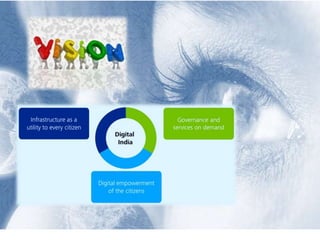
Digital India is a initiative by the Government of India to provide electronic access to government services to citizens by improving online infrastructure and internet connectivity. It was launched on July 1, 2015 with the goal of empowering citizens. Key goals include connecting 250,000 schools with broadband internet, setting up public WiFi hotspots, and training rural citizens for IT sector jobs. However, there are still challenges to overcome such as fully establishing optic fiber networks and acquiring needed skills labor.