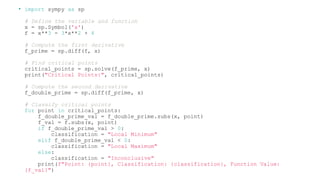
Python Methods for Numerical Differentiation
For instance, let's take the function y = f (x), y = x2. Then, let's set the function value in the form of pairs x, y with a step of 0.01 for the range of x from 0 to 4. We're going to use the scipy derivative to calculate the first derivative of the function