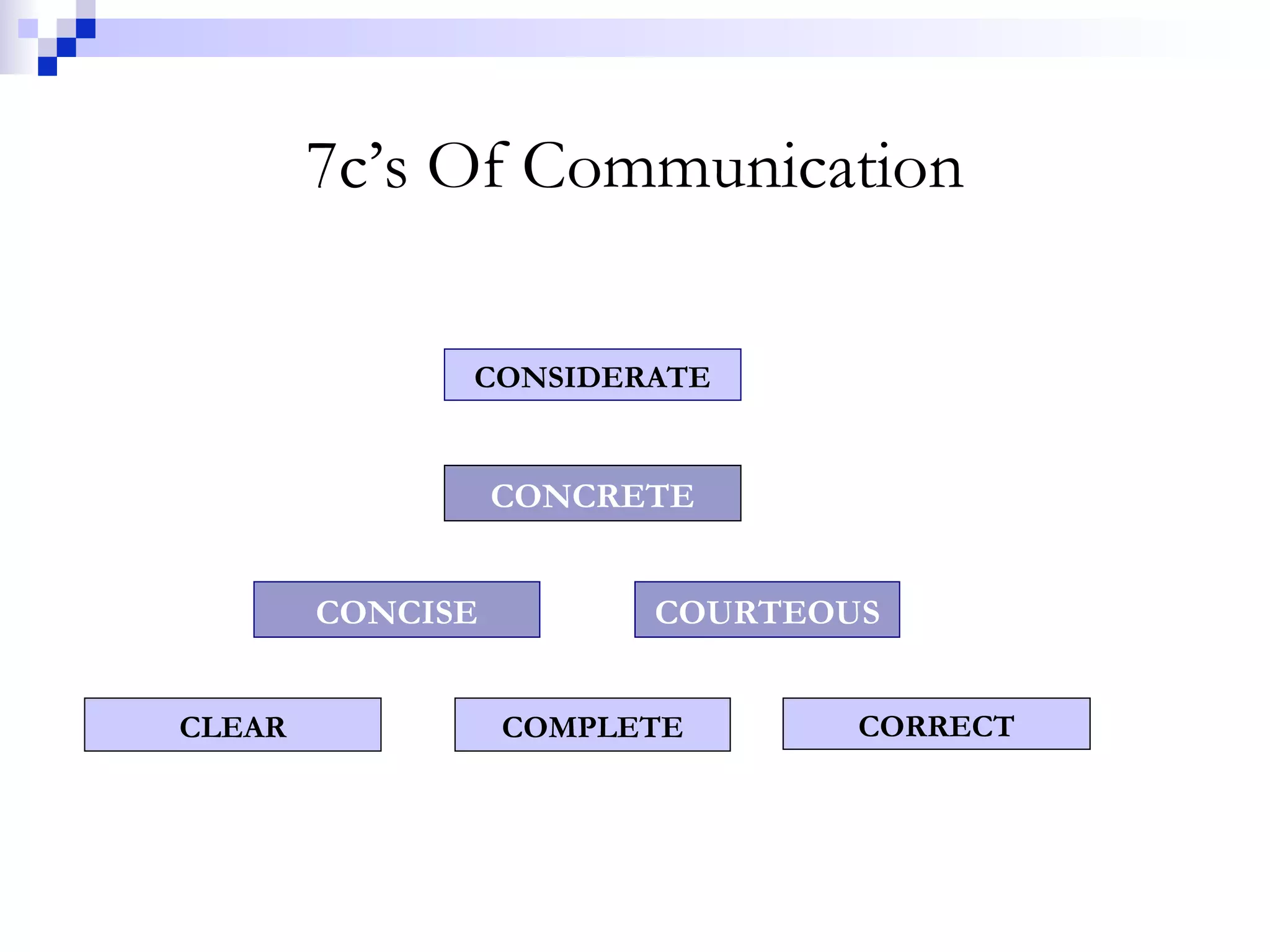
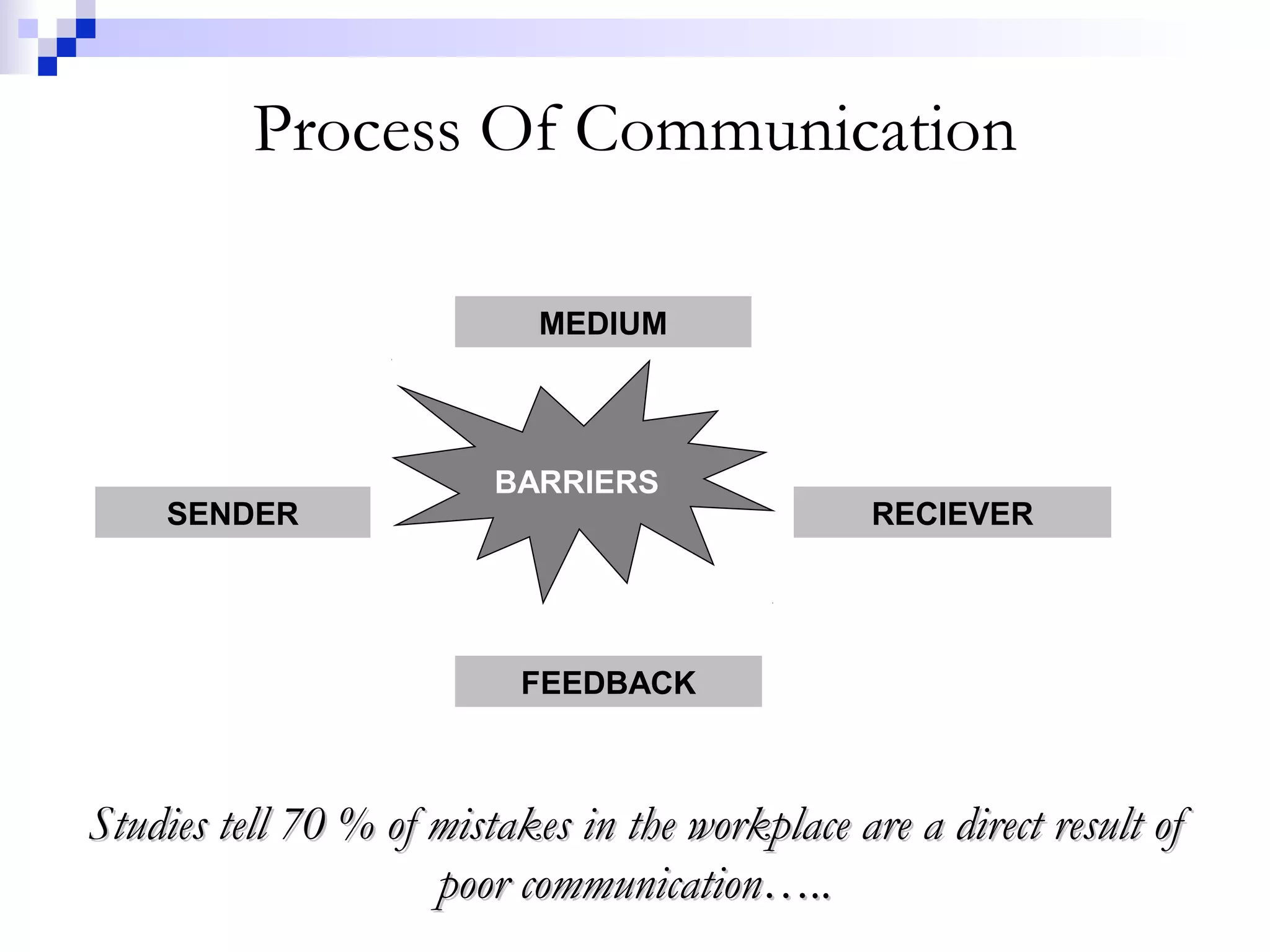
This document provides information on developing effective communication skills. It discusses basics of communication, telephone etiquettes, listening skills, and questioning. Some key points covered include the importance of clear communication, barriers to effective communication like assumptions and poor listening, communication process, and dos and don'ts of phone etiquette. The document aims to improve readers' communication abilities through understanding communication principles and practicing good listening and questioning techniques.