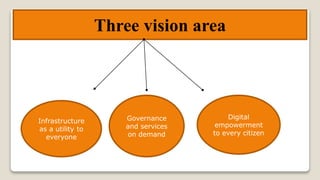
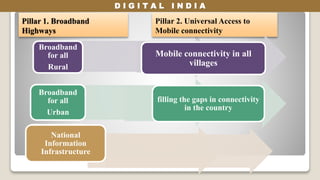
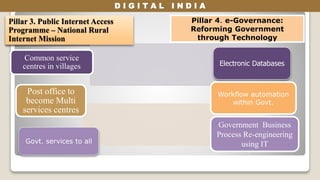
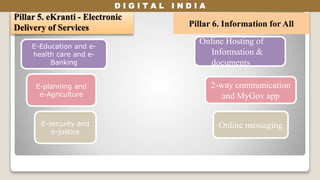
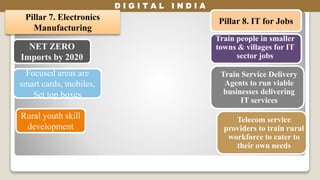
The Digital India initiative aims to empower the country through digital infrastructure, governance, and citizen engagement. It focuses on universal access to high-speed internet, digital literacy, and online services, while addressing economic, social, and environmental impacts. Challenges include project costs, infrastructure deficiencies, cyber security, and the need for skilled workforce development.