This document discusses different types of diodes:
- Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) emit light when current flows through them as electrons recombine with electron holes.
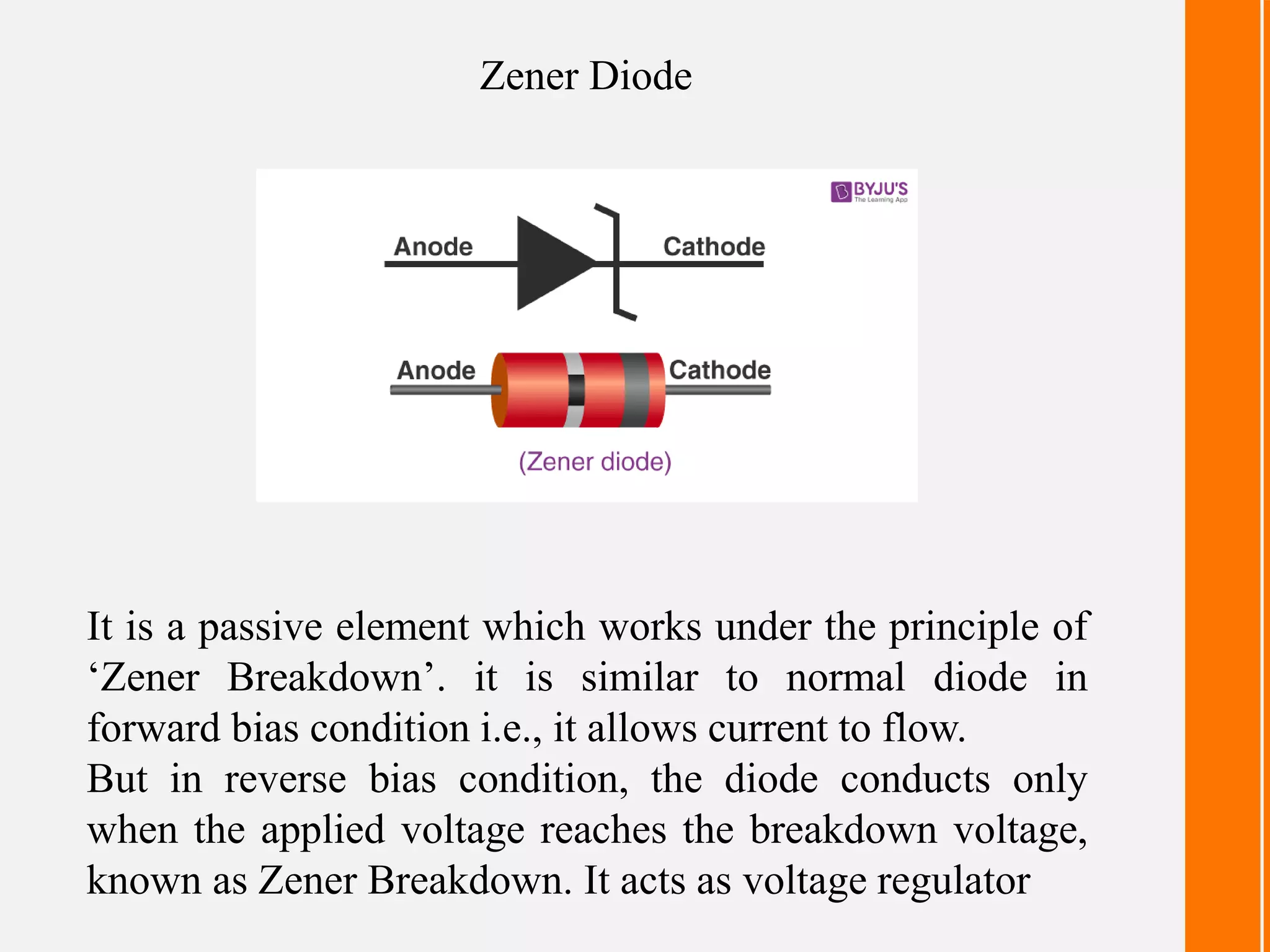
- Zener diodes allow current to flow in the forward bias direction but conduct in the reverse bias direction once the breakdown voltage is reached, acting as a voltage regulator.
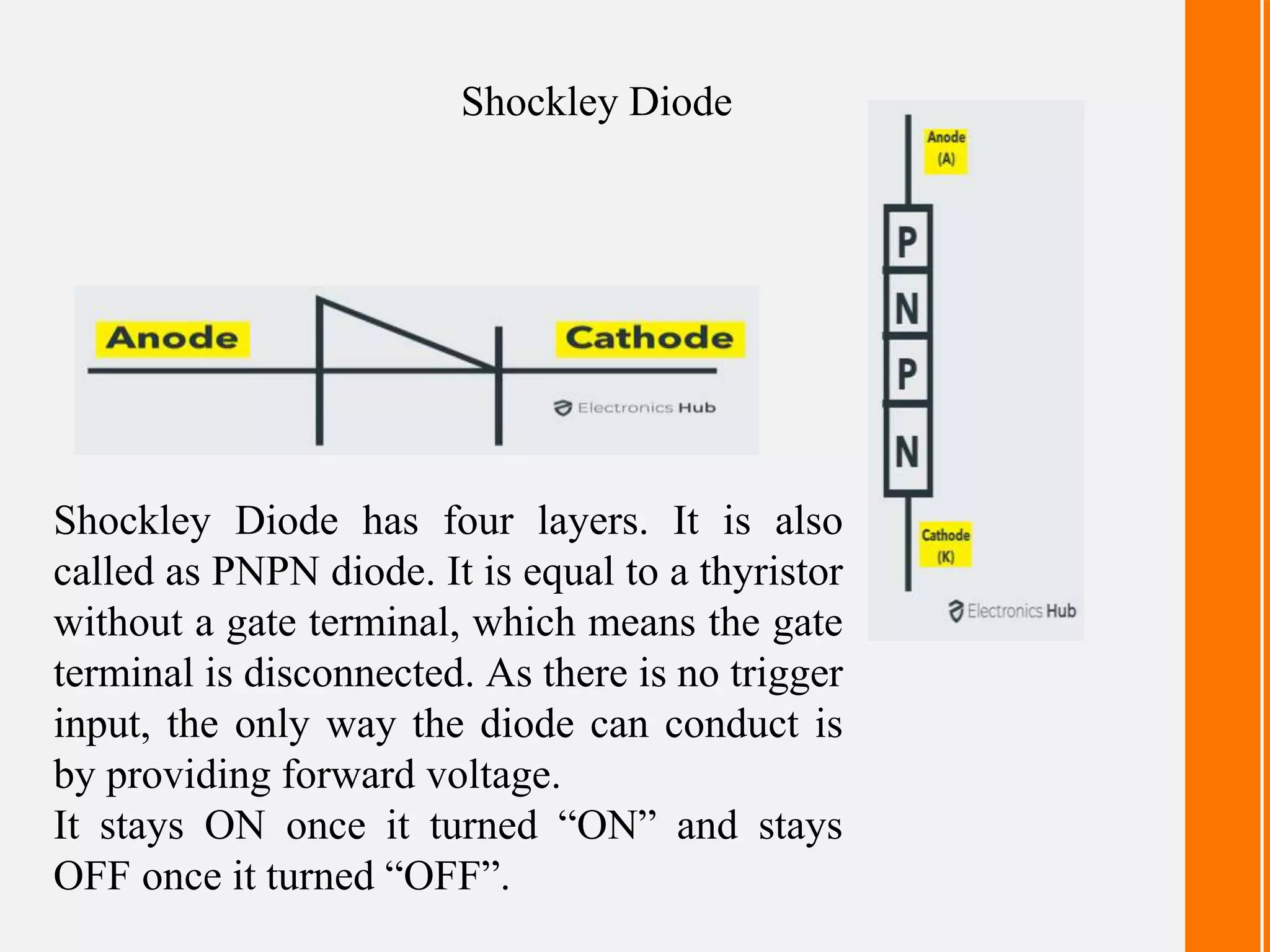
- Shockley diodes have four layers and stay on once turned on or off once turned off, like a thyristor without a gate terminal.
- Varactor diodes act like variable capacitors, changing capacitance in a circuit when a constant voltage is present.