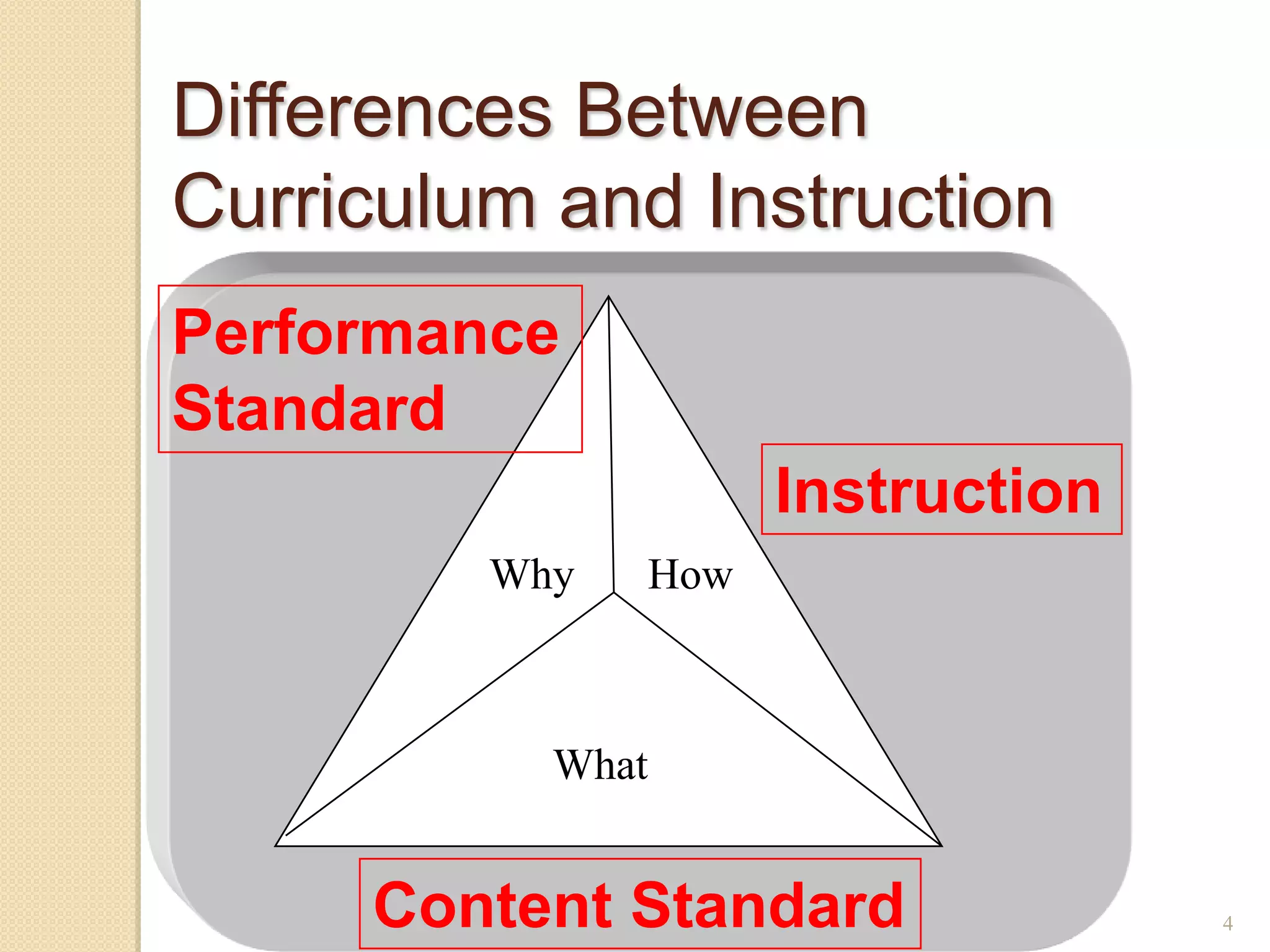
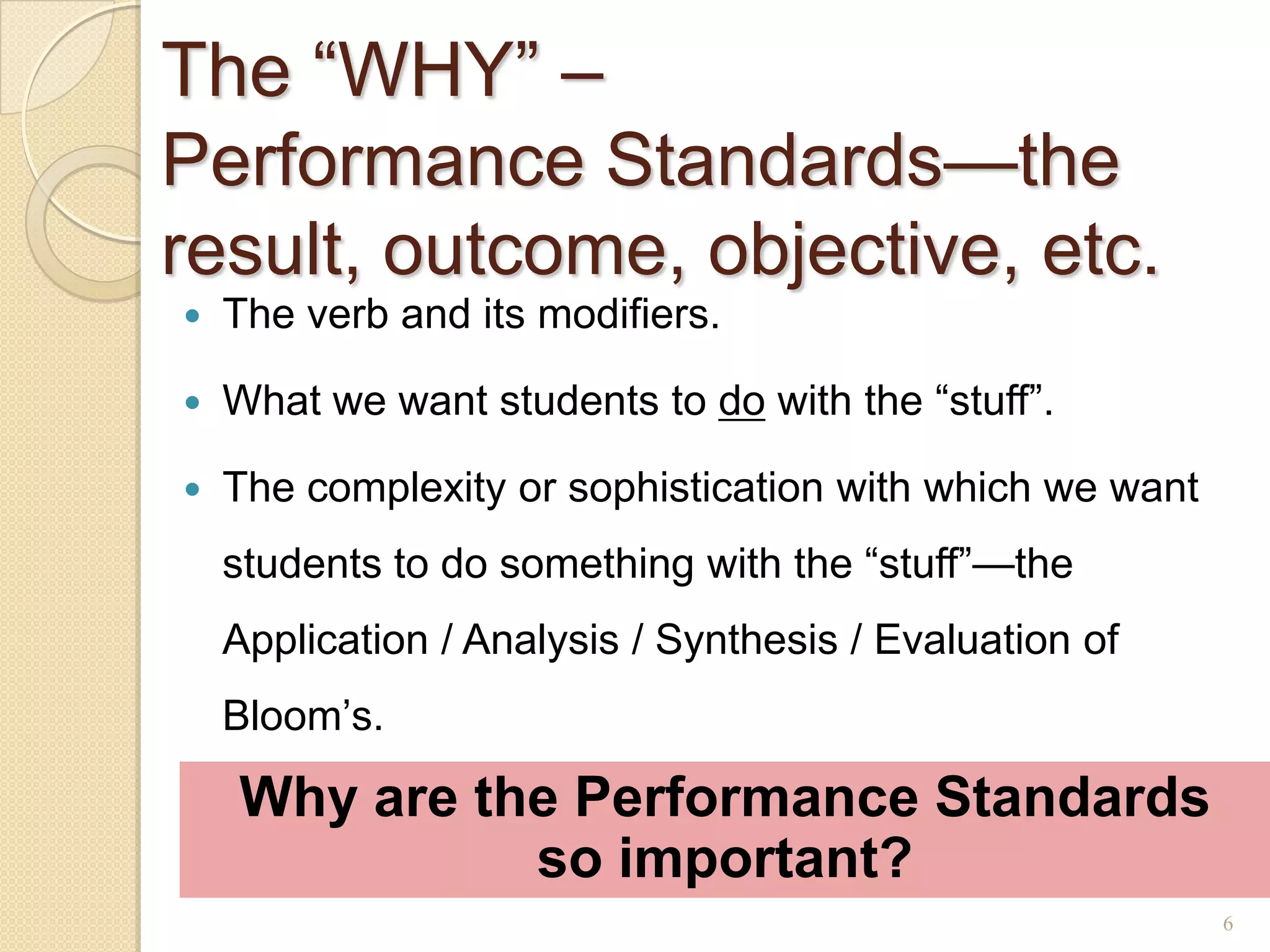
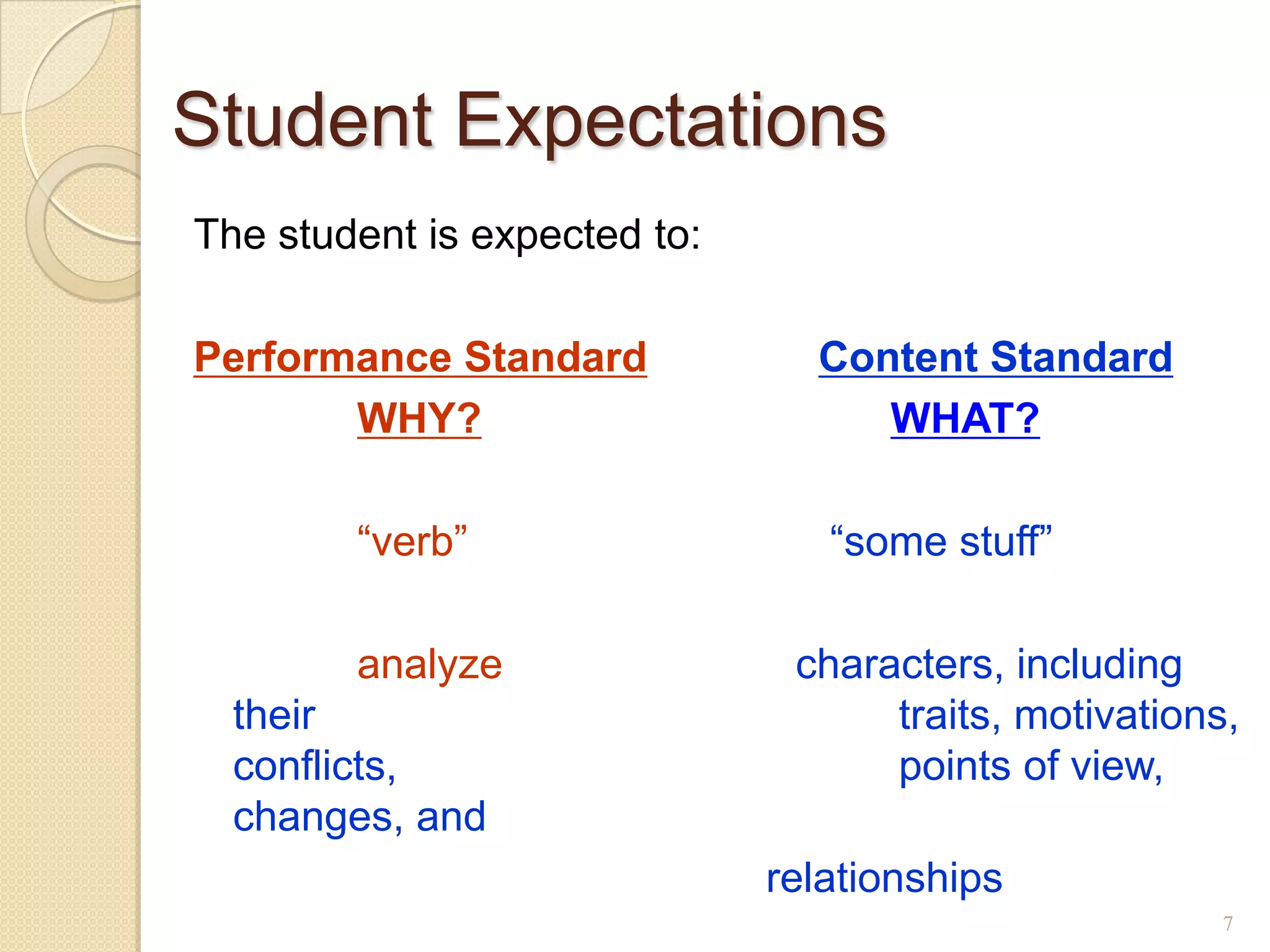
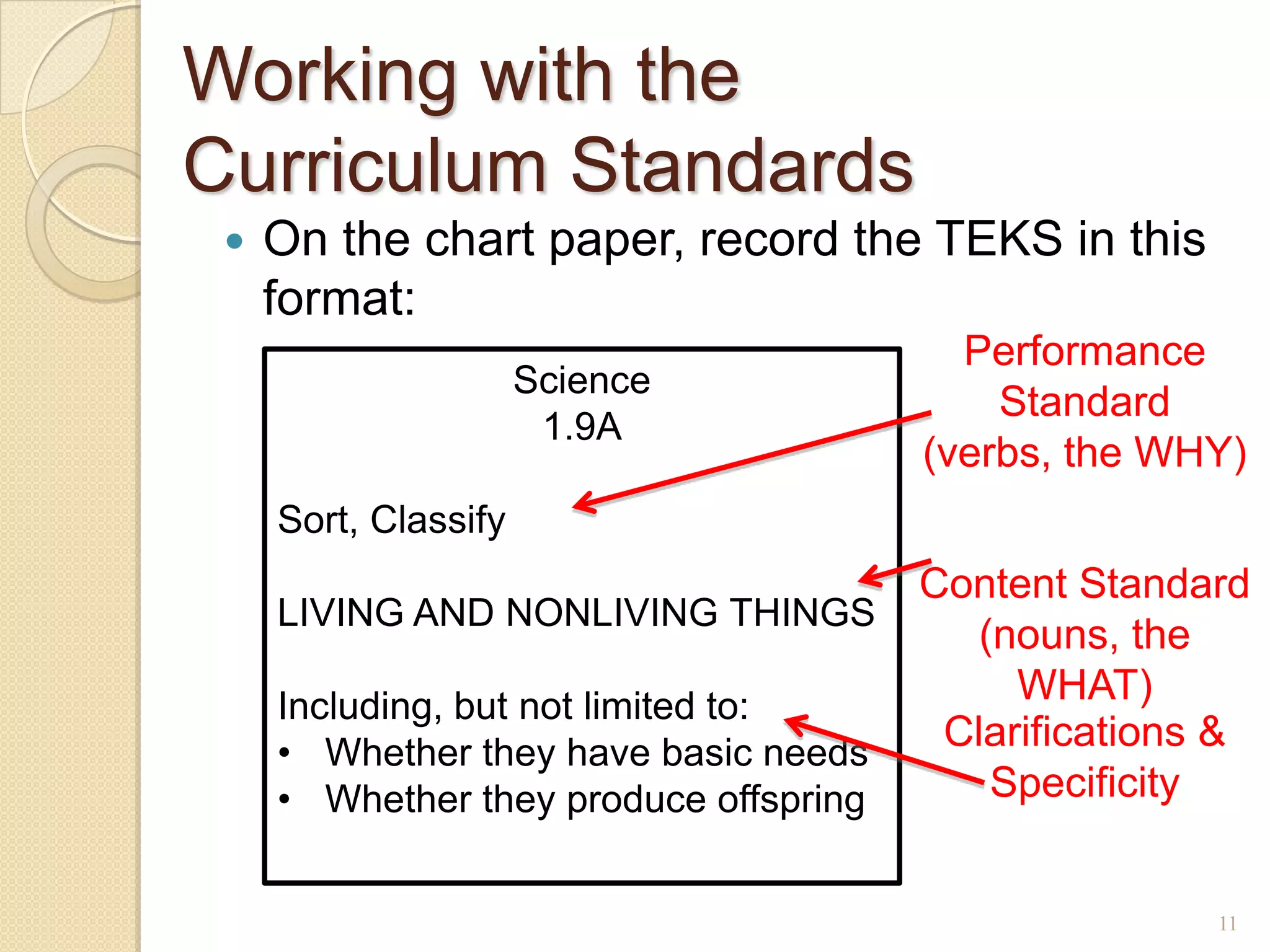
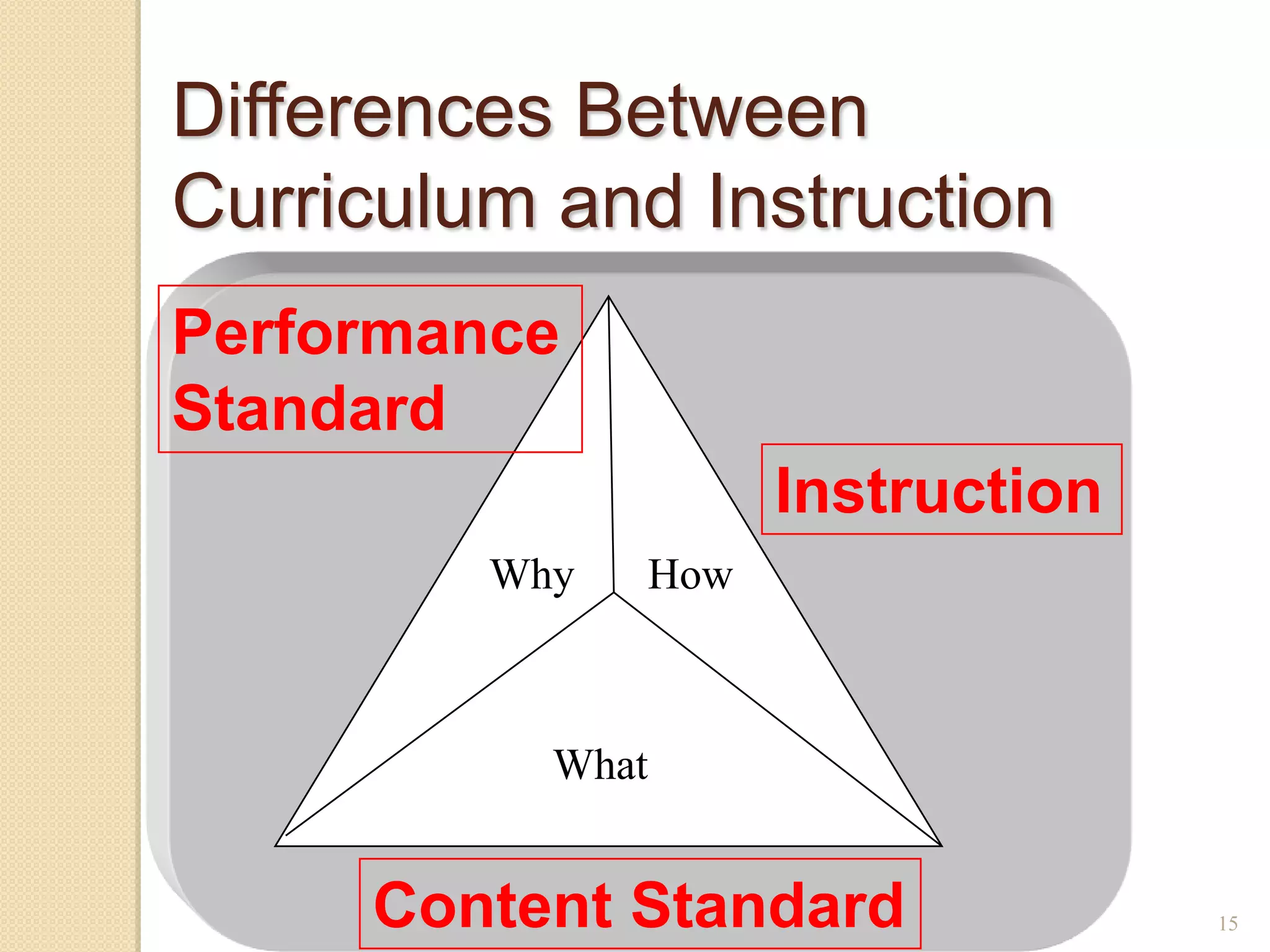
The document discusses developing a common language around curriculum. It defines key terms like curriculum, content standards, and performance standards. Curriculum refers to the what (content standards) and why (performance standards). It also distinguishes curriculum from instruction, which is the how. The document provides examples of standards and discusses making TEKS more specific and vertically aligned. It suggests using curriculum to guide instructional activities and materials. Overall, the document aims to establish a shared understanding of curriculum fundamentals.