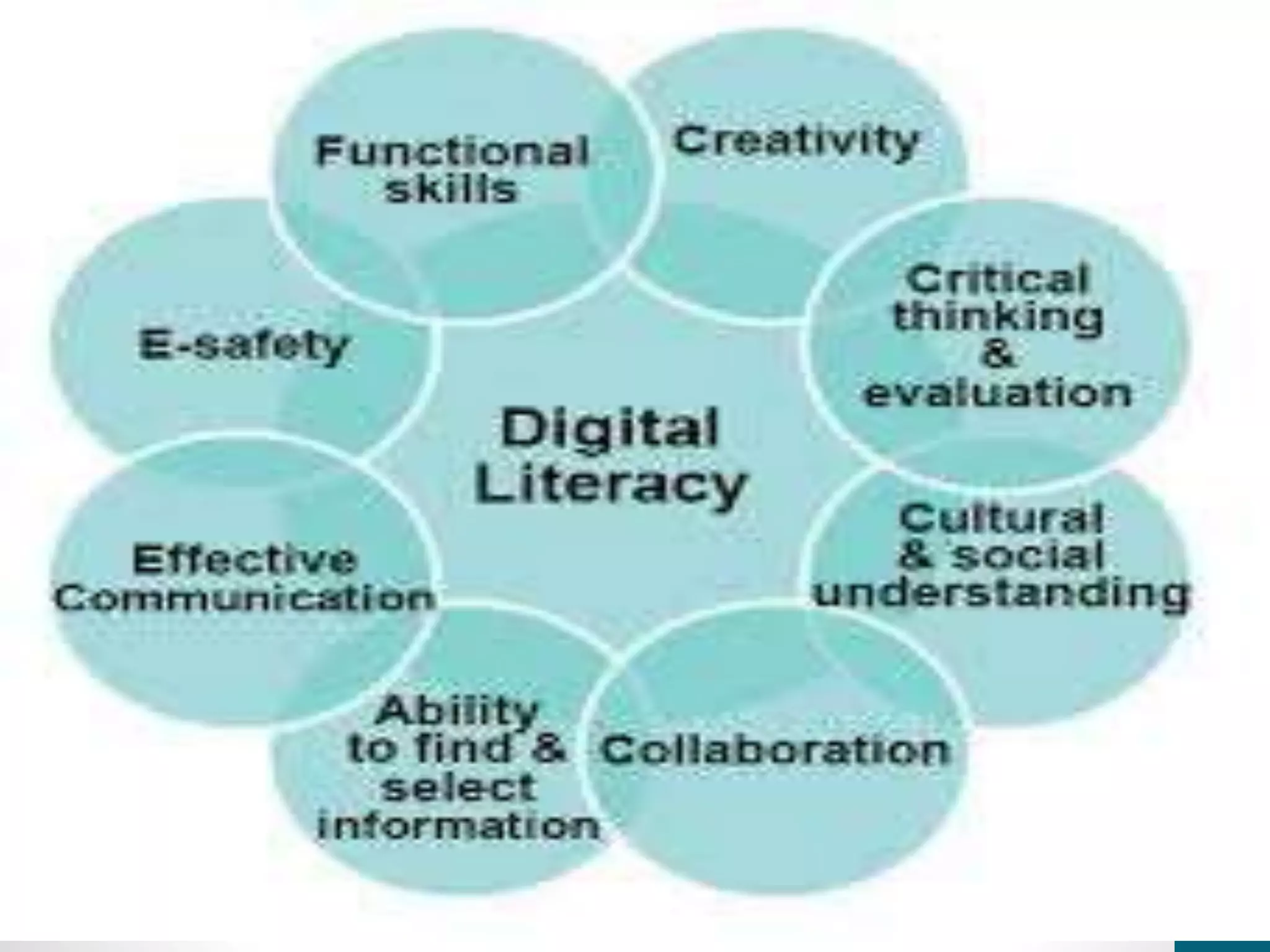
The document discusses 4 principles of digital literacy:
1) Comprehension of implicit and explicit ideas from media
2) Interdependence between different media forms
3) Social factors like how sharing content creates messages and determines success
4) Curation through storing favored content to make it accessible long-term
It also discusses components of digital literacy like ICT skills, information literacy, and technological literacy. Embedding digital literacy in all levels of education and teacher professional development is important to address in today's school systems. Digital literacy can have positive effects on basic skills, competences, and successful learning.