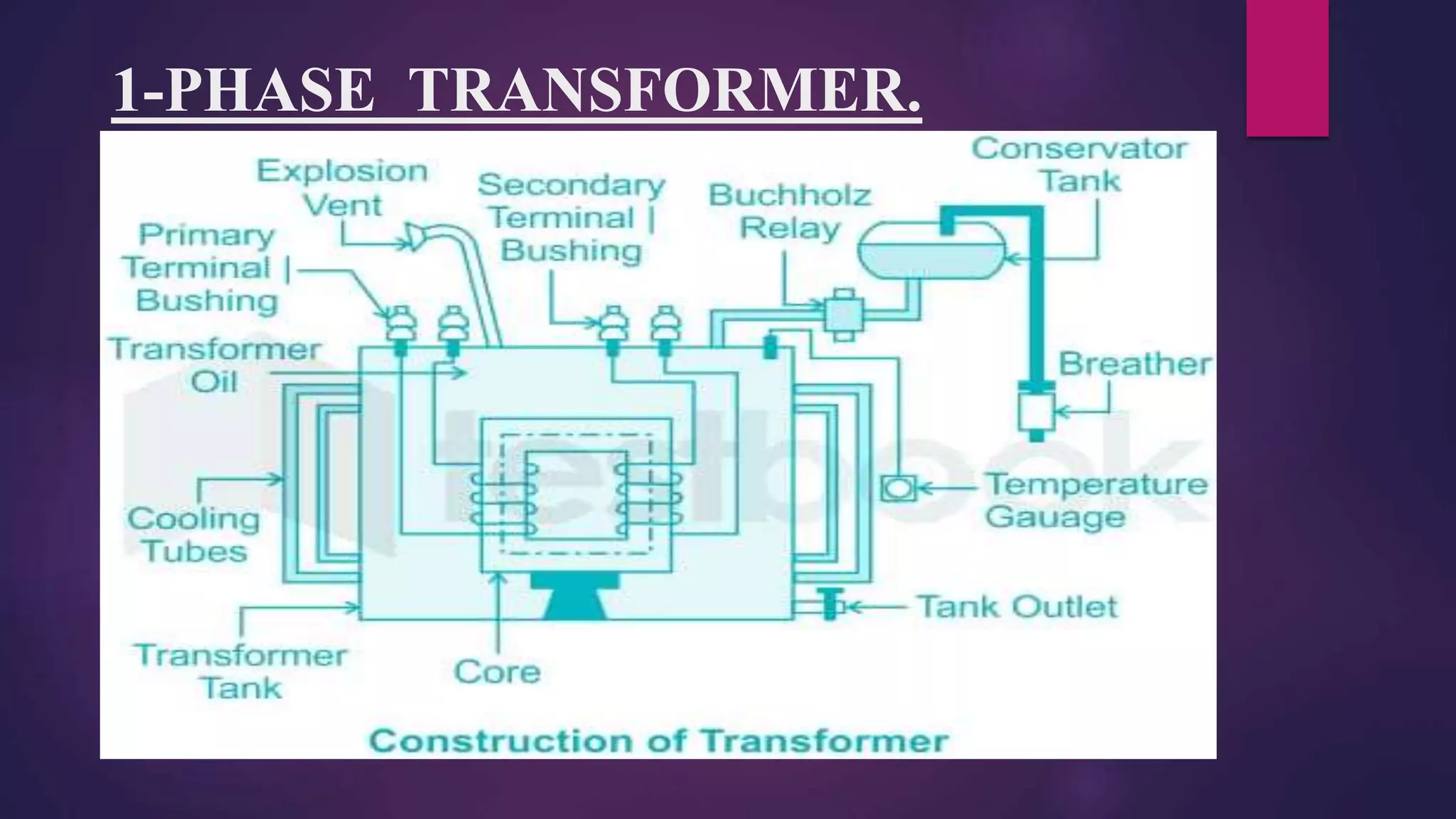
This document summarizes the key components and design of a single-phase transformer. It discusses that a transformer is a static device that transfers power between two circuits using electromagnetic induction. The two main parts are the transformer core and windings. The core is made of silicon steel laminations to reduce eddy current losses. Cold rolling the silicon steel orients the grains, which reduces the magnetic reluctance and improves efficiency by providing a lower reluctance path for magnetic flux.