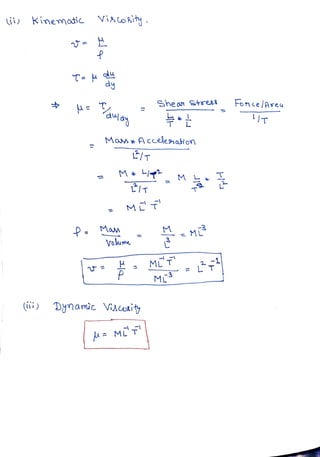
Dimensional analysis and similitude are mathematical techniques that use the study of dimensions and units to help solve engineering problems. Dimensional analysis is based on the principle of dimensional homogeneity and examines the dimensions of relevant variables affecting a phenomenon. It helps determine the systematic arrangement of variables in a physical relationship. Dimensional analysis has become important for analyzing fluid mechanics problems. It is especially useful for presenting experimental results in a concise form. Dimensional analysis ensures dimensional homogeneity. It is used to formulate equations and derive relationships between phenomena. Dimensional analysis can be used to derive equations expressed in terms of non-dimensional parameters to show the relative significance of each parameter.