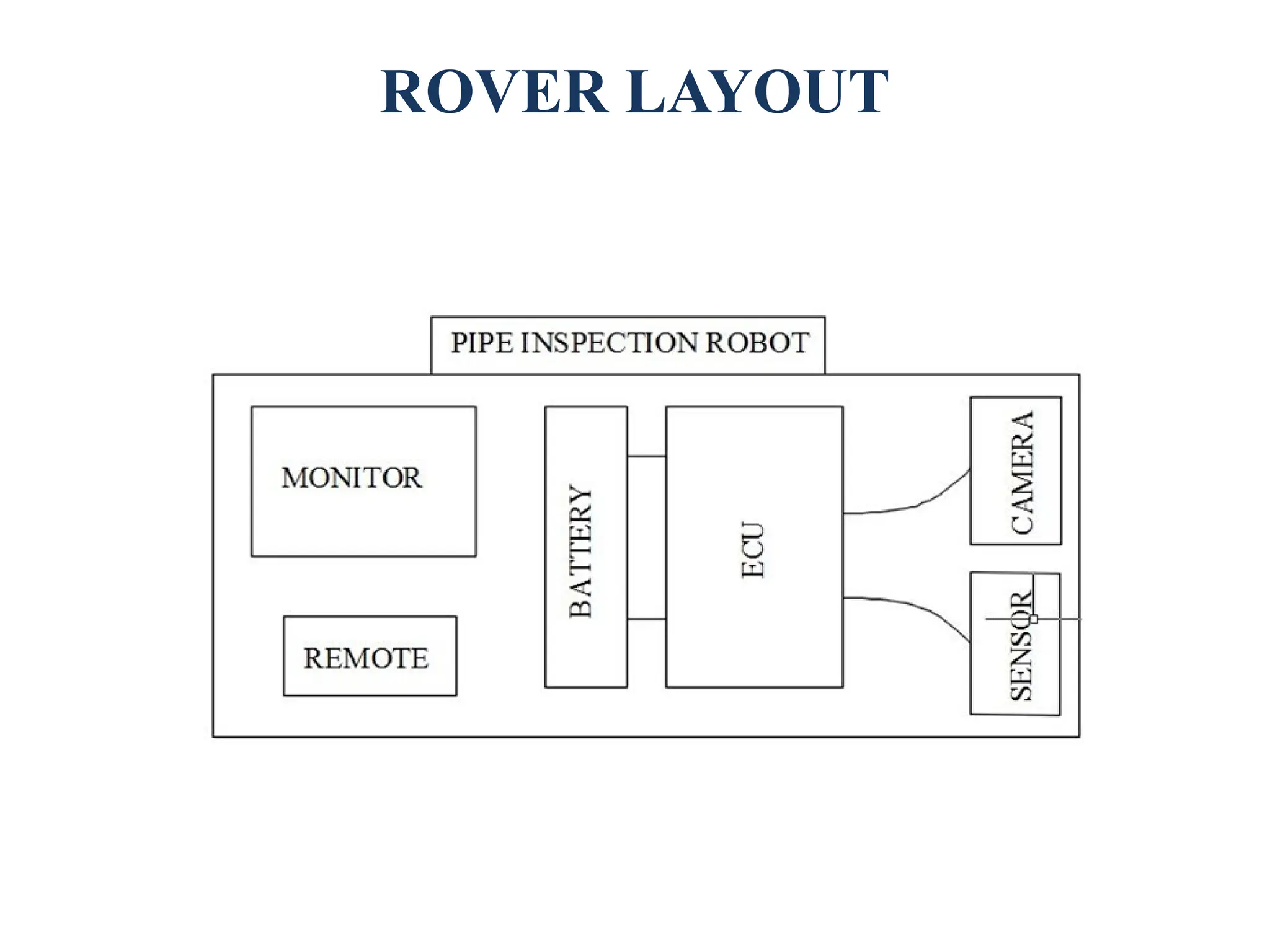
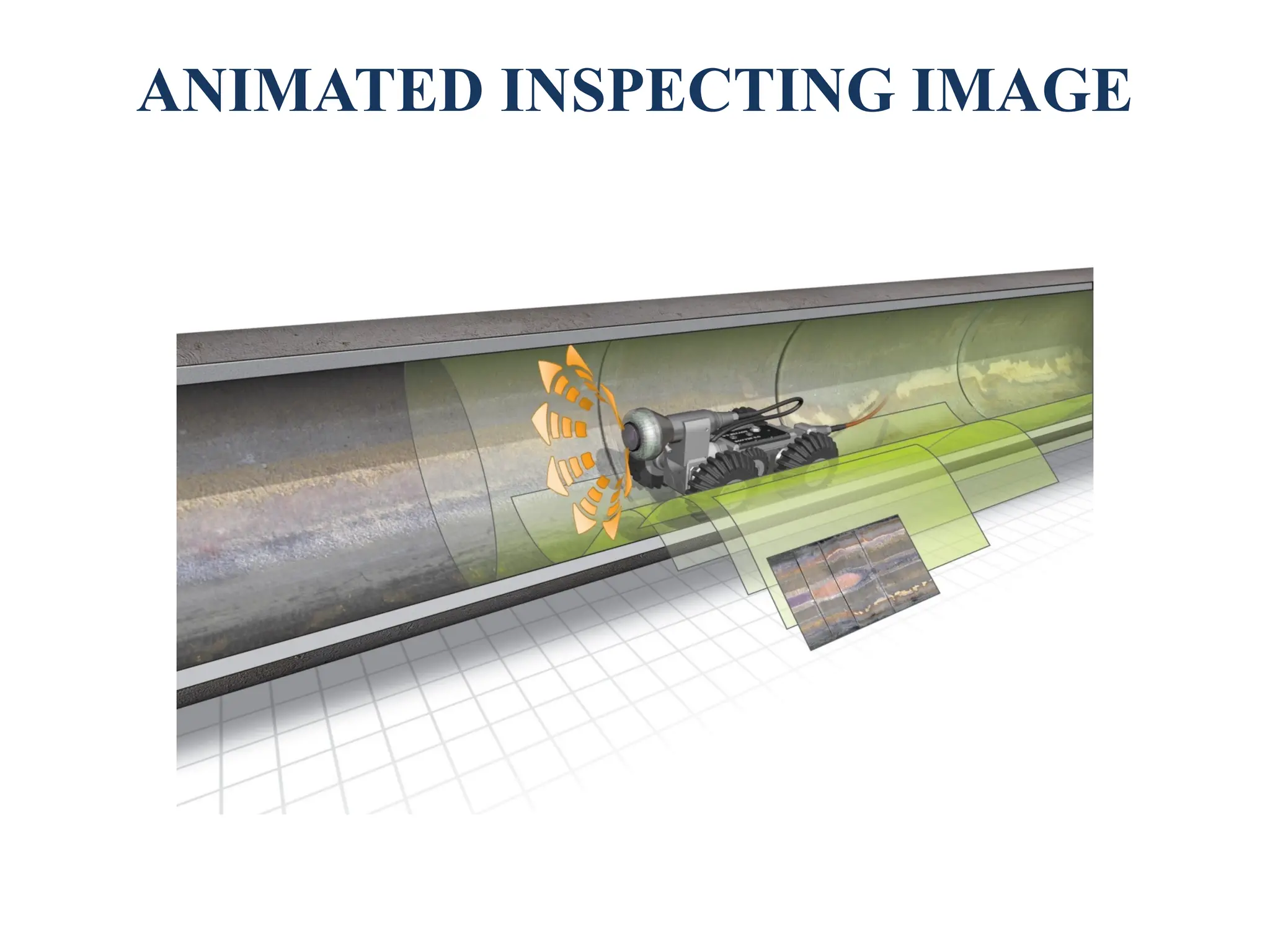
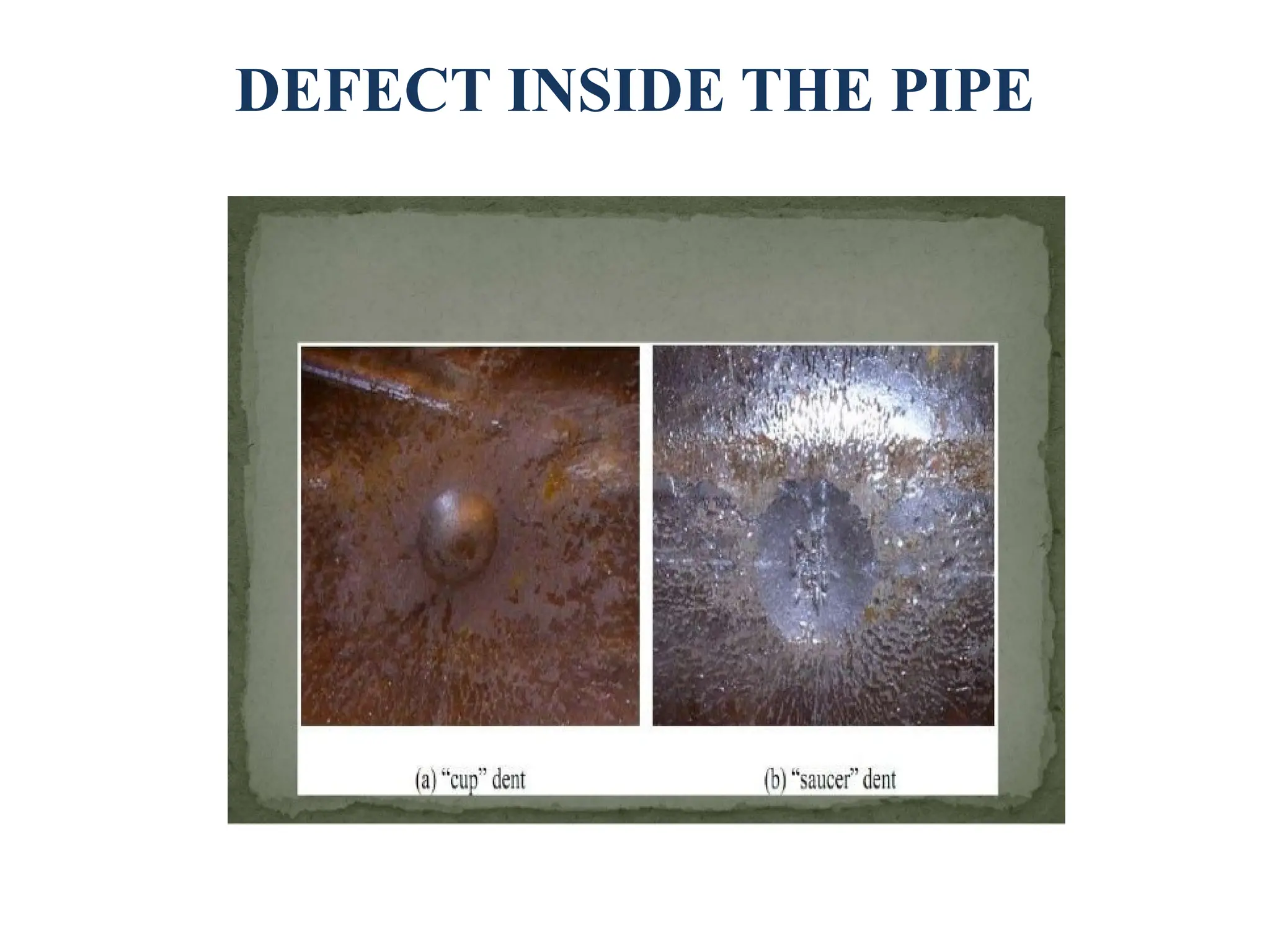
The document discusses the design and fabrication of a pipe inspection rover equipped with a wireless camera for monitoring the interiors of pipes, particularly to detect corrosion and other defects. It outlines the methodology, advantages, and limitations of the rover, emphasizing its importance for industries utilizing pipelines. The conclusion highlights the rover's adaptability to varying pipe diameters and its capacity to perform inspections efficiently despite challenges like obstacles within the pipelines.