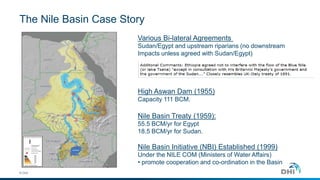
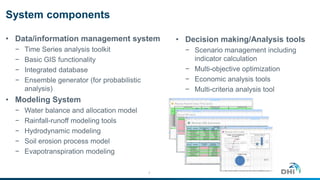
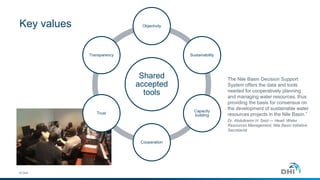
The document discusses innovative water resource management solutions developed by DHI, focusing on the Nile Basin's collaborative water management framework. It describes the Nile Basin Decision Support System, which integrates crucial climatological and hydrological data to aid in sustainable development and cooperation among upstream and downstream countries. The initiative seeks to address challenges in water allocation, environmental sustainability, and infrastructure development through shared tools and decision-making processes.