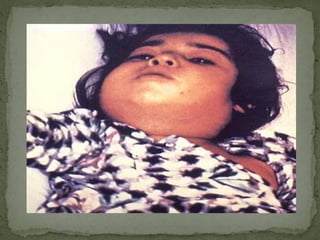
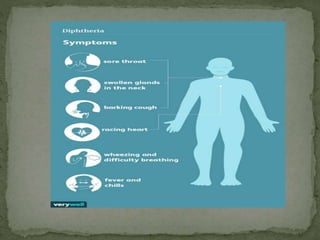
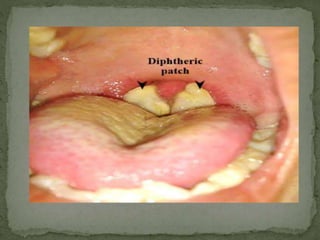
Diphtheria is a contagious and potentially deadly bacterial infection caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae, primarily affecting the throat and air passages but can also manifest on the skin. Transmission occurs through respiratory droplets, contaminated objects, or skin lesions, with symptoms including a grayish membrane in the throat, fever, fatigue, and potential airway obstruction. Prevention includes vaccination with DPT or pentavalent vaccines, and early detection through throat swabs and case isolation is crucial for controlling outbreaks.