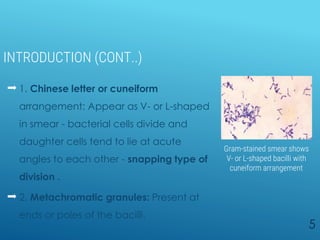
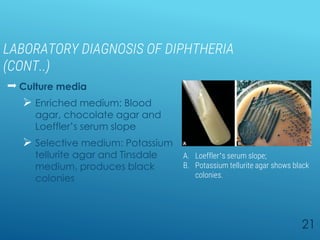
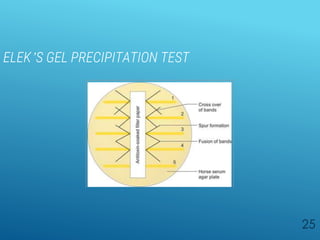
Diphtheria is a highly infectious disease caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheriae, characterized by throat infections and toxin production leading to severe complications. The bacterium exhibits unique morphological features such as club-shaped bacilli and metachromatic granules, and its diagnosis involves specific laboratory tests. Vaccination with diphtheria toxoid is crucial for prevention, and treatment includes antitoxin administration and antibiotics but must be initiated promptly upon suspicion of the disease.