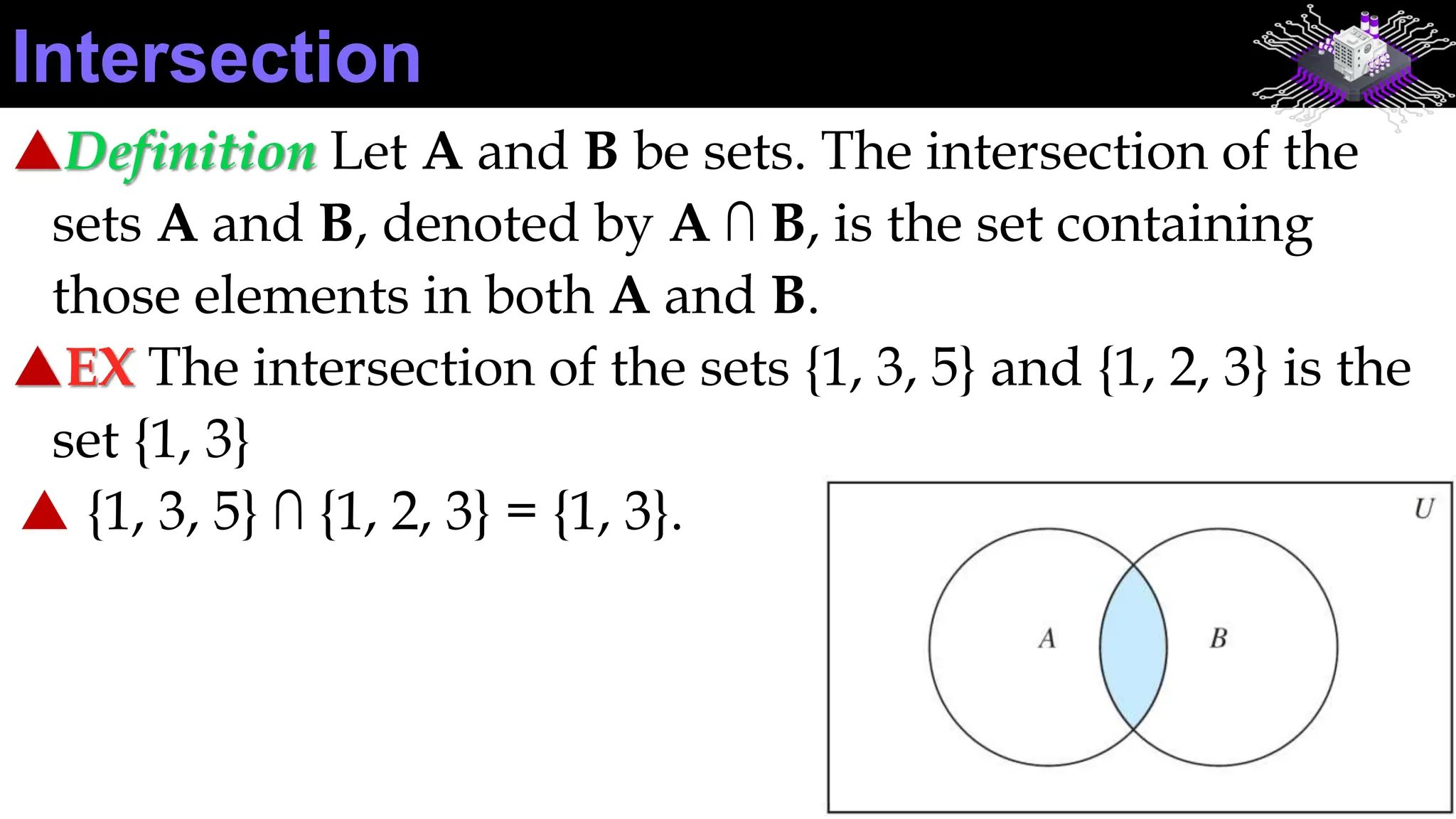
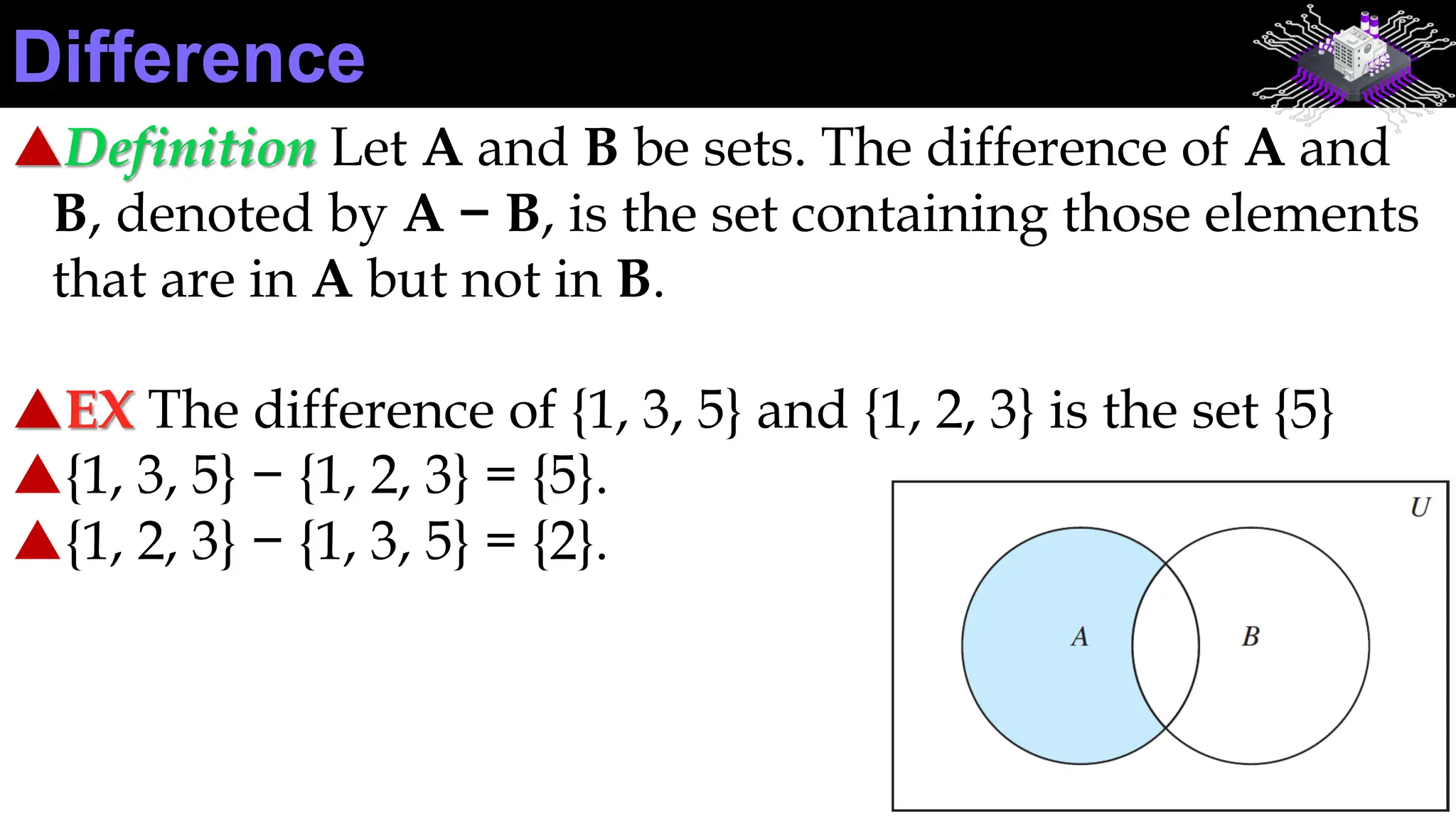
This document discusses sets and set operations. It defines what a set is and how elements of sets are denoted. It describes ways to represent sets, such as listing elements or using set-builder notation. It discusses operations on sets like union, intersection, difference, and complement. It provides examples of applying these set concepts and operations. Exercises are included for the reader to practice working with sets.
![Discrete
Mathematics
FWD 111
Lecture [05]
Sets](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dmathlec05-240401050702-e477983a/75/Discrete-mathematics-for-diploma-students-1-2048.jpg)