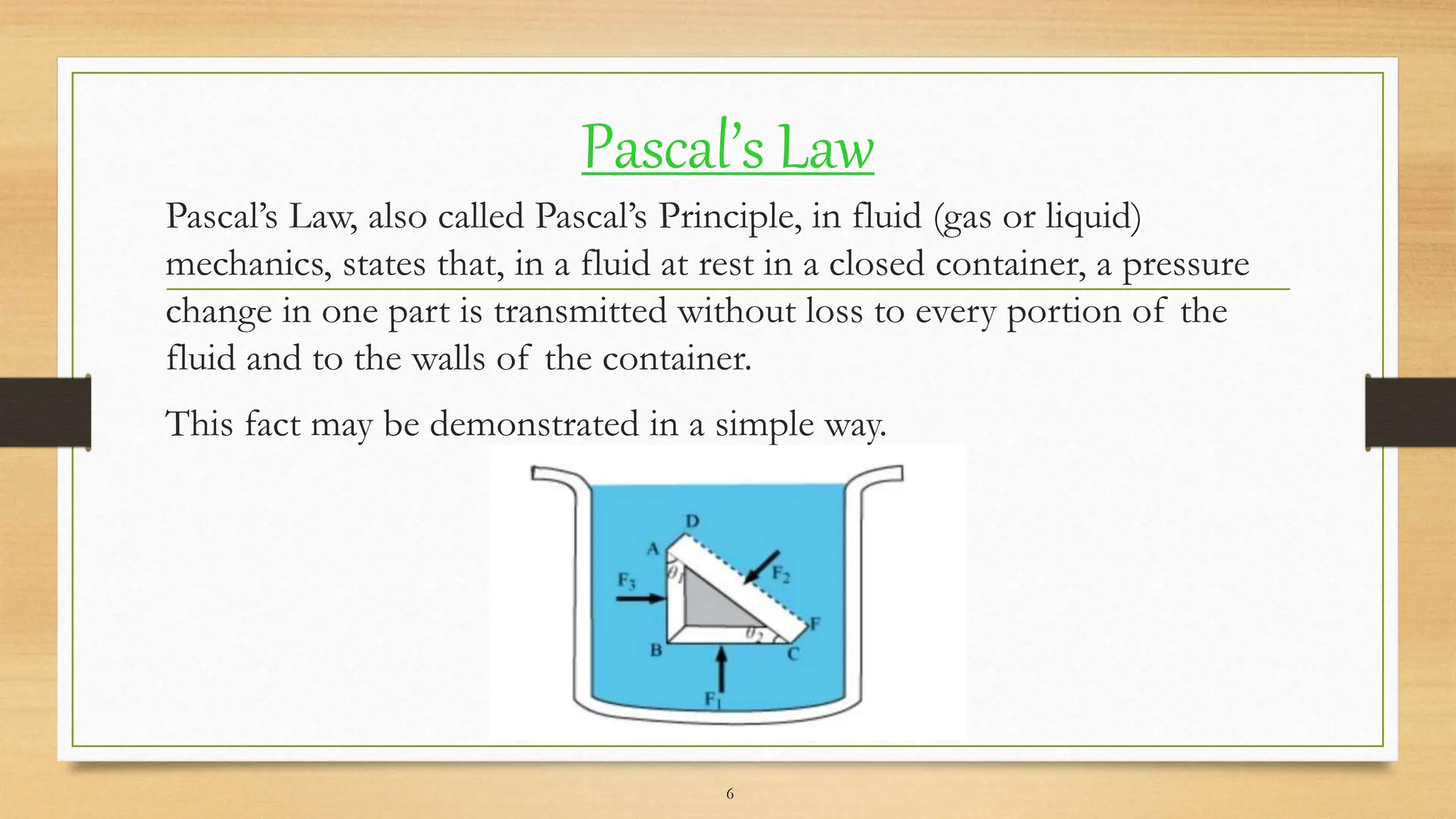
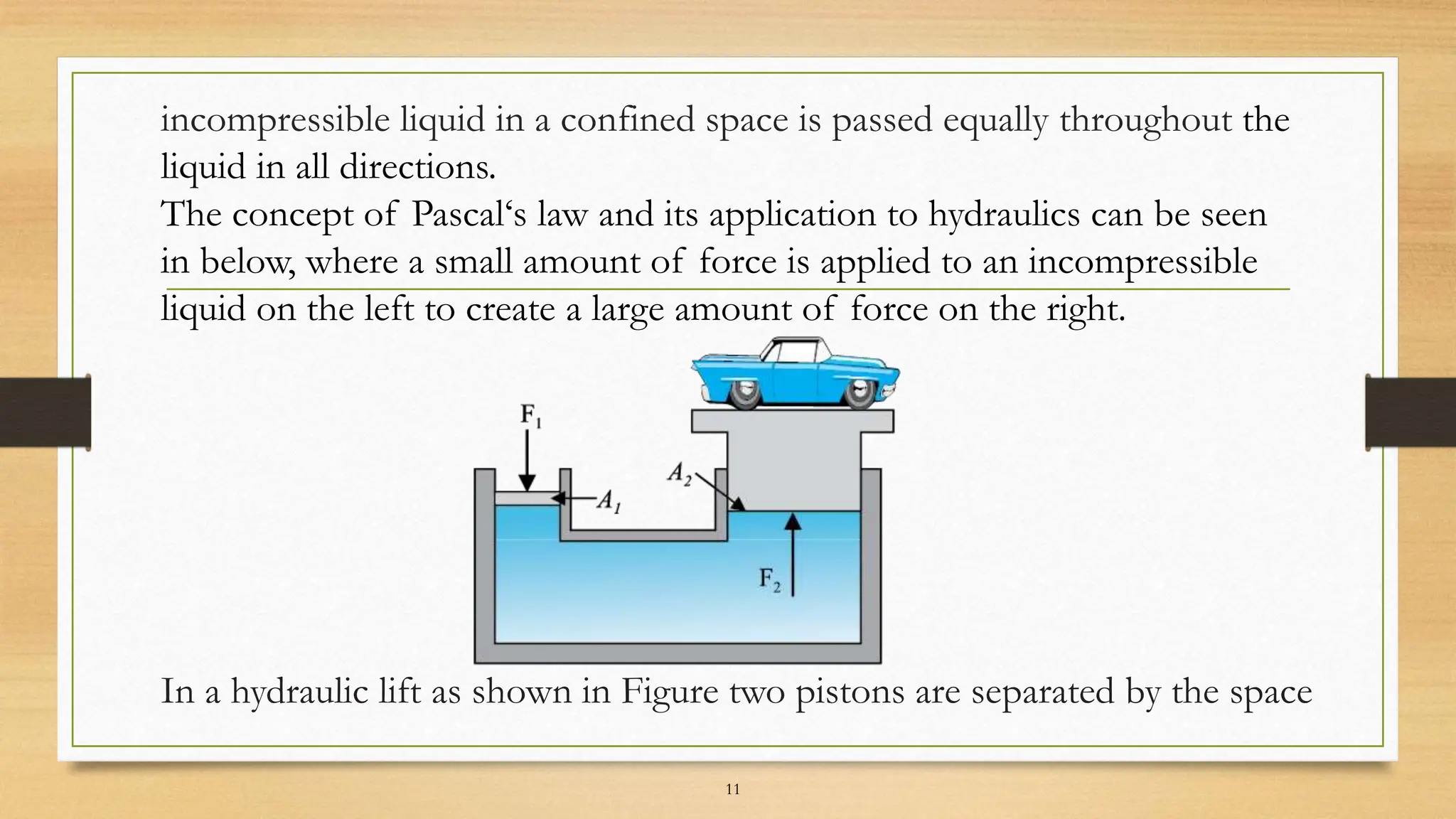
The document provides an overview of Pascal's Law, including its history, principles, and applications such as hydraulic lifts and brakes. Discovered by Blaise Pascal in the 1600s, the law states that a pressure change in a fluid at rest in a confined space is transmitted equally in all directions. The document also explores the mechanics of hydraulic systems based on this principle.