1) Netiquette on social media refers to the social code for using social media platforms appropriately. This includes sharing accurate information, respecting others' privacy, and avoiding hate, lies, and disrespect.
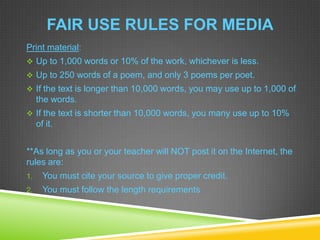
2) Copyright law gives creators exclusive rights over their work, while fair use allows limited use of copyrighted material for educational purposes if it meets certain criteria regarding length and credit.
3) Plagiarism, identity theft, cyberbullying, and viruses pose risks online that can be reduced through secure passwords, reputable antivirus software, educating children, and giving proper credit to sources.