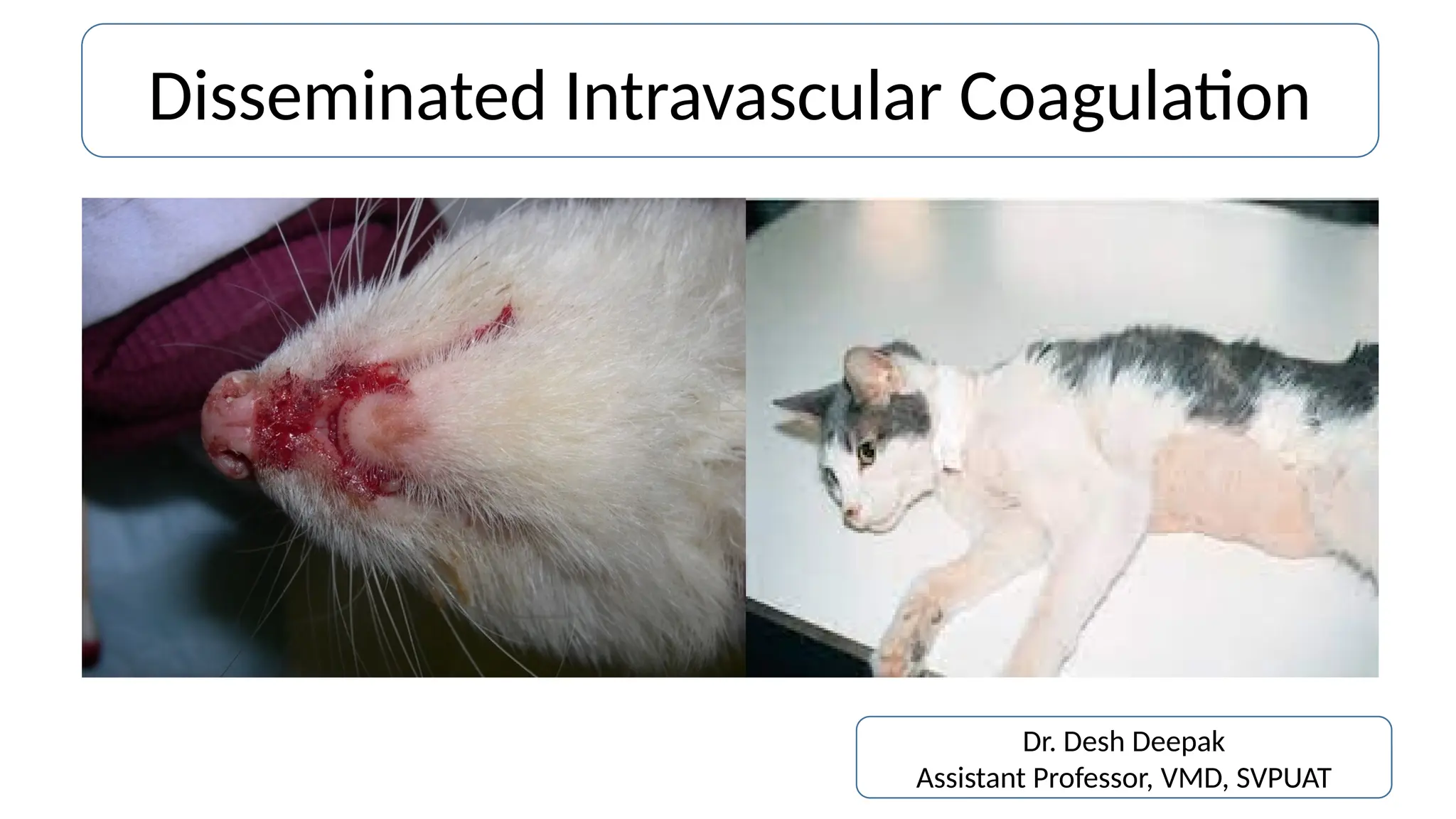
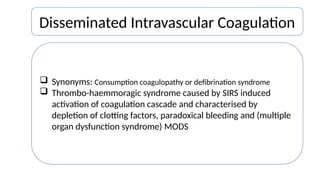
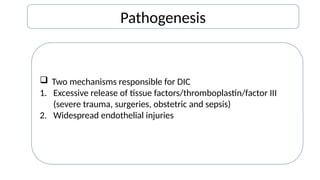
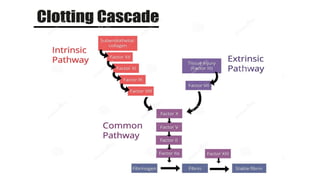
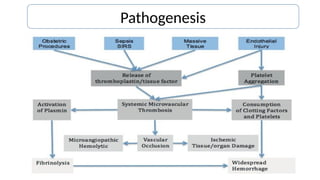
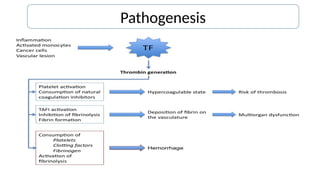
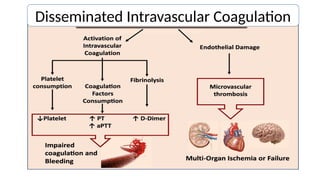
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a thrombo-haemorrhagic syndrome characterized by the activation of the coagulation cascade leading to clotting factor depletion and bleeding, often associated with severe underlying conditions. Diagnosis involves clinical assessment and coagulation profiles, and management focuses on treating the underlying cause, maintaining blood oxygen levels, correcting fluid imbalances, and restoring clotting factors. Anticoagulant therapy may be used in certain cases, though its application in animal practice remains controversial.