This document provides an overview of DevOps, including definitions, principles, challenges, and how DevOps addresses issues with traditional development approaches. Some key points:
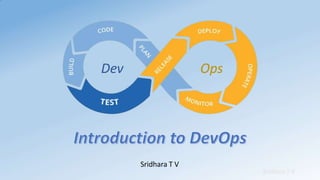
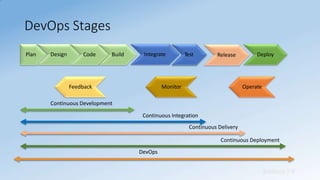
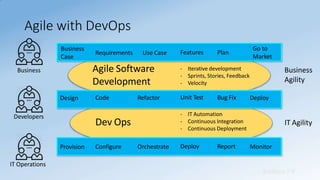
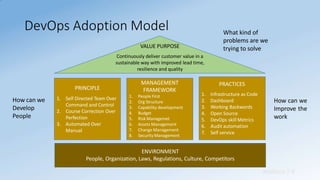
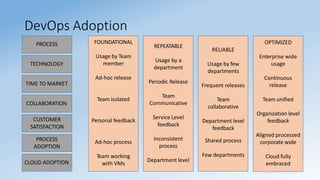
- DevOps aims to unify development and operations through shared culture, practices, and tools to accelerate software delivery while improving reliability.
- It promotes collaboration between development and IT operations teams to quickly release planned work while ensuring production stability.
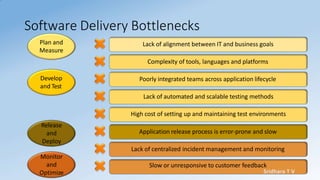
- DevOps focuses on culture, automation, measurement, and sharing to break down silos between teams and achieve business goals.