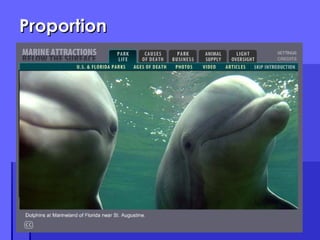
The document provides a comprehensive guide on effective web design principles, emphasizing the adaptation of aesthetic design for online usability. Key principles include relevance, proportion, consistency, contrast, and the strategic use of white space, all aimed at enhancing user experience and navigation. It also discusses the importance of SEO practices like optimizing page titles and keywords for better search engine visibility.
![Basic Web design Preliminary information you should know about online presentation and usability Laura Ruel Associate Professor, UNC-Chapel Hill [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designusabilitybasics-110110160120-phpapp02/75/Design-Usability-Basics-1-2048.jpg)