1) Joan Sullivan, a 52-year-old woman with a family history of type 2 diabetes, was initially prescribed lifestyle counseling, diet, and exercise based on her elevated blood work. However, after one year her glycemic control and weight had worsened.
2) Metformin monotherapy is often effective initially but beta cell function continues to decline over time, resulting in worsening glycemic control within a few years for most patients.
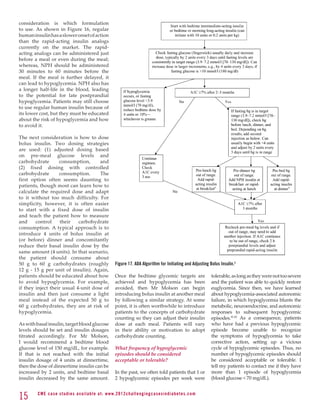
3) To both improve glycemic control now and preserve beta cell function long-term, the author recommends starting patients on metformin and adding a second agent with a different mechanism of action as soon as the maximum metformin dose is reached, regardless of current A
![especially if they are already taking an
extended-release formulation, I might No Single Class of Oral Antihyperglycemic
consider a metformin formulation Monotherapy Targets All Key Pathophysiologies
that is released more slowly in the
intestines, such as Glumetza. Incretin
Alpha- Meglitinides3 SUs4,5 Mimetics/
How would you discuss the treatment Glucosidase TZDs 6,7
Metformin 8
DPP-4
Inhibitors1,2 Inhibitors
plan with Mrs Sullivan?
Major Pathophysiologies
It is important to combine active
Insulin
deficiency
pharmacologic treatment with patient
education and counseling about the
goals of therapies, the therapeutic
Insulin
resistance *
strategy, and future treatment plans,
such as the plan to introduce a second Excess hepatic
agent after metformin therapy is glucose output
established. The goals of education
Intestinal
and counseling are to increase Mrs
Sullivan’s understanding of the disease
glucose
absorption
process and the potential of her diabetes 1. Glyset [package insert]. New York, NY: Pfizer Inc; 2004. 2. Precose [package insert]. West Haven, Conn: Bayer; 2004.
to worsen, and enhance her confidence 3. Prandin [package insert]. Princeton, NJ: Novo Nordisk; 2006. 4. Diabeta [package insert]. Bridgewater, NJ: Sanofi-Aventis; 2007.
5. Glucotrol [package insert]. New York, NY: Pfizer Inc; 2006. 6. Actos [package insert]. Lincolnshire, Ill: Takeda Pharmaceuticals; 2004.
in her ability to follow an effective 7. Avandia [package insert]. Research Triangle Park, NC: GlaxoSmithKline; 2005.
8. Glucophage [package insert]. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb; 2004.
treatment plan. * Applies only to GLP1 agonists
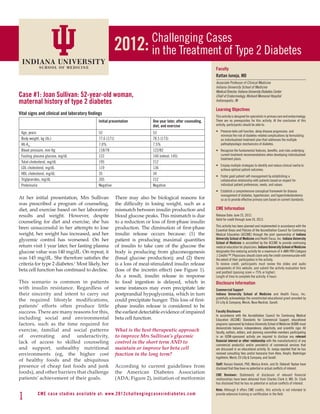
My discussion with Mrs Sullivan Figure 7. Pathophysiologic Processes Targeted by Different Antihyperglycemic Agents.
will include several important topics, Although metformin improves insulin resistance, its main effect is to reduce hepatic glucose output.
including:
• Why treatment is necessary and amount of glucose that enters your body, Because metformin can cause diarrhea, I’m
important and (2) improve the way your body uses the going to start you at a low dosage and then
• Goals of treatment glucose to produce the energy you need to gradually increase it, because the diarrhea
• Rationale for the treatment plan carry out your daily activities. goes away in most people once their body
• How to manage side effects gets used to the medication. I want you to
• Plans for monitoring What is the rationale for the treatment start taking 500 mg metformin as a single
• Managing any barriers or challenges plan? pill with every evening meal. Taking it
she anticipates To achieve these goals, we need to use 2 with the evening meal does 2 things: (1) it
different drugs that work together. The makes the diarrhea less bothersome, and (2)
More specifically, here is an example of safest drug – the one that has been around your liver tends to make the most glucose
how I would cover these issues with Mrs for the longest time – is metformin. Its main at nighttime, so taking metformin in the
Sullivan: effect is to reduce the amount of glucose evening will have the greatest effect.
that your liver produces. Our first step is
Why is treatment necessary and to get you started on metformin during Metformin will lower your blood sugar
important? this first month. After 2 to 3 months, without making it go below normal limits
Your blood sugar level (known as Hb A1c) your Hb A1c level may drop below 7.0% or because it only reduces the glucose your
is 7.5%, indicating that your blood sugar even 6.5%. But from the results of many liver is making, and, therefore, doesn’t
level is above the level known to increase studies, I know that it is likely that your carry the risk of making your blood sugar
your risk for damage to your eyes, nerves, blood sugar level may not stay low for very bottom out. The goal is to eventually get
and kidneys. So, we need to bring this long; therefore, we also need to use a drug you on the maximum dosage because it
blood sugar level down. that improves how your body uses glucose. is most effective that way. So, I will ask
you to gradually increase the amount you
What are our goals of treatment? So, I plan to introduce a second drug at your take in weekly increments. You start now
There are 2 main goals in bringing this blood next visit. This drug targets a different part by taking 500 mg for the first week with
sugar down. One goal is to reduce the chances of the disease process in a different way than your evening meal. Next week, you’ll take
that you’ll have complications related to high metformin. We will, however, need to make 500 mg in the morning with breakfast
glucose values. Keeping your Hb A1c values sure that the 2 drugs together do not cause and 500 mg in the evening with dinner.
below 7.0% will do that. your blood sugar to go too low. During the third week, you’ll take 500 mg
in the morning and 1000 mg (2 pills) in
The second goal is to help your body use What are the possible side effects of the the evening. And by the fourth week, you’ll
glucose efficiently for energy. To do this, medicine and how can they be avoided take 1000 mg (2 pills) in the morning and
we need to do 2 things: (1) decrease the or managed? 1000 mg (2 pills) in the evening.
5 C M E c a se st u di es av ai l abl e at: w w w. 2012chall e n g i n g c a s e s i n d i a b e te s . c o m](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diabeteschallengingcases-120929001306-phpapp01/85/Diabetes-challenging-cases-5-320.jpg)





![Just as important is that patients and many types of insulin now available REFERENCES
those around them know how to allow patients to mimic physiologic 1. American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2010;33 (suppl 1):
respond to a hypoglycemic episode. insulin secretion to a reasonable degree, S62-S699.
A simple rule of thumb is known as but this goal requires the eventual use 2. American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2012;35 (suppl
1):S11-S63.
the “rule of 15.”43 For a hypoglycemic of both basal and bolus insulin in most 3. Nathan DM, et al. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(1):193-203. Epub 2008
episode, take 15 g simple carbohydrates patients. As with all stages of diabetes Oct 22.
(eg, fruit juice, hard candy, pretzels, or therapy, thorough patient education is 4. Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Diabetes. 1995;44(11):1249-1258.
5. Kahn SE, et al. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(23):2427-2443.
crackers) and wait 15 minutes, during crucial for patients initiating insulin
6. Rodbard HW, et al. Endocr Pract. 2009;15(6):540-559.
which other essential functions (eg, therapy. 7. Festa A, et al. Diabetes. 2006;55(4):1114-1120.
airway, breathing, circulation, and so 8. Gale EA. Diabet Med. 2008;25(suppl 2):9-12
forth) should be monitored. Check the Finally, this case illustrates the importance 9. Inzucchi SE, et al. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(6):1364-1379. Epub
2012 Apr 19.
blood glucose level again after those 15 of establishing and maintaining trusting 10. smail-Beigi F, et al. Ann Intern Med. 2011;154(8):554-559.
I
minutes, and if still hypoglycemic, take relationships so your patients know that 11. Deacon CF, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14(8):762-7.
another 15 g carbohydrates. Repeat this you are aware of their concerns regarding 12. aedler K, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90(1):501-506.
M
Epub 2004 Oct 13.
process until hypoglycemia resolves. A treatment costs, whether a particular
13. apanas N, et al. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011;12(10):1457-1461.
P
very useful source of information about therapy fits with their lifestyle, and any 14. DeFronzo RA, et al. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(12):1104-1115.
foods containing 15 g carbohydrates potential side effects. This awareness 15. .K. Prospective Diabetes Study Group, et al. Diabetes.
U
can be found at http://iuhealth.org/ should translate into a willingness to 1995;44(11):1249-1258.
16. Meier C, et al. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168(8):820-825.
images/ril-doc-upl/Carbohydrate%20 work collaboratively with patients 17. iccinni C, et al. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(6):1369-1371. Epub
P
Counting%20Food%20List.pdf. Another to develop a strategy that the patient 2011 Apr 22.
list available on the same website embraces. 18. Bunck MC, et al. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(9):2041-2047.
provides the carbohydrate content of 19. unck MC, et al. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(5):762-768. Epub 2009
B
Feb 5.
popular candies: http://iuhealth.org/ CLINICAL RECOMMENDATIONS 20. Derosa G, et al. Diabet Med. April 30, 2012. [Epub ahead of print]
images/ril-doc-upl/Halloween%20 21. Amori RE, et al. JAMA. 2007;298(2):194-206.
Candy%20List.pdf. • For patients with a limited budget, 22. Pratley RE, et al. Lancet. 2010;375(9724):1447-1456.
23. Aschner P, et al. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(12):2632-2637.
find an affordable medication that
24. Charbonnel B, et al. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(12):2638-2643.
CASE SUMMARY will increase compliance with the 25. auck M, et al. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(1):84-90. Epub 2008 Oct 17.
N
chosen regimen. 26. Davidson JA. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010;85(12 suppl):S27-S37. Epub
Mr Molson’s case illustrates a practical • Unless medically necessary to 2010 Nov 26.
27. Drucker DJ, et al. Lancet. 2008;372(9645):1240-1250.
approach for addressing the medical make changes quickly, make 28. inelli NR, et al. J Clin Pharmacol. 2011;51(2):165-172. Epub
P
needs of someone who has multiple changes to complex medication 2010 May 19.
problems related to the metabolic regimens gradually, allowing 29. Klein S, et al. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(8):2067-2073.
syndrome. It also demonstrates the patients to adjust and detect and 30. arbo A, et al. Ann Neurol. 2011;69(4):628-634. Epub 2011 Feb 18.
V
31 K Prospective Diabetes Study 7. Metabolism. 1990;39(9):905-912..
U
importance of adapting therapeutic resolve any side effects that may 32. Bantle JP, et al. Diabetes Care. 2008;31 (suppl 1):S61-S78.
strategies to accommodate a patient’s hinder compliance. 33. Knowler WC, et al. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(6):393-403.
financial situation and other lifestyle • Work collaboratively with each 34. Penn L, et al. BMC Public Health. 2009;9:342.
35. Tuomilehto J, et al. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(18):1343-1350.
factors that can affect his or her ability patient to develop goals and 36 Williams KV, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2000;2(3):121-129.
to comply with treatment. It is usually strategies for weight loss that 37 iebenhofer A, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (Online).
S
impractical to solve all of a patient’s are achievable and sensitive to 2011(9):CD008274.
metabolic problems in a single clinic the patient’s needs, desires, and 38. he Practical Guide: Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment
T
of Overweight and Obesity in Adults. Rockville, MD: 2000. NIH
visit. Furthermore, determining the tolerances. Publication Number 00-4084. Available at: www.nhlbi.nih.gov/
diabetes therapy with which each patient • If not using a weight-based guidelines/obesity/prctgd_c.pdf. Accessed June 30, 2012.
can most easily comply may reduce the regimen for basal insulin, a 39. Hollis JF, et al. Am J Prev Med.. 2008;35(2):118-126.
40. Yki-Järvinen H, et al. Ann Intern Med. 1999;130(5):389-396.
severity of related metabolic complaints, simple approach is to initiate
41. Cryer PE. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2001;281(6):E1115-
such as dyslipidemia, making those treatment using 10 units per E1121.
problems easier to address in subsequent day at bedtime and to titrate the 42. Diedrich L, et al.Clin Auton Res. 2002;12(5):358-365.
visits. dose up in weekly increments 43. merican Diabetes Association website. Living with Diabetes:
A
Hypoglycemia. Available at: http://www.diabetes.org/living-with-
(2-4 units per week) until target diabetes/treatment-and-care/blood-glucose-control/hypoglyce-
Mr Molson is typical in that, like fasting blood glucose levels are mia-low-blood.html. Accessed June 30, 2012.
most patients, he continues to exhibit achieved (or a maximum dosage
declines in glycemic control and beta of 30-40 units is reached).
Read this newsletter and receive 4.0 hours of CME credit.
cell function even while receiving oral • In most cases, continue metformin
therapy. Physicians should closely therapy when patients begin both To get your CME credit immediately, simply log onto:
monitor patients for poor glycemic basal insulin and basal plus bolus www.2012challengingcasesindiabetes.com
to take the posttest and download your certificate.
control and be prepared to initiate insulin therapy.
insulin therapy when target Hb A1c • All patients using insulin should To access the complete case study tutorial, go to:
levels are no longer achieved using oral be educated about avoiding www.2012challengingcasesindiabetes.com
therapy alone. Although insulin therapy hypoglycemia and about how to
© 2012. Indiana University and Health Focus, Inc.
is complex, most patients can adapt if manage a hypoglycemic episode. All rights reserved.
the insulin is introduced gradually. The
16 To e a r n C M E c redi t, compl ete the pos ttes t and e v a l u a ti o n a t www. 2 0 1 2 c h a l l e n g i n g c a s e s i n d i a b e te s . c o m](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diabeteschallengingcases-120929001306-phpapp01/85/Diabetes-challenging-cases-16-320.jpg)