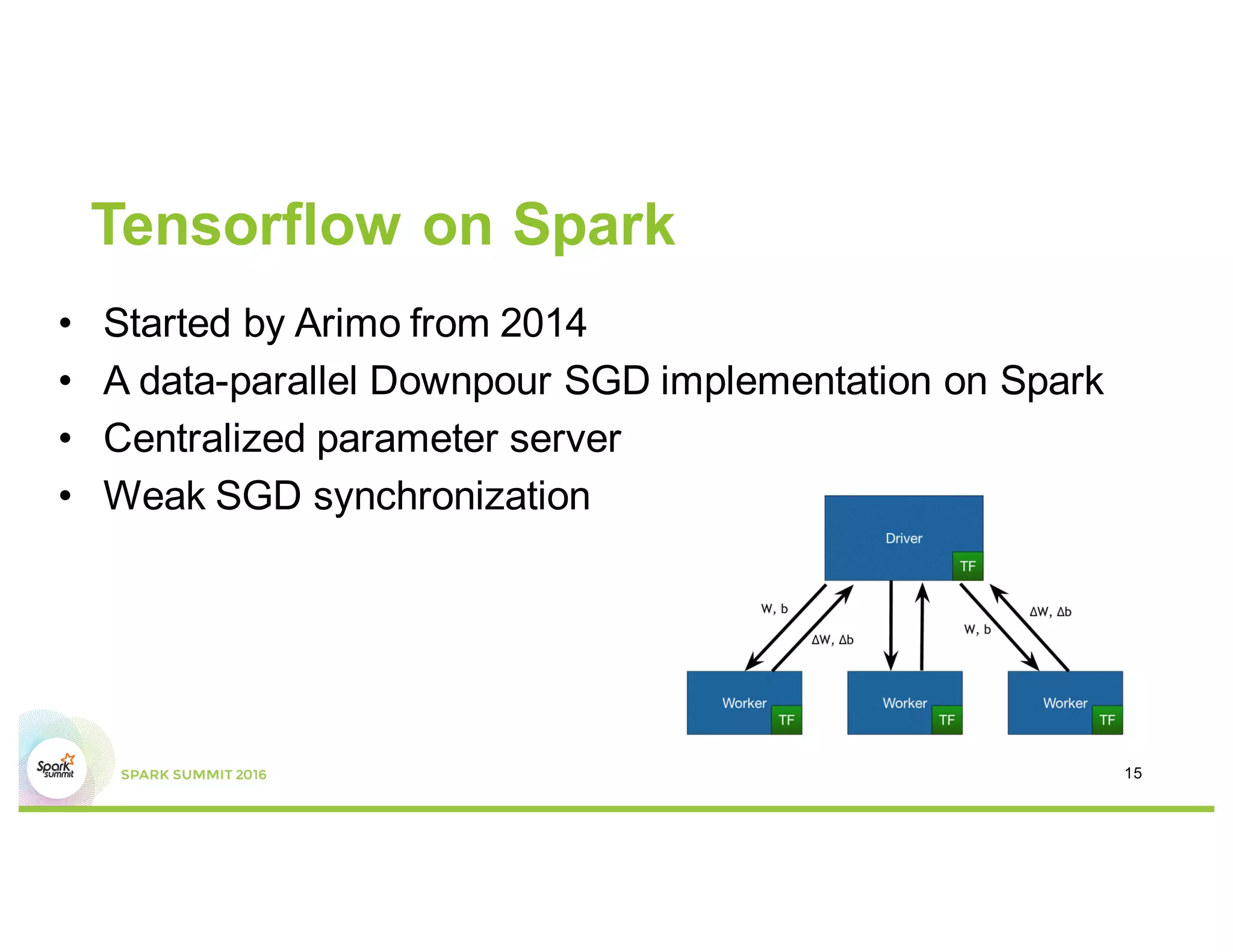
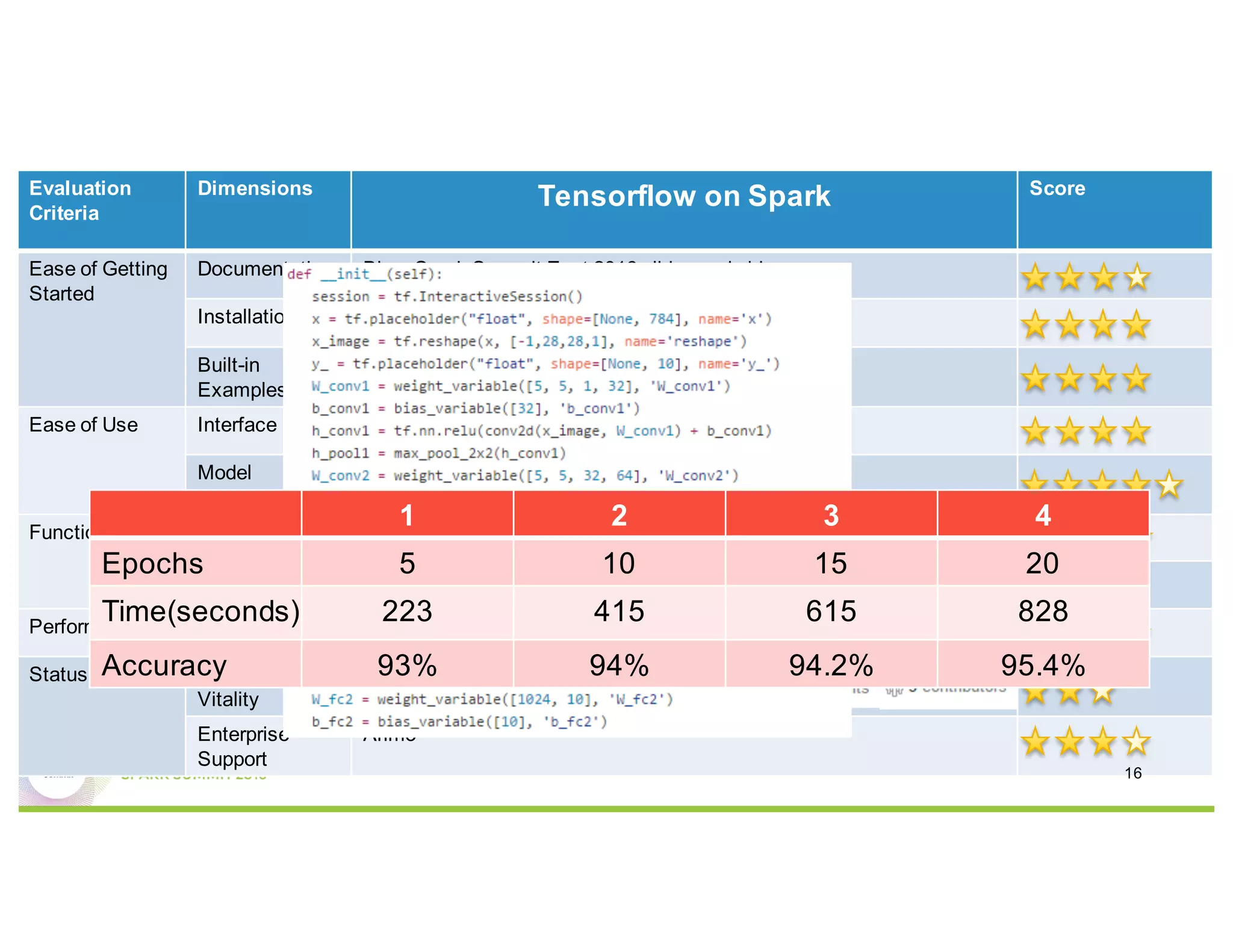
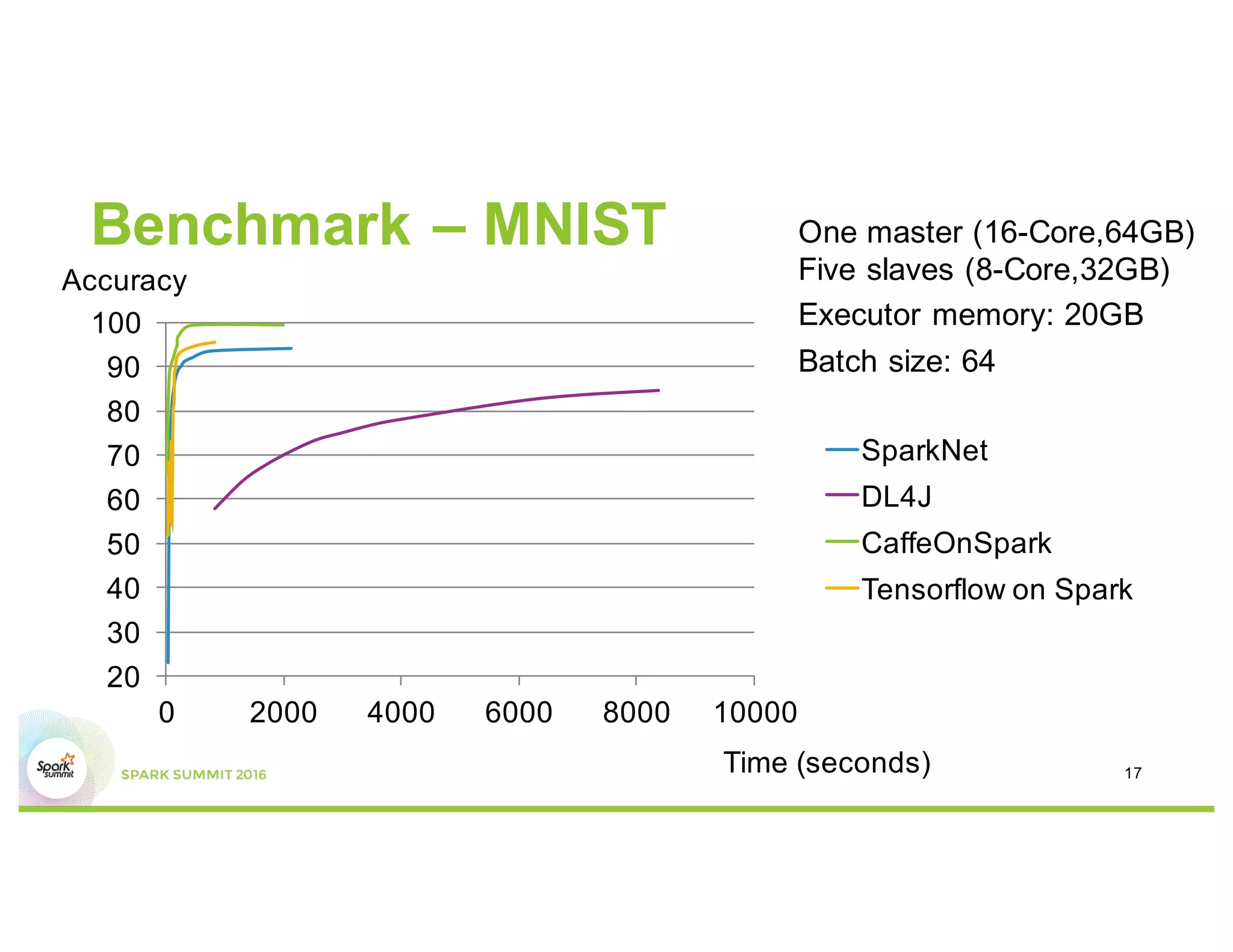
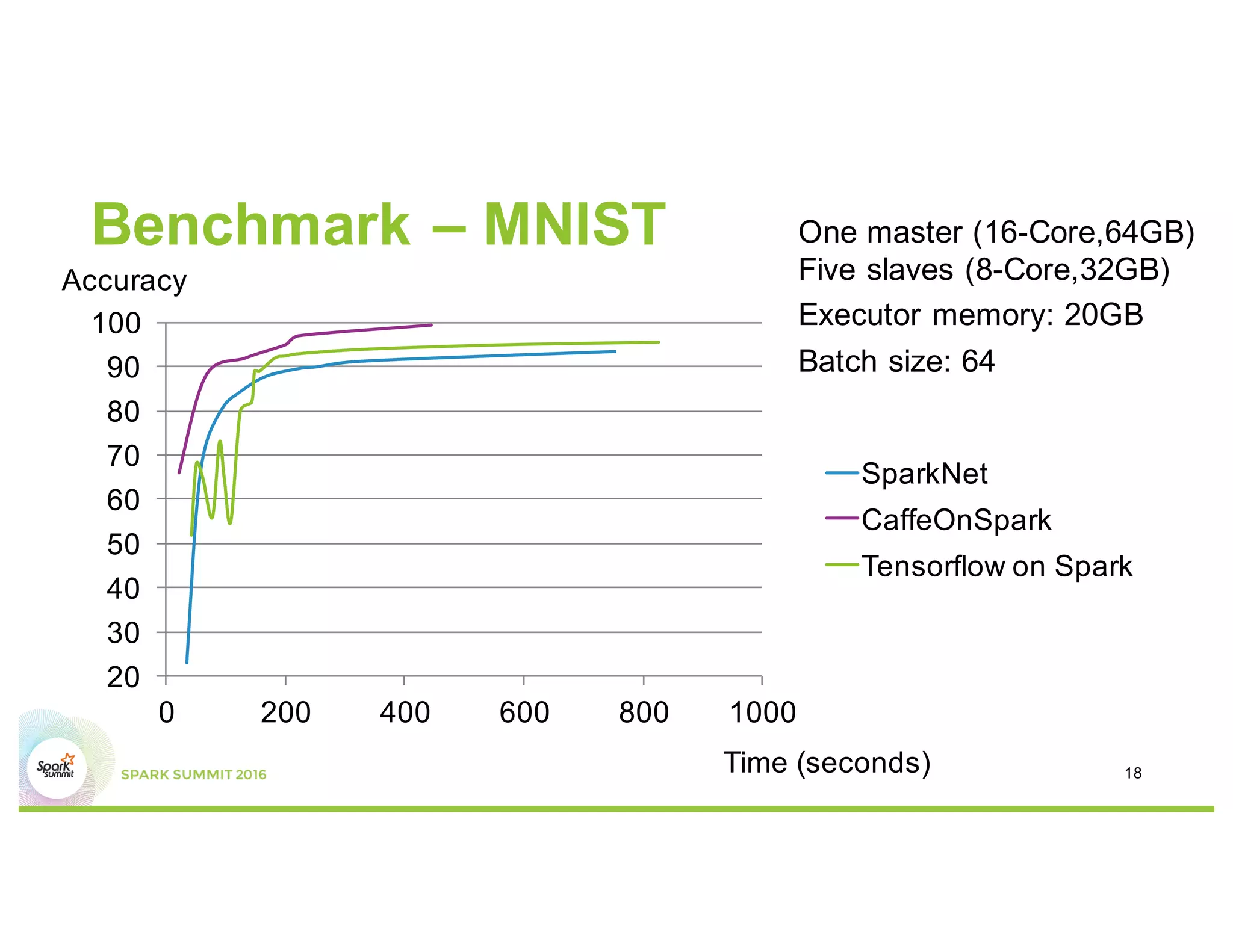
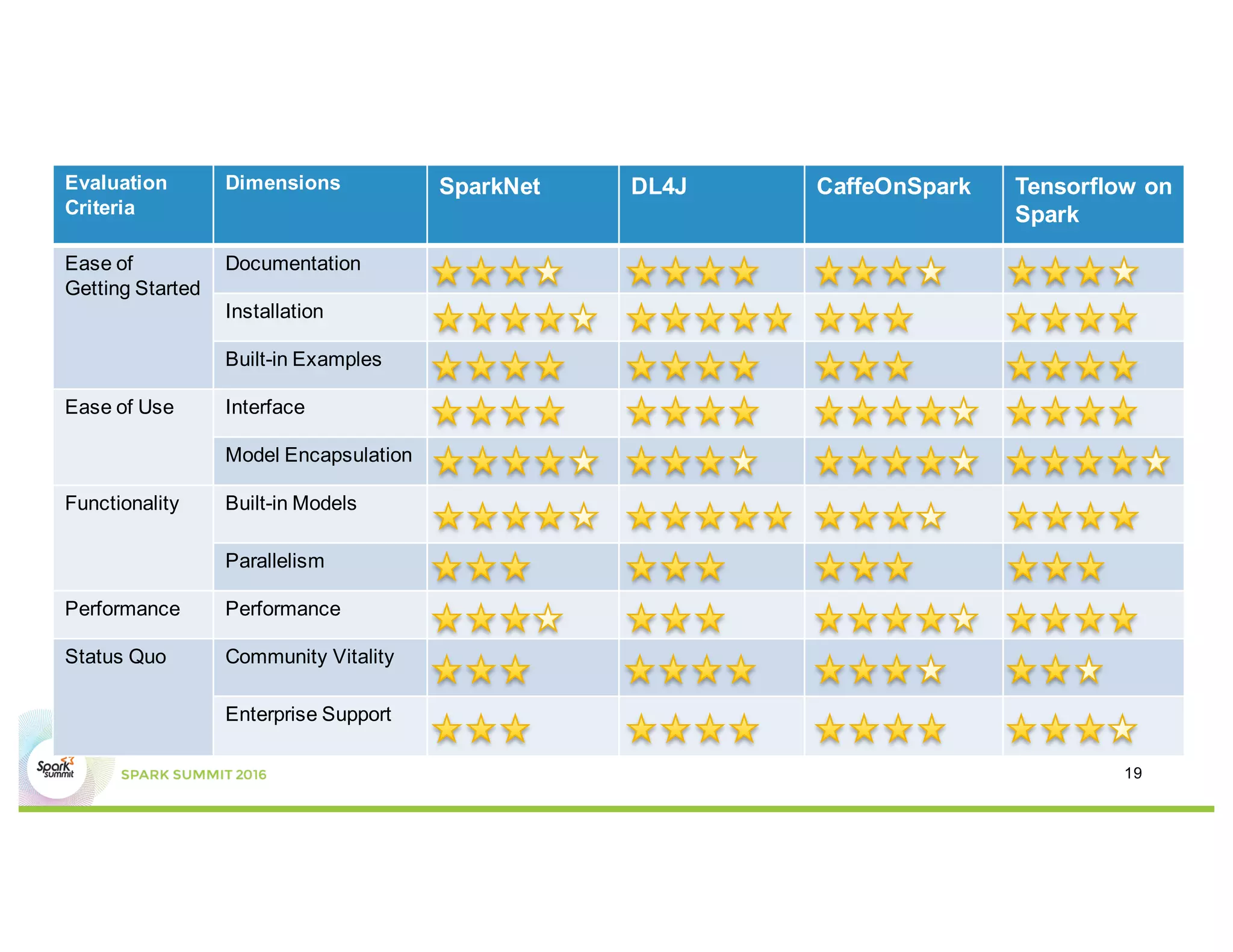
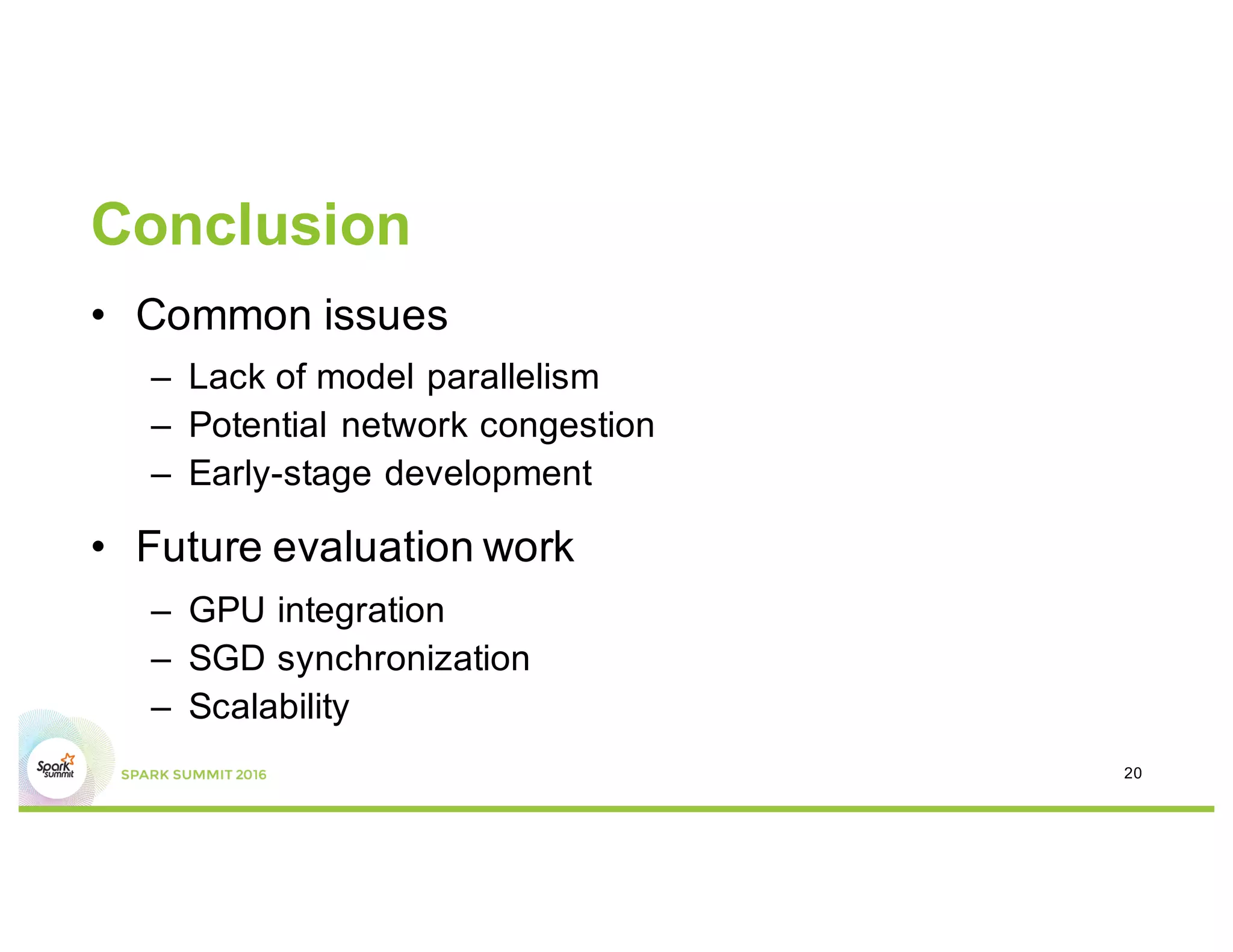
This document compares several deep learning frameworks that run on Apache Spark, including SparkNet, Deeplearning4J, CaffeOnSpark, and Tensorflow on Spark. It outlines the theoretical principles behind data parallelism for distributed stochastic gradient descent. It then evaluates and benchmarks each framework based on criteria like ease of use, functionality, performance, and community support. SparkNet, CaffeOnSpark, and Tensorflow on Spark are shown to have stronger communities and support from organizations. The document concludes that while these frameworks currently lack model parallelism and could experience network congestion, integrating GPUs and improving scalability are areas for future work.